Abstract
Aims
White adipose tissue (WAT) dysfunction has been associated with adipose tissue low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress leading to insulin resistance (IR). Adrenomedullin (ADM), an endogenous active peptide considered as an adipokine, is associated with adipocytes function.
Methods
We evaluated the protective effects of ADM against IR in 3T3-L1 adipocytes treated by palmitic acid (PA) and in visceral white adipose tissue (vWAT) of obese rats fed with high-fat diet.
Results
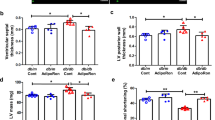
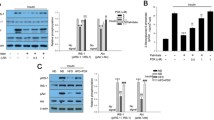
We found that endogenous protein expressions of ADM and its receptor in PA-treated adipocytes were markedly increased. PA significantly induced impaired insulin signaling by affecting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-protein kinase B (Akt) axis and glucose transporter-4 (GLUT-4) levels, whereas ADM pretreatment enhanced insulin signaling PI3K/Akt and GLUT-4 membrane protein levels, decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-6 levels, and improved oxidative stress accompanied with reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and increased anti-oxidant enzymes manganese superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), glutathione peroxidase (GPx1) and catalase (CAT) protein expressions. Furthermore, ADM treatment not only improved IR in obese rats, but also effectively restored insulin signaling, and reduced inflammation and oxidative stress in vWAT of obese rats.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates a prevention potential of ADM against obesity-related metabolic disorders, due to its protective effects against IR, inflammation and oxidative stress in adipocytes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed in this study will be made available by the authors on reasonable request.
References
Heyde I, Begemann K, Oster H (2021) Contributions of white and brown adipose tissues to the circadian regulation of energy metabolism. Endocrinology 162:bqab009.
Kuryszko J, Sławuta P, Sapikowski G (2016) Secretory function of adipose tissue. Pol J Vet Sci 19:441–446
Longo M, Zatterale F, Naderi J, et al (2019) Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications. Int J Mol Sci 20:2358
Kahn CR, Wang G, Lee KY (2019) Altered adipose tissue and adipocyte function in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 129:3990–4000
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L, et al (2015) Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15019
Petersen MC, Shulman GI (2018) Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol Rev 98:2133–2223
Kusminski CM, Bickel PE, Scherer PE (2016) Targeting adipose tissue in the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15:639–660
McCracken E, Monaghan M, Sreenivasan S (2018) Pathophysiology of the metabolic syndrome. Clin Dermatol 36:14–20
Boden G (2011) Obesity, insulin resistance and free fatty acids. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 18:139–143
Sobczak AIS, Blindauer CA, Stewart AJ (2019) Changes in plasma free fatty acids associated with type-2 diabetes. Nutrients 11:2022
Riant E, Waget A, Cogo H, et al (2009) Estrogens protect against high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in mice. Endocrinology 150:2109–2117
Liu TY, Shi CX, Gao R, et al (2015) Irisin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and increases glycogen synthesis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic mice and hepatocytes. Clin Sci (Lond) 129:839–850
Xiong XQ, Geng Z, Zhou B, et al (2018) FNDC5 attenuates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance via AMPK-mediated macrophage polarization in obesity. Metabolism 83:31–41
Xiong XQ, Chen D, Sun HJ, et al (2015) FNDC5 overexpression and irisin ameliorate glucose/lipid metabolic derangements and enhance lipolysis in obesity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852:1867–1875
Zhang H, Zhang SY, Jiang C, et al (2016) Intermedin/adrenomedullin 2 polypeptide promotes adipose tissue browning and reduces high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Int J Obes (Lond) 40:852–860
Achari AE, Jain SK (2017) Adiponectin, a therapeutic target for obesity, diabetes, and endothelial dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci 18:1321
Hay DL, Garelja ML, Poyner DR, Walker CS (2018) Update on the pharmacology of calcitonin/CGRP family of peptides: IUPHAR review 25. Br J Pharmacol 175:3–17
Andren-Sandberg A (2016) New findings may explain the onset of diabetes in pancreatic cancer. Adrenomedullin and exosomes may provide the connection. Lakartidningen 113: DRF3.
