Abstract
Purpose
To determine the relationship between postural sway and the severity of lumbar spinal canal stenosis as well as the effect on postoperative improvement.
Methods
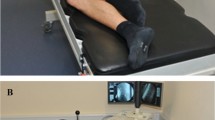
Stabilometry was performed before and 6 months after surgery in 52 patients (29 men and 23 women; mean age, 74.1 ± 7.8 years) who underwent decompression surgery for lumbar spinal canal stenosis. The environmental area (EA; the area surrounding the circumference of the stabilogram) and locus length per EA (L/EA) were evaluated. The patients were divided into moderate (n = 22) and severe (n = 30) groups according to the severity of canal stenosis. Patient characteristics and parameters were compared between the groups before and after surgery, including the visual analog scale (VAS) score for leg pain, Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), EA, and L/EA. In addition, factors affecting EA and L/EA were evaluated using multiple regression analysis.
Results
Age (p = 0.031), preoperative EA (p < 0.001), preoperative L/EA (p = 0.032), and sagittal vertical axis (p = 0.033) were significantly different between groups. The VAS score and ODI significantly improved postoperatively in both groups (p < 0.001). The EA significantly improved postoperatively only in the severe group (p < 0.001), whereas the L/EA did not significantly improve in either group. Multiple regression analysis showed that only the severity of canal stenosis was significantly associated with preoperative EA (p = 0.030), whereas age (p = 0.040) and severity of canal stenosis (p = 0.030) were significantly associated with preoperative L/EA. Diabetes was significantly associated with postoperative EA (p = 0.046) and L/EA (p = 0.030).
Conclusion
The severity of canal stenosis affected abnormal postural sway, which improved after decompression surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Manetti S, Turchetti G, Fusco F (2020) Determining the cost-effectiveness requirements of an exoskeleton preventing second hip fractures using value of information. BMC Health Serv Res 20:955. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05768-4
Karagul S, Kartaloglu IF (2022) The effect of single and dual-task balance exercises on balance performance in older adult patients with degenerative lumbar spondylosis: a randomized controlled trial. Geriatr Nurs 49:133–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2022.12.002
Kim HJ, Chun HJ, Han CD, Moon SH, Kang KT, Kim HS, Park JO, Moon ES, Kim BR, Sohn JS, Shin SY, Jang JW, Lee KI, Lee HM (2011) The risk assessment of a fall in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36:E588-592. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181f92d8e
Truszczynska A, Drzal-Grabiec J, Trzaskoma Z, Rapala K, Tarnowski A, Gorniak K (2014) A comparative analysis of static balance between patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis and asymptomatic participants. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 37:696–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmpt.2014.09.003
Kneis S, Bruetsch V, Dalin D, Hubbe U, Maurer C (2019) Altered postural timing and abnormally low use of proprioception in lumbar spinal stenosis pre- and post- surgical decompression. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 20:183. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2497-0
Yoshikawa M, Doita M, Okamoto K, Manabe M, Sha N, Kurosaka M (2008) Impaired postural stability in patients with cervical myelopathy: evaluation by computerized static stabilometry. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:E460-464. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e318178e666
Conable KM, Rosner AL (2011) A narrative review of manual muscle testing and implications for muscle testing research. J Chiropr Med 10:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2011.04.001
Schizas C, Theumann N, Burn A, Tansey R, Wardlaw D, Smith FW, Kulik G (2010) Qualitative grading of severity of lumbar spinal stenosis based on the morphology of the dural sac on magnetic resonance images. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:1919–1924. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181d359bd
Manoharan SR, Joshi D, Owen M, Theiss SM, Deinlein D (2018) Relationship of cervical sagittal vertical alignment after sagittal balance correction in adult spinal deformity: a retrospective radiographic study. Int J Spine Surg 12:269–275. https://doi.org/10.14444/5033
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 16:494–502. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.16.4.494
Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB (2000) The Oswestry disability index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25:2940–2952. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-200011150-00017
Copay AG, Glassman SD, Subach BR, Berven S, Schuler TC, Carreon LY (2008) Minimum clinically important difference in lumbar spine surgery patients: a choice of methods using the Oswestry disability index, medical outcomes study questionnaire short form 36, and pain scales. Spine J 8:968–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2007.11.006
