Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to compare the short-term efficacy of dry needling, corticosteroids, and platelet-rich plasma application (PRP) in the management of lateral epicondylitis.
Methods
The study included 72 patients diagnosed with lateral epicondylitis divided into three groups of 24 individuals using the sealed envelope method. Group 1 underwent dry needling, Group 2 received 40 mg methylprednisolone acetate, and Group 3 received PRP treatment. Patients were assessed using the visual analog scale (VAS) and the Disabilities of the Shoulder, Arm, and Hand (DASH) score, and Jamar grip strength before treatment and 3rd week and 3rd month.
Results
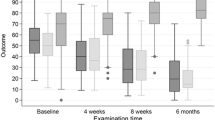
At the 3rd month, the mean VAS score was 1.16 ± 0.56 in dry needling group and 0.75 ± 0.60 in corticosteroids group, showing a statistically significant difference between dry needling and corticosteroids group, and between corticosteroids and PRP group (p = 0.015 and p = 0.000, respectively). At the 3rd week and 3rd month, VAS scores decreased in each treatment modality group, showing a statistically significant difference between the groups (p < 0.01). Jamar grip strength increased over time in all groups. There were no significant differences between the DASH scores of all groups at the 3rd week (p > 0.05). DASH scores decreased significantly from the 3rd week to the 3rd month in dry needling and corticosteroids group (p < 0.01), while it increased slightly in PRP group during the same period with a statistically insignificant change (p > 0.05). DASH scores decreased significantly at the 3rd month for all groups (p = 0.014).
Conclusion
Dry needling is an effective and safe application for the short-term treatment of lateral epicondylitis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waugh EJ (2005) Lateral epicondylalgia or epicondylitis: what’s in a name? J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 35:200–202
Hudak PL, Cole DC, Haines AT (1996) Understanding prognosis to improve rehabilitation: the example of lateral elbow pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 77(6):586–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-9993(96)90300-7
Hsieh LF, Kuo YC, Lee CC (2018) Comparison between corticosteroid and lidocaine injection in the treatment of tennis elbow: a randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 97:83–89
Vaquero-Picado A, Barco R, Antuña SA (2016) Lateral epicondylitis of the elbow. EFORT Open Rev 1:391–397
Luk JK, Tsang RC, Leung HB (2014) Lateral epicondylalgia: the midlife crisis of a tendon. Hong Kong Med J 20:145–151
Bhabra G, Wang A, Ebert JR (2016) Lateral elbow tendinopathy: development of a pathophysiology based treatment algorithm. Orthop J Sports Med 4:2325967116670635
Ozkut AT, Kilinçoğlu V, Ozkan NK, Eren A, Ertaş M (2007) Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in patients with lateral epicondylitis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 41:207–210
Tsikopoulos K, Tsikopoulos I, Simeonidis E, Papathanasiou E, Haidich AB, Anastasopoulos N et al (2016) The clinical impact of platelet rich plasma on tendinopathy compared to placebo or dry needling injections: a meta-analysis. Phys Ther Sport 17:87–94
Lewis M, Hay EM, Paterson SM, Croft P (2005) Local corticosteroid injections for tennis elbow: does the pain get worse before it gets better? Results from a randomized controlled trial. Clin J Pain 21(4):330–334
Assendelft WJ, Hay EM, Adshead R, Bouter LM (1996) Corticosteroid injections for lateral epicondylitis: a systematic overview. Br J Gen Pract 46(405):209–216
Smidt N, van der Windt DA, Assendelft WJ, Deville WL (2002) Corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy, or a wait-and-see policy for lateral epicondylitis: a randomized controlled trial. Lancet 359:657–662
Bisset L, Beller E, Jull G, Brooks P, Darnell R, Vicenzino B (2006) Mobilization with movement and exercise, corticosteroid injection, or wait and see for tennis elbow: a randomized trial. BMJ 333(7575):939
Buchbinder R, Johnston RV, Barnsley L, Assendelft WJJ, Bell SN, Smidt N (2011) Surgery for lateral elbow pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003525.pub2
Andia I, Rubio-Azpeitia E, Maffulli N (2015) Platelet rich plasma modulates the secretion of inflammatory/angiogenic proteins by inflamed tenocytes. Clin Orthop Relat Res 473(5):1624–1634