Bech EM, Voldum-Clausen K, Pedersen SL, et al (2019) Adrenomedullin and glucagon-like peptide-1 have additive effects on food intake in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 109:167–173
Tsuruda T, Kato J, Kuwasako K, Kitamura K (2019) Adrenomedullin: continuing to explore cardioprotection. Peptides 111:47–54
Wong HK, Tang F, Cheung TT, Cheung BM (2014) Adrenomedullin and diabetes. World J Diabetes 5(3):364–371
Ajith Kumar AK (2020) Adrenomedullin in sepsis: finally, a friend or an enemy? Indian J Crit Care Med 24(12):1151–1153
Li MY, Zhu XL, Zhao BX, et al (2019) Adrenomedullin alleviates the pyroptosis of Leydig cells by promoting autophagy via the ROS-AMPK-mTOR axis. Cell Death Dis 10:489
Zhang S, Patel A, Moorthy B, Shivanna B (2015) Adrenomedullin deficiency potentiates hyperoxic injury in fetal human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 464:1048–1053
Gonzalez-Rey E, Chorny A, Varela N, Robledo G, Delgado M (2006) Urocortin and adrenomedullin prevent lethal endotoxemia by down-regulating the inflammatory response. Am J Pathol 168:1921–1930
Go AG, Chow KH, Hwang IS, Tang F (2007) Adrenomedullin and its receptor components in adipose tissues: differences between white and brown fats and the effects of adrenergic stimulation. Peptides 28:920–927
Kim J, Lee SK, Kim D, et al (2020) Altered expression of adrenomedullin 2 and its receptor in the adipose tissue of obese patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 105:dgz066.
Li Y, Jiang C, Wang X, Zhang Y, Shibahara S, Takahashi K (2007) Adrenomedullin is a novel adipokine: adrenomedullin in adipocytes and adipose tissues. Peptides 28:1129–1143
Shimosawa T, Ogihara T, Matsui H, Asano T, Ando K, Fujita T (2003) Deficiency of adrenomedullin induces insulin resistance by increasing oxidative stress. Hypertension 41:1080–1085
Romain H, Jean-Michel S, Philippe R, Atul P, Fatima S (2007) Adrenomedullin inhibits adipogenesis under transcriptional control of insulin. Diabetes 56:553–563
Dong Y, Betancourt A, Belfort M, Yallampalli C (2017) Targeting adrenomedullin to improve lipid homeostasis in diabetic pregnancies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 102:3425–3436
Kim J, Lee SK, Kim D, et al (2020) Altered expression of adrenomedullin 2 and its receptor in the adipose tissue of obese patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 105:dgz066
Paulmyer-Lacroix O, Desbriere R, Poggi M, et al (2006) Expression of adrenomedullin in adipose tissue of lean and obese women. Eur J Endocrinol 155:177–185
Shen HH, Peterson SJ, Bellner L, et al (2020) Cold-pressed nigella sativa oil standardized to 3% thymoquinone potentiates omega-3 protection against obesity-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and markers of insulin resistance accompanied with conversion of white to beige fat in mice. Antioxidants (Basel) 9:489
Dai HB, Wang FZ, Kang Y, et al (2021) Adrenomedullin attenuates inflammation in white adipose tissue of obese rats through receptor-mediated PKA pathway. Obesity (Silver Spring) 29:86–97
Purkayastha S, Zhang H, Zhang G, Ahmed Z, Wang Y, Cai D (2011) Neural dysregulation of peripheral insulin action and blood pressure by brain endoplasmic reticulum stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:2939–2944
Chen JW, Kong ZL, Tsai ML, Lo CY, Ho CT, Lai CS (2018) Tetrahydrocurcumin ameliorates free fatty acid-induced hepatic steatosis and improves insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. J Food Drug Anal 26:1075–1085
Boucher J, Kleinridders A, Kahn CR (2014) Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 6:a009191.
