Abstract
Background
Nonunion after medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy (OWHTO) is a rare but serious complication with very limited data regarding its treatment. The aim of this study was to analyze the healing rate after operative treatment of nonunion after OWHTO.
Methods
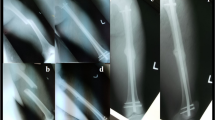
We performed a single-center, retrospective study that included 14 patients with nonunion after OWHTO between 2010 and 2018. The treatment for all patients consisted of local debridement and cancellous bone grafting at the osteotomy gap. Revision osteosynthesis due to a loss of correction/loosening of the locking screws or plates was performed in 5 patients. In 7 patients, lateral hinge fractures were treated with additional lateral plating. Union was confirmed using the modified “Radiographic Union Score for Tibial fractures”. Outcome measure was the Lysholm Knee Score at final follow-up.
Results
The mean age of the patients included in our study was 48.4 ± 6.7 years. Three patients were female (21.4%). The mean follow-up period was 20.8 ± 12.8 months. Union was achieved in 12/14 patients (85.7%) after a mean of 6 months (range, 3–13). The mean Lysholm Knee Score at the final follow-up was 83.2 ± 11.6. Two patients did not reach definitive union during the follow-up. In one patient, an infection of the nonunion following bone grafting was successfully treated with a two-stage procedure. Two patients needed additional cancellous bone grafting 6 and 8 months after the first revision surgery. All patients showed pain-free full weight bearing after union was achieved.
Conclusions
Nonunions after OWHTO can generally be treated successfully with cancellous bone grafting. For patients who have loss of correction, loosening of the osteosynthetic material or fracture of the lateral hinge, an additional revision or additive osteosynthesis may be required.
Level of evidence
Grade III



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All of the data are electronically available.
References
Meidinger G, Imhoff AB, Paul J, Kirchhoff C, Sauerschnig M, Hinterwimmer S (2011) May smokers and overweight patients be treated with a medial open-wedge HTO? Risk factors for non-union. Knee Surg Sports TraumatolArthrosc 19(3):333–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1335-6
Amendola A, Bonasia DE (2010) Results of high tibial osteotomy: review of the literature. IntOrthop 34(2):155–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-009-0889-8
Coventry MB, Ilstrup DM, Wallrichs SL (1993) Proximal tibial osteotomy a critical long-term study of eighty-seven cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75(2):196–201
W-Dahl A, Toksyig-Larsen S, Lindstrand A (2017) Ten-year results of physical activity after high tibial osteotomy in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports TraumatolArthrosc 25(3):902–909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3693-6
Duivenvoorden T, Brouwer RW, Baan A, Bos PK, Reijman M, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Verhaar JA (2014) Comparison of closing-wedge and opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled trial with a six-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96(17):1425–1432. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.M.00786
Lu J, Tang S, Wang Y, Li Y, Liu C, Niu Y, Cao P, Wang F (2019) Clinical outcomes of closing- and opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy for treatment of anteromedialunicompartmental knee osteoarthritis. J Knee Surg 32(8):758–763. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1668124
Wang Z, Zeng Y, She W, Luo X, Cai L (2018) Is opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy superior to closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy in treatment of unicompartmental osteoarthritis? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg 60:153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.10.045
Wu L, Lin J, Jin Z, Cai X, Gao W (2017) Comparison of clinical and radiological outcomes between opening-wedge and closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a comprehensive meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 12(2):e0171700. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171700
Woodacre T, Ricketts M, Evans JT, Pavlou G, Schranz P, Hockings M, Toms A (2016) Complications associated with opening wedge high tibial osteotomy–a review of the literature and of 15 years of experience. Knee 23(2):276–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2015.09.018
Valkering KP, van den Bekerom MP, Kappelhoff FM, Albers GH (2009) Complications after tomofix medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Knee Surg 22(3):218–225
Miller BS, Downie B, McDonough EB, Wojtys EM (2009) Complications after medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arthroscopy 25(6):639–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2008.12.020
Spahn G (2004) Complications in high tibial (medial opening wedge) osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124(10):649–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0588-7
Dexel J, Fritzsche H, Beyer F, Harman MK, Lutzner J (2017) Open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: incidence of lateral cortex fractures and influence of fixation device on osteotomy healing. Knee Surg Sports TraumatolArthrosc 25(3):832–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3730-5
