Abstract
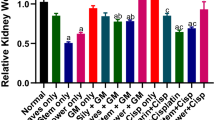
Disruption of homeostasis, detoxification and excretion in kidney functions by endogenous or exogenous toxicants results in the occurrence of nephrotoxicity. The study aimed to explore Boerhaavia diffusa L., a Nyctaginaceae herbal medicine that has been used commonly for nephrotic syndrome for its nephroprotective property against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Swiss albino mice were administered with gentamicin and pre-treated with B. diffusa. Biochemical aspects and antioxidants of the kidney were estimated. Histological impacts along with expressions of kidney injury markers and mediators were examined. The phytochemical analyses resulted in the presence of several herbal metabolites with therapeutic influence on kidney injury. Determination of changes in biochemical constituents of the kidney such as urea, uric acid and creatinine suggests that kidney function has been altered in the presence of gentamicin. Examination of histopathological changes revealed that oral administration of mice with an aqueous or ethanolic extract from the leaves of B. diffusa attenuated the kidney damage caused by gentamicin. Levels of cellular antioxidants responsible for scavenging ROS during nephrotoxic conditions were increased with modulation in the gene expression of acute kidney injury biomarkers in extract-treated animals showing their potential nephroprotective action against gentamicin. Inflammatory genes which are responsible for producing pro-inflammatory cytokines, namely, iNOS and IL-6 were downregulated upon B. diffusa administration. B. diffusa potentially mitigates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity which can be a potential therapeutic drug as a nephroprotectant.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achyut BR, Arbab AS (2015) Tracking of administered progenitor cells in brain injury and stroke by magnetic resonance imaging. Cell Therapy for Brain Injury. 187–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15063-5_12
Ahuja N, Andres-Hernando A, Altmann C, Bhargava R, Bacalja J, Webb RG, He Z, Edelstein CL, Faubel S (2012) Circulating IL-6 mediates lung injury via CXCL1 production after acute kidney injury in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 303(6):F864–F872. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00025.2012
Ansari MN, Rehman NU, Karim A, Imam F, Hamad AM (2021) Protective effect of Thymus serrulatus essential oil on cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in rats, through suppression of oxidative stress and downregulation of NF-κB, iNOS, and Smad2 mRNA expression. Molecules 26(5):1252
Balakumar P, WitnessKoe WE, Gan YS, JemayPuah SM, Kuganesswari S, Prajapati SK, Varatharajan R, Jayachristy SA, Sundram K, Bahari MB (2017) Effects of pre and post-treatments with dipyridamole in gentamicin-induced acute nephrotoxicity in the rat. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 84:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2016.12.007
Barwal A, Kumari S, Verma SK, Goyal PK, Sharma I, Sharma S, Sharma AK (2015) Evaluation of herbal formulation Neeri (NS-RF) for protective effect against heavy metal induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Indo Am J Pharma Res 5(09):2790–2798
Bayomy NA, Elbakary RH, Ibrahim MA, Abdelaziz EZ (2017) Effect of lycopene and rosmarinic acid on gentamicin induced renal cortical oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy in adult male albino rat. Ana Rec 300(6):1137–1149. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.23525
Beers RF, Sizer IW (1952) A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalases. J Biol Chem 195:133–140
Bolignano D, Donato V, Coppolino G, Campo S, Buemi A, Lacquaniti A, Buemi M (2008) Neutrophil gelatinase–associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of kidney damage. Am J Kidney Dis 52(3):595–605. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.01.020
Borrelli F, Ascione V, Capasso R, Izzo AA, Fattorusso E, Taglialatela-Scafati O (2006) Spasmolytic effects of nonprenylated rotenoid constituents of Boerhaavia diffusa roots. J Nat Prod 69(6):903–906. https://doi.org/10.1021/np060073h
Brod J, Sirota JH (1948) The renal clearance of endogenous “creatinine” in man. J Clin Invest 27(5):645–654
Bryman A, Cramer D (2012) Quantitative data analysis with IBM SPSS 17, 18 & 19: a guide for social scientists. Routledge
Caraway WT, Hald PM (1963) Uric acid. In: Standard Methods of Clinical Chemistry, vol 4. pp 239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4831-9685-5.50029-7
Costello HM, Johnston JG, Juffre A, Crislip GR, Gumz ML (2022) Circadian clocks of the kidney: function, mechanism, and regulation. Physiol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00045.2021