Muretta JM, Mastick CC (2009) How insulin regulates glucose transport in adipocytes. Vitam Horm 80:245–286
Al-Sulaiti H, Diboun I, Agha MV, et al (2019) Metabolic signature of obesity-associated insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. J Transl Med 17:348
González N, Moreno-Villegas Z, González-Bris A, Egido J, Lorenzo Ó (2017) Regulation of visceral and epicardial adipose tissue for preventing cardiovascular injuries associated to obesity and diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 16:44
Unamuno X, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Rodríguez A, Becerril S, Frühbeck G, Catalán V (2018) Adipokine dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in human obesity. Eur J Clin Invest 48:e12997.
Metwalley KA, Farghaly HS, Sherief T (2018) Plasma adrenomedullin level in children with obesity: relationship to left ventricular function. World J Pediatr 14:84–91
Nomura I, Kato J, Tokashiki M, Kitamura K (2009) Increased plasma levels of the mature and intermediate forms of adrenomedullin in obesity. Regul Pept 158:127–131
Del Ry S, Cabiati M, Bianchi V, et al (2016) Mid-regional-pro-adrenomedullin plasma levels are increased in obese adolescents. Eur J Nutr 55:1255–1260
Oyar EÖ, Kiriş I, Gülmen S, et al (2011) Adrenomedullin attenuates aortic cross-clamping-induced myocardial injury in rats. Am J Surg 201:226–232
Holmes D, Campbell M, Harbinson M, Bell D (2013) Protective effects of intermedin on cardiovascular, pulmonary and renal diseases: comparison with adrenomedullin and CGRP. Curr Protein Pept Sci 14:294–329
Ashizuka S, Kita T, Inatsu H, Kitamura K (2021) Adrenomedullin: a novel therapeutic for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Biomedicines 9:1068
Koyama T, Kuriyama N, Uehara R (2020) Midregional proadrenomedullin can reflect the accumulation of visceral adipose tissue: a key to explaining the obesity paradox. Int J Environ Res Public Health 1:3968
Dong Y, Chauhan M, Betancourt A, Belfort M, Yallampalli C (2018) Adipose tissue inflammation and adrenomedullin overexpression contribute to lipid dysregulation in diabetic pregnancies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103:3810–3818
Dong Y, Banadakoppa M, Chauhan M, Balakrishnan M, Belfort M, Yallampalli C (2019) Circulating adrenomedullin is elevated in gestational diabetes and its role in impaired insulin production by beta-cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 104:697–706
Mottillo EP, Shen XJ, Granneman JG (2010) beta3-adrenergic receptor induction of adipocyte inflammation requires lipolytic activation of stress kinases p38 and JNK. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801:1048–1055
Paglialunga S, Ludzki A, Root-McCaig J, Holloway GP (2015) In adipose tissue, increased mitochondrial emission of reactive oxygen species is important for short-term high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice. Diabetologia 58:1071–1080
Okumura H, Nagaya N, Itoh T, et al (2004) Adrenomedullin infusion attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway. Circulation 109:242–248
Dong Y, van der Walt N, Pennington KA, Yallampalli C (2019) Impact of adrenomedullin blockage on lipid metabolism in female mice exposed to high-fat diet. Endocrine 65:278–285
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81970356 and 81470539) and the generous support of the Collaborative Innovation Center for Cardiovascular Disease Translational Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors reviewed of the manuscript. Ye-Bo Zhou designed the study. Hang-Bing Dai, Hong-Yu Wang, Pei-Qian and Hong Zhou conducted the experiments. Fang-Zheng Wang and Qing Gao performed the data analysis. Hang-Bing Dai and Ye-Bo Zhou wrote the manuscript. Ye-Bo Zhou revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Managed by Antonio Secchi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, HB., Wang, HY., Wang, FZ. et al. Adrenomedullin ameliorates palmitic acid-induced insulin resistance through PI3K/Akt pathway in adipocytes. Acta Diabetol 59, 661–673 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-021-01840-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-021-01840-5