Abstract
Purpose
Augmentation strategies for surgical fixation of proximal humerus fractures (PHF) are available to address their relatively high failure rate. The purpose of this study was to compare two medial-buttress augmentation strategies for PHF fixation.
Methods
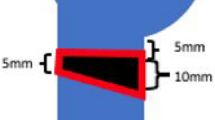
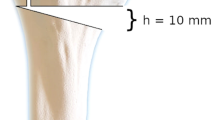
A two-part PHF model with loss of medial buttress was created in 16 synthetic bones. The PHFs were fixed with locking plates and either calcium phosphate cement (CPC) or fibula strut (FS) augmentation. After cadaveric validations, the fixation constructs were subjected to nondestructive axial compression tests, followed by a cyclic test. Construct stiffness and angular displacement of the humerus head were recorded.
Results
Humeral head angular displacement was statistically greater in the CPC group than in the FS group at the applied force of 300 N and higher (p < 0.05). Axial stiffness was statistically greater in the FS fixation group than in the CPC group at initial and final phases of cyclic loading protocol (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
In an osteoporotic cadaveric model of a 2-part PHF with loss of a medial buttress, locked plate constructs augmented with FS have a higher resistance to varus collapse compared to those augmented with CPC.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
DRYAD/ORCID.
Change history
18 January 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03192-w
References
Court-Brown CM, Caesar B (2006) Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury 37:691–697
Hintermann B, Trouillier HH, Schafer D (2000) Rigid internal fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus in older patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 82:1107–1112
Südkamp N, Bayer J, Hepp P, Voigt C, Oestern H, Kääb M, Luo C, Plecko M, Wendt K, Köstler W, Konrad G (2009) Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with use of the locking proximal humerus plate. Results of a prospective, multicenter, observational study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(6):1320–1328
Krappinger D, Bizzotto N, Riedmann S, Kammerlander C, Hengg C, Kralinger FS (2011) Predicting failure after surgical fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Injury 42:1283–1288
Seebeck J, Goldhahn J, Städele H, Messmer P, Morlock MM, Schneider E (2004) Effect of cortical thickness and cancellous bone density on the holding strength of internal fixator screws. J Orthop Res 22:1237–1242
Chow RM, Begum F, Beaupre LA, Carey JP, Adeeb S, Bouliane MJ (2011) Proximal humeral fracture fixation: locking plate construct±intramedullary fibular allograft. J Shoulder Elb Surg 21(7):894–901
Egol KA, Sugi MT, Ong CC et al (2012) Fracture site augmentation with calcium phosphate cement reduces screw penetration after open reduction-internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elb Surg 21:741–748
Gardner M, Weil Y, Barker J, Kelly B, Helfet D, Lorich D (2007) The importance of medial support in locked plating of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma 21:185–191
Gradl G, Knobe M, Stoffel M et al (2013) Biomechanical evaluation of locking plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures augmented with calcium phosphate cement. J Orthop Trauma 27:399–404
Hast MW, Chin M, Schmidt EC, Sanville J, Van Osten GK, Mehta S (2020) Mechanical effects of bone substitute and far-cortical locking techniques in 2-part proximal humerus fracture reconstruction: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma 34:4
Mathison C, Chaudhary R, Beaupre L, Reynolds M, Adeeb S, Bouliane M (2010) Biomechanical analysis of proximal humeral fixation using locking plate fixation with an intramedullary fibular allograft. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon) 25:642–646
Kwon BK, Goertzen DJ, O’Brien PJ, Broekhuyse HM, Oxland TR (2002) Biomechanical evaluation of proximal humeral fracture fixation supplemented with calcium phosphate cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84(6):951–961
Schliemann B, Seifert R, Rosslenbroich SB, Theisen C, Wähnert D, Raschke MJ, Weimann A (2015) Screw augmentation reduces motion at the bone-implant interface: a biomechanical study of locking plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elb Surg 24:1968–1973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.06.028
Elfar J, Stanbury S, Menorca RMG, Reed JD (2014) Composite bone models in orthopaedic surgery research and education. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 22(2):111–120. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-22-02-111
Bae JH, Oh JK, Chon CS, Oh CW, Hwang JH, Yoon YC (2011) The biomechanical performance of locking plate fixation with intramedullary fibular strut graft augmentation in the treatment of unstable fractures of the proximal humerus. Bone Joint J 93(7):937–4
Zhao L, Qi YM, Yang L, Wang GR, Zheng SN, Wang Q, Liang B, Jiang CZ (2019) Comparison of the effects of proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS) alone and PHILOS combined with fibular allograft in the treatment of neer three- or four-part proximal humerus fractures in the elderly. Department of orthopaedic surgery, Nanjing first hospital, Nanjing medical university, Nanjing, China: orthopaedic surgery published by Chinese orthopaedic association and John Wiley & Sons, Australia Ltd
Jung WB, Moon ES, Kim SK, Kovacevic D, Kim MS (2013) Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate? BMC Musculoskelet Disord 14:102
Meinberg EG, Agel J, Roberts CS, Karam MD, Kellam JF (2018) Fracture and dislocation classification compendium-2018. J Orthop Trauma 32(1):S1–S170
Brianza S, Plecko M, Gueorguiev B, Windolf M, Schwieger K (2010) Biomechanical evaluation of a new fixation technique for internal fixation of three-part proximal humerus fractures in a novel cadaveric model. Clin Biomech 25:886–892
Rusimov L, Zderic I, Ciric D, Barcik JP, Enchev D, Rashkov M, Hadzhinikolova M, Geoff R, Gueorguiev B, Baltov A (2018) Does supplemental intramedullary grafting increase stability of plated proximal humerus fractures? J Orthop Trauma. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000001376
Katthagen JC, Schwarze M, Meyer-Kobbe J, Voigt C, Hurschler C, Lill H (2014) Biomechanical effects of calcar screws and bone block augmentation on medial support in locked plating of proximal humeral fractures. Clin Biomech 29:735–741
Rothstock S, Plecko M, Kloub M, Schiuma D, Windolf M, Gueorguiev B (2012) Biomechanical evaluation of two intramedullary nailing techniques with different locking options in a three-part fracture proximal humerus model. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 27(7):686–691
Funding
OTA resident grant. This study was funded by the Orthopaedic Trauma Association (OTA), USA (Grant 254: OTA Resident Research Grant; UCSF Grant#: A126762; PI: Austin Pitcher, MD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P. Dmitry, MD, PhD–data analysis, manuscript preparation. R. Knox, BS–data analysis, biomechanical testing, manuscript preparation. M. Herring, MD–biomechanical testing, study design, manuscript preparation. S. Herfat, PhD–data analysis, biomechanical testing, study design, manuscript preparation. M. Tibrin Marmor, MD–study idea/conception, biomechanical testing, study design, manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests or competing interests. Author Pokhvashchev Dmitry declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Riley Knox declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Matthew Herring declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Safa Herfat declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Meir Tibrin Marmor declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Biomechanics study IRB exam. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The first and last names of the few authors have been switched in the author names, Authors’ contribution section and Conflict of interest section.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pokhvashchev, D., Knox, R., Herring, M. et al. Comparison of fibula strut and calcium phosphate cement augmentation of the medial buttress in 2-part proximal humerus fractures reconstruction: a biomechanical study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 33, 67–72 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03147-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03147-1