Abstract
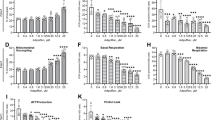
The expression of adiponectin receptors has been demonstrated in human and rat pancreatic beta cells, where globular (g) adiponectin rescues rat beta cells from cytokine and fatty acid-induced apoptosis. The aim of our study was to evaluate whether adiponectin has a direct effect on insulin secretion and the metabolic pathways involved. Purified human pancreatic islets and rat beta cells (INS-1E) were exposed (1 h) to g-adiponectin, and glucose-induced insulin secretion was measured. A significant increase in glucose-induced insulin secretion was observed in the presence of g-adiponectin (1 nmol/l) with respect to control cells in both human pancreatic islets (n = 5, p < 0.05) and INS-1E cells (n = 5, p < 0.001). The effect of globular adiponectin on insulin secretion was independent of AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK) activation or glucose oxidation. In contrast, g-adiponectin significantly increased oleate oxidation (n = 5, p < 0.05), and the effect of g-adiponectin (p < 0.001) on insulin secretion by INS-1E was significantly reduced in the presence of etomoxir (1 μmol/l), an inhibitor of fatty acid beta oxidation. g-Adiponectin potentiates glucose-induced insulin secretion in both human pancreatic islets and rat beta cells via an AMPK independent pathway. Increased fatty acid oxidation rather than augmented glucose oxidation is the mechanism responsible. Overall, our data indicate that, in addition to its anti-apoptotic action, g-adiponectin has another direct effect on beta cells by potentiating insulin secretion. Adiponectin, therefore, in addition to its well-known effect on insulin sensitivity, has important effects at the pancreatic level.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T (2005) Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr Rev 26:439–451
King GA, Deemer SE, Thompson DL (2012) Adiponectin is associated with risk of the metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in women. Acta Diabetol 49(suppl 1):41–49
Baratta R, Amato S, Degano C et al (2004) Adiponectin relationship with lipid metabolism is independent of body fat mass: evidence from both cross-sectional and intervention studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(6):2665–2671
Su SC, Pei D, Hsieh CH et al (2011) Circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and adiponectin in young men with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 48(2):113–119
Kishida K, Funahashi T, Shimomura I (2012) Molecular mechanisms of diabetes and atherosclerosis: role of adiponectin. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 12(2):118–131
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y et al (2003) Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 423:762–769
Tomas E, Tsao TS, Saha AK et al (2002) Enhanced muscle fat oxidation and glucose transport by ACRP30 globular domain: acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibition and AMP-activated protein kinase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16309–16313
Kharroubi I, Rasschaert J, Eizirik DL, Cnop M (2003) Expression of adiponectin receptors in pancreatic beta cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312:1118–1122
Musso G, Gambino R, Biroli G et al (2005) Hypoadiponectinemia predicts the severity of hepatic fibrosis and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in nondiabetic nonobese patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 100(11):2438–2446
Rakatzi I, Mueller H, Ritzeler O, Tennagels N, Eckel J (2004) Adiponectin counteracts cytokine- and fatty acid-induced apoptosis in the pancreatic beta-cell line INS-1. Diabetologia 47:249–258
Beylot M, Pinteur C, Peroni O (2006) Expression of the adiponectin receptors AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 in lean rats and in obese Zucker rats. Metabolism 55:396–401
Staiger K, Stefan N, Staiger H et al (2005) Adiponectin is functionally active in human islets but does not affect insulin secretory function or beta-cell lipoapoptosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(12):6707–6713
Wijesekara N, Krishnamurthy M, Bhattacharjee A et al (2010) Adiponectin-induced ERK and Akt phosphorylation protects against pancreatic beta cell apoptosis and increases insulin gene expression and secretion. J Biol Chem 285(44):33623–33631
Gu W, Li X, Liu C et al (2006) Globular adiponectin augments insulin secretion from pancreatic islet beta cells at high glucose concentrations. Endocrine 30:217–221
Okamoto M, Ohara-Imaizumi M, Kubota N et al (2008) Adiponectin induces insulin secretion in vitro and in vivo at a low glucose concentration. Diabetologia 51:827–835
Winzell MS, Nogueiras R, Dieguez C, Ahren B (2004) Dual action of adiponectin on insulin secretion in insulin-resistant mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321:154–160
Lupi R, Dotta F, Marselli L et al (2002) Prolonged exposure to free fatty acids has cytostatic and pro-apoptotic effects on human pancreatic islets: evidence that beta-cell death is caspase mediated, partially dependent on ceramide pathway, and Bcl-2 regulated. Diabetes 51:1437–1442
Di Paola R, Caporarello N, Marucci A et al (2011) ENPP1 affects insulin action and secretion: evidences from in vitro studies. PLoS ONE 6(5):e19462
Andersson U, Filipsson K, Abbott CR et al (2004) AMP-activated protein kinase plays a role in the control of food intake. J Biol Chem 279:12005–12008
Patane G, Anello M, Piro S et al (2002) Role of ATP production and uncoupling protein-2 in the insulin secretory defect induced by chronic exposure to high glucose or free fatty acids and effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma inhibition. Diabetes 51:2749–2756
Patane G, Piro S, Rabuazzo AM et al (2000) Metformin restores insulin secretion altered by chronic exposure to free fatty acids or high glucose: a direct metformin effect on pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 49:735–740
Marchetti P, Dotta F, Lauro D et al (2008) An overview of pancreatic beta-cell defects in human type 2 diabetes: implications for treatment. Regul Pept 146(1–3):4–11
Fischer S, Santos AN, Thieme R et al (2010) Adiponectin stimulates glucose uptake in rabbit blastocysts. Biol Reprod 83(5):859–865
Iwabu M, Yamauchi T, Okada-Iwabu M et al (2010) Adiponectin and AdipoR1 regulate PGC-1alpha and mitochondria by Ca(2 +) and AMPK/SIRT1. Nature 464(7293):1313–1319
Huypens P, Moens K, Heimberg H et al (2005) Adiponectin-mediated stimulation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in pancreatic beta cells. Life Sci 77(11):1273–1282
Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE (2001) The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med 7:947–953
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N et al (2006) Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 116:1784–1792
Kantartzis K, Rittig K, Balletshofer B et al (2006) The relationships of plasma adiponectin with a favorable lipid profile, decreased inflammation, and less ectopic fat accumulation depend on adiposity. Clin Chem 52:1934–1942
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Guido Pozza.
G. Patané and N. Caporarello contributed equally to the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patané, G., Caporarello, N., Marchetti, P. et al. Adiponectin increases glucose-induced insulin secretion through the activation of lipid oxidation. Acta Diabetol 50, 851–857 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0458-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-013-0458-x