Aydogdu S, Cullu E, Arac N, Varolgunes N, Sur H (2000) Prolonged peroneal nerve dysfunction after high tibial osteotomy: pre- and postoperative electrophysiological study. Knee Surg Sports TraumatolArthrosc 8(5):305–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001670000138
Naudie D, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Bourne TJ (1999) The install award. Survivorship of the high tibial valgus osteotomy. A 10- to -22-year followup study. ClinOrthopRelat Res 367:18–27
Tjornstrand B, Hagstedt B, Persson BM (1978) Results of surgical treatment for non-union after high tibial osteotomy in osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 60(7):973–977
Lobenhoffer P, Agneskirchner J, Zoch W (2004) Open valgus alignment osteotomy of the proximal tibia with fixation by medial plate fixator. Orthopade 33(2):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00132-003-0593-0
van Houten AH, Heesterbeek PJ, van Heerwaarden RJ, van Tienen TG, Wymenga AB (2014) Medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy: can delayed or nonunion be predicted? ClinOrthopRelat Res 472(4):1217–1223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-3383-y
Warden SJ, Morris HG, Crossley KM, Brukner PD, Bennell KL (2005) Delayed- and non-union following opening wedge high tibial osteotomy: surgeons’ results from 182 completed cases. Knee Surg Sports TraumatolArthrosc 13(1):34–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-003-0485-1
Takeuchi R, Ishikawa H, Kumagai K, Yamaguchi Y, Chiba N, Akamatsu Y, Saito T (2012) Fractures around the lateral cortical hinge after a medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a new classification of lateral hinge fracture. Arthroscopy 28(1):85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2011.06.034
Whelan DB, Bhandari M, Stephen D, Kreder H, McKee MD, Zdero R, Schemitsch EH (2010) Development of the radiographic union score for tibial fractures for the assessment of tibial fracture healing after intramedullary fixation. J Trauma 68(3):629–632. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181a7c16d
Wolff AM, Krackow KA (1990) The treatment of nonunion of proximal tibial osteotomy with internal fixation. ClinOrthopRelat Res 250:207–215
Schatzker J, Burgess RC, Glynn MK (1985) The management of nonunions following high tibial osteotomies. ClinOrthopRelat Res 193:230–233
Gillooly JJ, Tilkeridis K, Simonis RB, Monsell F (2012) The treatment of high tibial osteotomy non-union with the Ilizarov external fixator. Strateg Trauma Limb Reconstr 7(2):93–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-012-0138-3
Ming TS, Koon WM (2016) Autologous bone grafting and revision plating in a case of persistent high tibial osteotomy non-union. J Orthop Case Rep 6(3):91–93. https://doi.org/10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.530
Gandhi R, Alomran A, Mahomed N (2008) Bilateral non-union of high tibial osteotomies treated by total knee arthroplasty: a case report. Knee 15(3):242–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2008.01.011
Lysholm J, Gillquist J (1982) Evaluation of knee ligament surgery results with special emphasis on use of a scoring scale. Am J Sports Med 10(3):150–154. https://doi.org/10.1177/036354658201000306
Cameron HU, Welsh RP, Jung YB, Noftall F (1993) Repair of nonunion of tibial osteotomy. ClinOrthopRelat Res 287:167–169
Martin R, Birmingham TB, Willits K, Litchfield R, Lebel ME, Giffin JR (2014) Adverse event rates and classifications in medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Am J Sports Med 42(5):1118–1126. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546514525929
Schroter S, Freude T, Kopp MM, Konstantinidis L, Dobele S, Stockle U, van Heerwaarden R (2015) Smoking and unstable hinge fractures cause delayed gap filling irrespective of early weight bearing after open wedge osteotomy. Arthroscopy 31(2):254–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2014.08.028
Stoffel K, Stachowiak G, Kuster M (2004) Open wedge high tibial osteotomy: biomechanical investigation of the modified arthrex osteotomy plate (Puddu plate) and the tomofix plate. ClinBiomech (Bristol, Avon) 19(9):944–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2004.06.007
Raja Izaham RM, Abdul Kadir MR, Abdul Rashid AH, Hossain MG, Kamarul T (2012) Finite element analysis of Puddu and Tomofix plate fixation for open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Injury 43(6):898–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2011.12.006
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Thomas Rosteius, Dominik Seybold and Jan Geßmann. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Thomas Rosteius, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
TR, VR, SL, DS, TAS and JG confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
All patients agreed to participate in the study.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved the publication.
Ethical Approval
There is a positive statement of the Institutional Review Board for this work (registered number 16–5871-BR).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosteius, T., Rausch, V., Lotzien, S. et al. Treatment of aseptic nonunion after medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 31, 755–762 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-020-02825-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-020-02825-w