Cuzzocrea S, Mazzon E, Dugo L, Serraino I, Di Paola R, Britti D, De Sarro A, Pierpaoli S, Caputi AP, Masini E, Salvemini D (2002) A role for superoxide in gentamicin-mediated nephropathy in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 450(1):67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(02)01749-1
Duraisamy P, Manikandan B, Koodalingam A, Munusamy A, Ramar M (2021) Anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive and anti-oxidant activities of carvacrol containing leaf extracts of edible Indian borage plant Plectranthus amboinicus: an in vivo and in vitro approach. Comp Clin Path 30(3):397–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03230-3
Fischer AH, Jacobson KA, Rose J, Zeller R (2008) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 1:pdb-rot4986. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot073411
Garofalo C, Borrelli S, Liberti ME, Andreucci M, Conte G, Minutolo R, Provenzano M, De Nicola L (2019) SGLT2 inhibitors: nephroprotective efficacy and side effects. Medicina 55(6):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060268
Ghaznavi R, Kadkhodaee M (2007) Comparative effects of selective and non-selective nitric oxide synthase inhibition in gentamicin-induced rat nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 81(6):453–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0157-2
Ghosh S (2018) Boerhavia diffusa: one plant with many functions. Int J Green Pharm 12(03). https://doi.org/10.22377/ijgp.v12i03.2003
Guessan NK, Kadja B, Zirihi G, Traoré D, Aké-Assi L (2009) Screening phytochimique de quelques plantes médicinales ivoiriennes utilisées en pays Krobou (Agboville, Côte-d’Ivoire). Sci Nat 6(1). https://doi.org/10.4314/scinat.v6i1.48575
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biochem 249(22):7130–7139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)42083-8
Haddad JJ (2002) Antioxidant and prooxidant mechanisms in the regulation of redox (y)-sensitive transcription factors. Cell Sign 14(11):879–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0898-6568(02)00053-0
Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, Thadhani R, Bonventre JV (2002) Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int 62(1):237–244. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00433.x
Hu J, Yang L, Cheng X, Li Y, Cheng Y (2021) Aminoglycoside-based biomaterials: from material design to antibacterial and gene delivery applications. Adv Funct Mater 31(36):2103718. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202103718
Karahan İ, Ateşşahin A, Yılmaz S, Çeribaşı AO, Sakin F (2005) Protective effect of lycopene on gentamicin-induced oxidative stress and nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicology 215(3):198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2005.07.007
Katary M, Salahuddin A (2017) Ameliorative effect of gossypin against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Life Sci 176:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.03.009
Kaviya M, Balasubramanian B, Bharathi K, Malaisamy A, Al-Dhabi NA, Mariadhas VA, Anand AV, Liu W (2022) Evaluation of nutritional substances and investigation of antioxidant and antimicrobial potentials of Boerhavia diffusa with in silico molecular docking. Molecules 27(4):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041280
Manikandan R, Beulaja M, Thiagarajan R, Priyadarsini A, Saravanan R, Arumugam M (2011a) Ameliorative effects of curcumin against renal injuries mediated by inducible nitric oxide synthase and nuclear factor kappa B during gentamicin-induced toxicity in Wistar rats. Eur J Pharmacol 670(2–3):578–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.08.037
Manikandan R, Thiagarajan R, Beulaja S, Sivakumar MR, Meiyalagan V, Sundaram R, Arumugam M (2011b) 1, 2 di‐substituted idopyranose from Vitex negundo l. Protects against streptozotocin‐induced diabetes by inhibiting nuclear factor‐kappa B and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression. Micros Res Tech 74(4):301–307. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.20904
Manu KA, Kuttan G (2009) Immunomodulatory activities of Punarnavine, an alkaloid from Boerhaavia diffusa. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 31(3):377–387. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923970802702036
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247(10):3170–3175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)45228-9
Mohamed HZ, Shenouda MB (2021) Amelioration of renal cortex histological alterations by aqueous garlic extract in gentamicin induced renal toxicity in albino rats: a histological and immunohistochemical study. Alexandria J Med 57(1):28–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/20905068.2020.1871179
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B (1979) Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 582(1):67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(79)90289-7
