Abstract
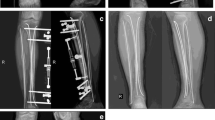
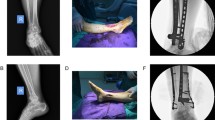
We studied the outcome of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using locking plate for closed fractures of distal tibia in a consecutive study consisting of 25 patients. Preoperative variables were age of patient, mode of trauma, type of fracture, and soft tissue status. Postoperative variables included wound status, time to union, return to activity, and AO foot and ankle score. After 1 year, all the fractures had united. The average time to union was 16.8 weeks. There were two cases of superficial infection. We also had two cases of deep infection, which required removal of hardware after the fracture was united. The average AO foot and ankle score was 83.6 in our study. We concluded that using MIPPO is a safe and effective method for the treatment for distal tibial fractures in properly selected patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJM (2004) Fractures of distal tibia: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury 35:615–620
Ronga M, Longa UG, Maffulli N (2010) Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:975–982
Borrelli J Jr, Prickett W, Song E, Becker D, Ricci W (2002) Extra osseous blood supply of the distal tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: a human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma 16(10):691–695
Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, Chow SP (2008) Wound complications of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures. Int Orthop (SICOT) 32:697–703
Toms AD, McMurtie A, Maffulli N (2004) Percutaneous plating of the distal tibia. J Foot Ankle Surg 43:199–203
Whiteside LA, Lesker PA (1978) The effects of extraperiosteal and subperiosteal dissection on fracture healing. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 60:26–30
Leonard M, Magill P et al (2009) Minimally invasive treatment of high velocity intraarticular fractures of the distal tibia. Int Orthop (SICOT) 33:1149–1153
Mockford BJ, Ogenda L, Warnock D, Barr RJ, Andrews C (2003) The early management of severe tibial pilon fractures using a temporary ring fixator. Surgeon 1:104–107
Bahari S, Lenehan B, Khan H, McElwain JP (2007) Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures. Acta Orthop Belg 73:635–640
Helfet DL, Koval K, Pappas J, Sanders RW, Di Pasquale T (1994) intaarticular “pilon” fractures of tibia. Clin Orthop 298:221–228
Muller ME, Nazarian S, Koch P, Schatzker J (1990) The comprehensive classification of fractures of long bones. Springer, Berlin
Leunig M, Hertel R, Sienbenrock KA, Ballmer FT (2000) The evolution of indirect reduction techniques for the treatment of fractures. Clin Orthop 375:7–14
Assal M,Stern R (2009) Surgical management of distal tibial fractures in adults. European Instructional Course Lectures 9, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-00966-2
Egol KA, Weisz R, Hiebert R, Tejwani NC, Koval KJ, Sanders RW (2006) Does fibular plating improve the alignment after intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibia fractures? J Orthop Trauma 20(2):94–103
Borg T, Larsson S, Lindsjo U (2004) Percutaneous plating of distal tibia fractures. Preliminary results in 21 patients. Injury 35:608–614
Ozsoy MH, Tuccar E, Demiryurek D, Bayramoglu A, Hayran M, Cavusoglu AT, Dincel VE, Sakaogullari A (2009) Do we really sacrifice saphenous vein and nerve? A cadaver study. J Orthop Trauma 23(2):132–138
Hazarika S, Chakravarthy J, Cooper J (2006) Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia: results in 20 patients. Injury 37(9):877–887
Guo JJ, Tang N, Yang HL, Tang TS (2010) A prospective, randomised trial comparing closed intramedullary nailing with percutaneous plating in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 92-B:984–988
Kitaoka HB, Alaxander IJ et al (1994) Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int 15(7):349–353
Bedi A, Le TT, Karunakar MA (2006) Surgical treatment of non articular distal tibia fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14:406–416
Sarmiento A (1970) A Functional below the knee brace for tibial fractures. J Bone and Joint Surg (Am) 52(2):295–311
Othman M, Strzelczyk P (2003) Results of conservative treatment of “pilon” fractures. Orthop Traumatol Rehabil 5(6):787–794
Mitkovic MB, Bumbasirevic MZ, Lesic A, Golubovic Z (2002) Dynamic external fixation of comminuted intraarticular fractures of the distal tibia. Acta Orthop Belg 68(5):508
Pattersen MJ, Cole JD (1999) Two staged delayed open reduction and internal fixation of severe pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma 13(2):85–91
Sirkin M, Sanders R, Di Pasquale T, Herscovici D Jr (1999) A staged protocol for soft tissue management in the treatment of complex pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma 13(2):78–84
Teeny SM, Wiess OA (1993) Open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures. Clin Orthop 292:108–117
Borens O, Kloen P, Richmond J, Roedrer G, Levine PS, Helfet DL (2009) Minimally invasive treatment of pilon fractures with a low profile plate: preliminary results in 17 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129(5):649–659
Shanmugam C, Rahmatalla A, Maffulli N (2007) Percutaneous fixation of distal tibial fractures using locking plates. Tech Orthop 22(30):162–166
Collinge C, Protzman R (2010) Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma 24(1):24–29
Oh CW, Kyung H-S, Park I-H, Kim P-T, Ihn J-C (2003) Distal Tibia Metaphyseal Fractures treated by percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 408:286–291
Shon OJ, Park CH (2012) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal tibial fractures: a comparison of medial and lateral plating. J Orthop Sci 17(5):562–566
Sitnik AA, Beletsky AV (2013) Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of tibia fractures: results in 80 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:2783–2789
Buckley R, Mohanty K, Malish D (2011) Lower limb malrotation following MIPO technique of distal femur and proximal tibial fractures. Injury 42:194–199
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhat, R., Wani, M.M., Rashid, S. et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis for closed distal tibial fractures: a consecutive study based on 25 patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 25, 563–568 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-014-1539-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-014-1539-4