Galatz LM, Gerstenfeld L, Heber-Katz E, Rodeo SA (2015) Tendon regeneration and scar-formation: the concept of scarless healing. J Orthop Res 33(6):823–831
Hudgens JL, Sugg KB, Grekin JA, Gumucio JP, Bedi A, Mendias CL (2016) Platelet rich plasma activates pro-inflammatory signaling pathways and induces oxidative stress in tendon fibroblasts. Am J Sports Med 44(8):1931–1940
Chen X, Jones A, Park C, Vangsness CT Jr (2018) The efficacy of platelet rich plasma on tendon and ligament healing: a systematic review and meta-analysis with bias assessment. Am J Sports Med 46(8):2020–2032
Krey D, Borchers J, McCamey K (2015) Tendon-needling for treatment of tendinopathy:a systematic review. Phys Sportsmed 43:80–86
Tsikopoulos K, Tsikopoulos I, Simeonidis E, Papathanasiou E, Haidich AB, Anastasopoulos N et al (2016) The clinical impact of platelet-rich plasma on tendinopathy compared to placebo or dry needling injections: a meta-analysis. Phys Ther Sport 17:87–94
McShane JM, Shah VN, Nazarian LN (2008) Sonographically guided percutaneous-needle tenotomy for treatment of common extensor tendinosis in the elbow: is a corticosteroid necessary? J Ultrasound Med 27:1137–1144
Mattie R, Wong J, McCormick Z, Yu S, Saltychev M, Laimi K (2017) Percutaneous-needle tenotomy for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: a systematic review of the literature. PM R 9:603–611
James SLJ, Ali K, Pocock C, Robertson C, Walter J, Bell J et al (2007) Ultrasound guided dry needling and autologous blood injection for patellar tendinosis. Br J Sports Med 41(8):518–522. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.2006.034686
Stenhouse G, Sookur P, Watson M (2013) Do blood growth factors offer additional benefit in refractory lateral epicondylitis? A prospective, randomized pilot trial of dry needling as a stand-alone procedure versus dry-needling and autologous conditioned plasma. Skelet Radiol 42:1515–20
Mishra AK, Skrepnik NV, Edwards SG, Jones GL, Sampson S, Vermillion DA et al (2014) Efficacy of platelet rich plasma for chronic tennis elbow:a double-blind, prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial of 230 patients. Am J Sports Med 42:463–471. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546513494359
Suzuki T, Iwamoto T, Matsumura N, Nakamura M, Matsumoto M, Sato K (2019) Percutaneous tendon-needling without ultrasonography for lateral epicondylitis. Keio J Med. https://doi.org/10.2302/kjm.2019-0004-OA
Barnes DE, Beckley JM, Smith J (2015) Percutaneous ultrasonic tenotomy for chronic elbow tendinosis: a prospective study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2014.07.017
Tsikopoulos K, Tsikopoulos I, Simeonidis E, Papathanasiou E (2016) The clinical impact of platelet rich plasma on tendinopathy compared to placebo or dry needling injections: a meta-analysis. Phys Ther Sport 17:87–94
De Vos RJ, Windt J, Weir A (2014) Strong evidence against platelet-rich plasma injections for chronic lateral epicondylar tendinopathy: a systematic review. Br J Sports Med 48:952–956
Chard MD (2003) Regional and wide spread pain. In: Hochberg MC, Silman AJ, Smolen JS, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH (eds) The elbow. Rheumatology, 3rd edn. Mosby, Philadelphia, pp 631–41
Genc H, Cakit BD, Saracoglu M (2010) The effects of local steroid injection on pain, disability, and hand functions in patients with lateral epicondylitis. J Musculoskelet Pain 18:49–57
Mardani-Kivi M, Karimi-Mobarakeh M, Karimi A (2013) The effects of corticosteroid injection versus local anesthetic injection in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: a randomized single-blinded clinical trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133:757–763
Price R, Sinclair H, Heinrich I, Gibson T (1991) Local injection treatment of tennis elbow–hydrocortisone, triamcinolone, and lignocaine compared. Br J Rheumatol 30(1):39–44
Bellapianta J, Swartz F, Lisella J, Czajka J, Neff R, Uhl R (2011) Randomized prospective evaluation of injection techniques for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis. Orthopedics 34(11):e708–e712. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20110922-13
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güngör, E., Karakuzu Güngör, Z. Comparison of the efficacy of corticosteroid, dry needling, and PRP application in lateral epicondylitis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 32, 1569–1575 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03138-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03138-2