Abstract
Purpose
There are limited studies that have reported the middle- to long-term outcomes of combined procedures consisting of more than two procedures for patellofemoral instability. The current study aims to investigate and report the middle- to long-term outcomes of a combination procedure of tibial tubercle transfer, medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction, trochleoplasty and lateral release for patellofemoral instability in patients aged 18 years and below.
Methods
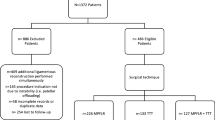
In the cohort study, all patients aged 18 years old or younger who underwent a combination procedure of tibial tubercle transfer, medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction, trochleoplasty and lateral release for recurrent patellofemoral instability were included.
Results
A total of 21 patients were included in the study. All patients had no further patellofemoral dislocation, pain and apprehension following the 4-in-1 surgery (p < 0.01). There was a significant improvement in the Kujala score from 36.1 (SD 12.9) pre-operatively to 93.1 (SD 3.6) post-operatively (p < 0.001). The patients also had a statistically significant improvement in their radiological factors, including the patellar tilt angle (p < 0.001), sulcus angle (p = 0.001), trochlear groove depth (p = 0.041), tibial tubercle-trochlear groove distance (p < 0.001) and Caton–Deschamps index (p = 0.001).
Conclusion
A combination procedure of tibial tubercle transfer, medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction, trochleoplasty and lateral release leads to good middle- to long-term subjective, functional and radiographic outcomes for patients with recurrent patellofemoral instability and underlying predisposing factors of increased TT-TG distance of more than 20 mm, Dejour B or D trochlear dysplasia and medial patellofemoral ligament rupture.
Level of evidence
IV.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parikh SN, Veerkamp M, Redler LH, Schlechter J, Williams BA, Yaniv M, Friel N, Perea SH, Shannon SR, Green DW (2022) Patellar instability in young athletes. Clin Sports Med 41(4):627–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csm.2022.05.005
Redziniak DE, Diduch DR, Mihalko WM, Fulkerson JP, Novicoff WM, Sheibani-Rad S, Saleh KJ (2009) Patellar instability. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(9):2264–2275
Tan SHS, Tan LYH, Lim AKS, Hui JH (2019) Hemiepiphysiodesis is a potentially effective surgical management for skeletally immature patients with patellofemoral instability associated with isolated genu valgum. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27(3):845–849. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-5127-8
Tan SHS, Chua CXK, Doshi C, Wong KL, Lim AKS, Hui JH (2019) The outcomes of isolated lateral release in patellofemoral instability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Knee Surg. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1688961
Jaquith BP, Parikh SN (2017) Predictors of recurrent patellar instability in children and adolescents after first-time dislocation. J Pediatr Orthop 37(7):484–490. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000674
Lampros RE, Tanaka MJ (2022) Return to play considerations after patellar instability. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 15(6):597–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-022-09792-1
Dean CS, Chahla J, Cruz RS, Cram TR, LaPrade RF (2016) Patellofemoral joint reconstruction for patellar instability: medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction, trochleoplasty, and tibial tubercle osteotomy. Arthrosc Tech 5(1):e169–e175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eats.2015.10.016
Steensen RN, Bentley JC, Trinh TQ, Backes JR, Wiltfong RE (2015) The prevalence and combined prevalences of anatomic factors associated with recurrent patellar dislocation: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Am J Sports Med 43(4):921–927. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546514563904
Balcarek P, Rehn S, Howells NR, Eldridge JD, Kita K, Dejour D, Nelitz M, Banke IJ, Lambrecht D, Harden M, Friede T (2017) Results of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction compared with trochleoplasty plus individual extensor apparatus balancing in patellar instability caused by severe trochlear dysplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25(12):3869–3877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4365-x
Longo UG, Rizzello G, Ciuffreda M, Loppini M, Baldari A, Maffulli N, Denaro V (2016) Elmslie-trillat, maquet, fulkerson, roux goldthwait, and other distal realignment procedures for the management of patellar dislocation: systematic review and quantitative synthesis of the literature. Arthroscopy 32(5):929–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2015.10.019
Longo UG, Vincenzo C, Mannering N, Ciuffreda M, Salvatore G, Berton A, Denaro V (2018) Trochleoplasty techniques provide good clinical results in patients with trochlear dysplasia. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26(9):2640–2658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4584-9
Nelitz M, Dreyhaupt J, Lippacher S (2013) Combined trochleoplasty and medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for recurrent patellar dislocations in severe trochlear dysplasia: a minimum 2-year follow-up study. Am J Sports Med 41(5):1005–1012. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546513478579
Schneider DK, Grawe B, Magnussen RA, Ceasar A, Parikh SN, Wall EJ, Colosimo AJ, Kaeding CC, Myer GD (2016) Outcomes after isolated medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for the treatment of recurrent lateral patellar dislocations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med 44(11):2993–3005. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546515624673
Tan SHS, Ibrahim MM, Lee ZJ, Chee YKM, Hui JH (2018) Patellar tracking should be taken into account when measuring radiographic parameters for recurrent patellar instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26(12):3593–3600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4795-0
Tan SHS, Lim SY, Wong KL, Doshi C, Lim AKS, Hui JH (2019) The outcomes of isolated distal realignment procedures in patellofemoral instability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Knee Surg. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1681052
Vogel LA, Lee Pace J (2019) Trochleoplasty, medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction, and open lateral lengthening for patellar instability in the setting of high-grade trochlear dysplasia. Arthrosc Tech 8(9):e961–e967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eats.2019.05.005
von Engelhardt LV, Weskamp P, Lahner M, Spahn G, Jerosch J (2017) Deepening trochleoplasty combined with balanced medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for an adequate graft tensioning. World J Orthop 8(12):935–945. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.935
Zhao Y, Huang J, Li D, Hu W (2019) Arthroscopic medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction combined with tibial tuberosity transfer for recurrent patellar dislocation. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 33(8):960–964. https://doi.org/10.7507/1002-1892.201811111
Floyd ER, Ebert NJ, Carlson GB, Monson JK, LaPrade RF (2021) Medial patellofemoral reconstruction using quadriceps tendon autograft, tibial tubercle osteotomy, and sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty for patellar instability. Arthrosc Tech 10(5):e1249–e1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eats.2021.01.019
Hiemstra LA, Kerslake S, Lafave MR, Tucker A (2021) Patella alta is reduced following MPFL reconstruction but has no effect on quality-of-life outcomes in patients with patellofemoral instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 29(2):546–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-05977-8
Dong Z, Xu C, Yan L, Liu J, Wang F (2023) Isolated medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction is valid to stabilize patellofemoral joint but uncertain to reduce patellar height in setting of lateral patellar dislocation and patella alta. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143(3):1505–1512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04429-x
Lykissas MG, Li T, Eismann EA, Parikh SN (2014) Does medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction decrease patellar height? A Prelim Rep J Pediatr Orthop 34(1):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3182a12102
Zhou K, Bai P, Sun Z, Jia Y, Wang F, Wang X, Niu Y (2022) Distalization of tibial tubercle osteotomy is not necessary for patients with recurrent patellar dislocation accompanied by patella alta and increased TT-TG distance. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 23(1):838. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-022-05779-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Ethical approval
The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee.
Informed consent
Waiver of informed consent was obtained from the institutional research committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, S.H.S., Sin, Q.S., Tan, L.Y.H. et al. Combination of tibial tubercle transfer, medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction, trochleoplasty and lateral release for patellofemoral instability provides good middle- to long-term outcomes in adolescents. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 34, 1551–1556 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-024-03837-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-024-03837-6