Ogikubo O, Forsberg L, Hansson T (2007) The relationship between the cross-sectional area of the cauda equina and the preoperative symptoms in central lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32:1423–1428. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e318060a5f5
Burgstaller JM, Schuffler PJ, Buhmann JM, Andreisek G, Winklhofer S, Del Grande F, Mattle M, Brunner F, Karakoumis G, Steurer J, Held U, Group LS (2016) Is there an association between pain and magnetic resonance imaging parameters in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 41:E1053–E1062. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000001544
Alsaleh K, Ho D, Rosas-Arellano MP, Stewart TC, Gurr KR, Bailey CS (2017) Radiographic assessment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: Is MRI superior to CT? Eur Spine J 26:362–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4724-9
Andrasinova T, Adamova B, Buskova J, Kerkovsky M, Jarkovsky J, Bednarik J (2018) Is there a correlation between degree of radiologic lumbar spinal stenosis and its clinical manifestation? Clin Spine Surg 31:E403–E408. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0000000000000681
Leinonen V, Maatta S, Taimela S, Herno A, Kankaanpaa M, Partanen J, Kansanen M, Hanninen O, Airaksinen O (2002) Impaired lumbar movement perception in association with postural stability and motor- and somatosensory-evoked potentials in lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27:975–983. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-200205010-00019
Blaszczyk JW, Beck M, Sadowska D (2014) Assessment of postural stability in young healthy subjects based on directional features of posturographic data: vision and gender effects. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 74:433–442
Hue O, Simoneau M, Marcotte J, Berrigan F, Dore J, Marceau P, Marceau S, Tremblay A, Teasdale N (2007) Body weight is a strong predictor of postural stability. Gait Posture 26:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2006.07.005
Gerdhem P, Ringsberg KA, Akesson K, Obrant KJ (2005) Clinical history and biologic age predicted falls better than objective functional tests. J Clin Epidemiol 58:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.06.013
Lee HR, Park J, Ham DW, Kwon BT, Go SJ, Kim HJ (2022) functional mobility tests for evaluation of functionalities in patients with adult spinal deformity. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 23:391. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-022-05342-5
Masui T, Hasegawa Y, Yamaguchi J, Kanoh T, Ishiguro N, Suzuki S (2006) Increasing postural sway in rural-community-dwelling elderly persons with knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sci 11:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-006-1034-9
Shao X, Wang Z, Luan L, Sheng Y, Yu R, Pranata A, Adams R, Zhang A, Han J (2022) Impaired ankle inversion proprioception during walking is associated with fear of falling in older adults. Front Aging Neurosci 14:946509. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.946509
Afsharian T, Azhari S, Mostafazadeh B (2017) Comparison of postoperative clinical outcome after repairing surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis between diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Asian J Neurosurg 12:424–427. https://doi.org/10.4103/1793-5482.175623
Ogura Y, Kitagawa T, Kobayashi Y, Yonezawa Y, Takahashi Y, Yoshida K, Yasuda A, Shinozaki Y, Ogawa J (2020) Risk factors for persistent numbness following decompression surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 196:105952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105952
Liang Z, Xu X, Rao J, Chen Y, Wang R, Chen C (2022) Clinical evaluation of paraspinal mini-tubular lumbar decompression and minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis grade i with lumbar spinal stenosis: a cohort study. Front Surg 9:906289. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2022.906289
Stucki G, Liang MH, Fossel AH, Katz JN (1995) Relative responsiveness of condition-specific and generic health status measures in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. J Clin Epidemiol 48:1369–1378. https://doi.org/10.1016/0895-4356(95)00054-2
Yoshimura N, Muraki S, Oka H, Mabuchi A, En-Yo Y, Yoshida M, Saika A, Yoshida H, Suzuki T, Yamamoto S, Ishibashi H, Kawaguchi H, Nakamura K, Akune T (2009) Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis, lumbar spondylosis, and osteoporosis in Japanese men and women: the research on osteoarthritis/osteoporosis against disability study. J Bone Miner Metab 27:620–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-009-0080-8
Neville SE, Boye KS, Montgomery WS, Iwamoto K, Okamura M, Hayes RP (2009) Diabetes in Japan: a review of disease burden and approaches to treatment. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 25:705–716. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.1012
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding
No funds were received in support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ujigo, S., Kamei, N., Yamada, K. et al. Balancing ability of patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Eur Spine J 32, 4174–4183 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07782-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07782-6