Nechemia-Arbely Y, Barkan D, Pizov G, Shriki A, Rose-John S, Galun E, Axelrod JH (2008) IL-6/IL-6R axis plays a critical role in acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(6):1106–1115. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2007070744
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Oladele GM, Ode OJ, Ogunbodede MA (2011) Evaluation of anti-inflammatory and membrane stabilizing effects of aqueous root extract of Boerhavia diffusa Linn. in rats. Int J Appl Biol Pharm Technol 2:84
Özbek E, Turkoz Y, Sahna E, Ozugurlu F, Mizrak B, Ozbek M (2000) Melatonin administration prevents the nephrotoxicity induced by gentamicin. BJU Int 85(6):742–746. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410x.2000.00531.x
Pan MH, Lai CS, Ho CT (2010) Anti-inflammatory activity of natural dietary flavonoids. Food Funct 1(1):15–31. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0FO00103A
Pareta SK, Patra KC, Harwansh R, Kumar M, Meena KP (2011) Protective effects of Boerhaavia diffusa against acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol 2:698–706
Parlakpinar H, Ozer MK, Sahna E, Vardi N, Cigremis Y, Acet A (2003) Amikacin-induced acute renal injury in rats: protective role of melatonin. J Pineal Res 35(2):85–90. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-079X.2003.00059.x
Pereira DM, Faria J, Gaspar L, Valentão P, Andrade PB (2009) Boerhaavia diffusa: metabolite profiling of a medicinal plant from Nyctaginaceae. Food Chem Toxicol 47(8):2142–2149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.05.033
Phatak RS, Khanwelkar CC, Matule SM, Hendre AS, Datkhile KD (2021) Antioxidant activity of Murraya koenigii leaves methanolic and aqueous extracts on oxidative stress in high fat-fructose fed rats. Pravara Med Rev 13(3)
Promsan S, Lungkaphin A (2020) The roles of melatonin on kidney injury in obese and diabetic conditions. BioFactors 46(4):531–549. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1637
Rajpoot K, Mishra RN (2011) Boerhaavia diffusa roots (Punarnava mool)–review as rasayan (rejuvenator/antiaging). Int J Res Pharm Biomed Sci 2:1451–1460
Rosenthal HL (1955) Determination of urea in blood and urine with diacetyl monoxime. Anal Chem 27(12):1980–1982. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60108a039
Shang W, Wang Z (2017) The update of NGAL in acute kidney injury. Curr Protein Pept Sci 18(12):1211–1217. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203717666160909125004
Sharma K, Sahai M (2017) Chemical constituents of Boerhavia diffusa leaves. J Med Plants Stud 5(4):166–169
Shi B, Li S, Ju H, Liu X, Li D, Li Y (2019) Protein kinase C inhibitor chelerythrine attenuates partial unilateral ureteral obstruction induced kidney injury in neonatal rats. Life Sci 1(216):85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.11.025
Shivalinge GKP (2014) Study of protective effects of stem bark extracts of Ficus racemosa in drug-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and nephrotoxicity in animal models. Shodhganga. http://hdl.handle.net/10603/14584
Sundararajan R, Bharampuram A, Koduru R (2014) A review on phytoconstituents for nephroprotective activity. Pharmacophore 5(1):160–182
Tolba MF, Omar HA, Azab SS, Khalifa AE, Abdel-Naim AB, Abdel-Rahman SZ (2016) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester: a review of its antioxidant activity, protective effects against ischemia-reperfusion injury and drug adverse reactions. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 56(13):2183–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2013.821967
Vaidya VS, Ferguson MA, Bonventre JV (2008) Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:463. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094615
Yadav N, Khandelwal S (2009) Therapeutic efficacy of Picroliv in chronic cadmium toxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 47(4):871–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.01.021
Yasir F, Waqar MA (2011) Effect of indigenous plant extracts on calcium oxalate crystallization having a role in urolithiasis. Urolo Res 39(5):345–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-011-0374-x
Zhou Y, Vaidya VS, Brown RP, Zhang J, Rosenzweig BA, Thompson KL, Miller TJ, Bonventre JV, Goering PL (2008) Comparison of kidney injury molecule-1 and other nephrotoxicity biomarkers in urine and kidney following acute exposure to gentamicin, mercury, and chromium. Toxicol Sci 101(1):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfm260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable national and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Consent for publication
For this type of study, consent for publication is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramar, M., Ravi, S., Duraisamy, P. et al. Gentamicin-induced acute nephrotoxicity counteraction using Boerhaavia diffusa in Swiss albino mice. Comp Clin Pathol 32, 1005–1017 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03512-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03512-y