Abstract
Background
External fixation of tibial fractures using a locking plate has been reported with favorable results in some selected patients. However, the stability of external plate fixation in this fracture pattern has not been previously demonstrated. We investigated the stability of external plate fixation with different plate–bone distances.
Methods
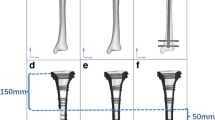
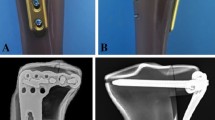
In this study, the computational processing model of external fixation of a distal tibial metaphyseal fracture utilizing the contralateral femoral less invasive stabilization system plate was analyzed. The plate was placed on the anteromedial aspect of tibia with different plate–bone distances: 1, 10, 20, and 30 mm.
Results
Under axial load, the stiffness of construct in all groups was higher than intact tibia. Under axial load with an internal rotational force, the stiffness of construct with 1 and 10 mm plate–bone distances was similar to that of an intact tibia and the stiffness of the construct with 20 and 30 mm distances was lower than that of an intact tibia. Under axial load with an external rotational force, the stiffness of the construct in all groups was lower than that of an intact tibia. The maximum plate stresses were concentrated at the two most distal screws and were highest in the construct with the 10 mm plate–bone distance, and least in the construct with a 1 mm plate–bone distance.
Conclusions
To guarantee a stable external plate fixation in distal tibial fracture, the plate–bone distance should be less than 30 mm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katsoulis E, Court-Brown C, Giannoudis PV (2006) Incidence and aetiology of anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of the femur and tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:576–580
Keating JF, Orfaly R, O’Brien PJ (1997) Knee pain after tibial nailing. J Orthop Trauma 11:10–13
Cannada LK, Anglen JO, Archdeacon MT, Herscovici D Jr, Ostrum RF (2008) Avoiding complications in the care of fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90:1760–1768
Lau T, Leung F, Chan C (2008) Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures. Int Orthop 32:697–703
Leonard M, Magill P, Khayyat G (2009) Minimally-invasive treatment of high velocity intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia. Int Orthop (SICOT) 33:1149–1153
Ma CH, Tu YK, Yeh JH, Yang SC, Wu CH (2011) Using external and internal locking plates in a two-stage protocol for treatment of segmental tibial fractures. J Trauma 71:614–619
Woon CYL, Wong MK, Howe TS (2010) LCP external fixation—external application of an internal fixator: two cases and a review of the literature. J Orthop Surg Res 5:19
Xusheng Q, Han Y, Xin Z, Junfei W, Jin X, Yixin C (2014) Locking plate as a definitive external fixator for treating tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue envelop. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134:383–388
Bessho M, Ohnishi I, Matsuyama J, Matsumoto T, Imai K, Nakamura K (2007) Prediction of strength and strain of the proximal femur by a CT-based finite element method. J Biomech 40:1745–1753
Dragomir-Daescu D, Op Den Buijs J, McEligot S, Dai Y, Entwistle RC, Salas C (2011) Robust QCT/FEA models of proximal femur stiffness and fracture load during a sideways fall on the hip. Ann Biomed Eng 39:742–755
KazImoglu C, Akdogan Y, Sener M, Kurtulmus A, KarapInar H, Uzun B (2008) Which is the best fixation method for lateral cortex disruption in the medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy? A biomechanical study. Knee 15:305–308
Stoffel K, Stachowiak G, Kuster M (2004) Open wedge high tibial osteotomy: biomechanical investigation of the modified Arthrex Osteotomy Plate (Puddu Plate) and the TomoFix Plate. Clin Biochem 19:944–950
Granowski R, Ramotowski W, Kamiński E, Pilawski K (1984) “Zespol”—a new type of osteosynthesis. I. An internal self-compressing stabilizer of bone fragments. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol 49:301–305
Hopf T, Osthege S (1987) Interfragmental compression of the Zespol osteosynthesis system. Experimental biomechanical studies. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 125:546–552
Ramotowski W, Zespol Granowski R (1991) An original method of stable osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 272:67–75
Kloen P (2009) Supercutaneous plating: use of a locking compression plate as an external fixator. J Orthop Trauma 23:72–75
Appivatthakakul T, Sanapanich K (2007) The locking compression plate as an external fixator for bone transport in the treatment of a large distal tibial defect: a case report. Injury. 38:1318–1325
Kerkhoffs GMMJ, Kuipers MM, Marti RK, Werken C (2003) External fixation with standard AO-plates: technique, indications, and results in 31 cases. J Orthop Trauma 17:61–64
Marti RK, Werken C (1991) The AO-plate for external fixation in 12 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 62:60–62
Ahmad M, Nanda R, Bajwa AS, Candal-Couto J, Green S, Hui AC (2007) Biomechanical testing of the locking compression plate: when does the distance between bone and implant significantly reduce construct stability? Injury 38:358–364
Conflict of interest
All authors of this study disclose that there are no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) their work.
Ethical standard
All human studies have been approved by our ethics committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. The national laws have been observed, too.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Ebraheim, N., Li, M. et al. External fixation using locking plate in distal tibial fracture: a finite element analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 25, 1099–1104 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1604-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1604-7