Abstract
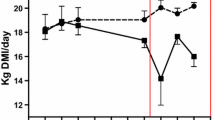
Impact of defaunation (removal of protozoa from the rumen) on animal health and productivity is still controversial. This study quantified the effects of defaunation intervals using two defaunating agents; sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) and dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate (DSS), on serum and milk profiles in lactating goats. Ten apparently healthy female Egyptian native breed lactating goats were assigned into two experimental groups. The administration of both defaunating agents was carried out daily for the first three days of the experiment then once weekly for three consecutive weeks. The research samples were collected before defaunation, 7, 14, and 21 days post defaunation. Milk parameters were determined using milk lactometer and selected serum parameters were measured using specific kits. Generally, defaunation resulted in a significant decrease in milk fat, solid not fat, and salt%, with significant increment in serum calcium (Ca) and inorganic phosphorous (P). Serum Ca and albumin decreased significantly at 14 days than 21 days post defaunation. Serum inorganic P decreased significantly due to DSS than SLS and at 14 days than 7 days post defaunation. Milk profile was significantly undesirably influenced by using DSS more than SLS, and at time point of 14 days post defaunation. Defaunation using DSS or SLS for 14–21 days has a dramatically negative influence on milk profile. It is recommended not to use DSS for treatment of rumen bloat or indigestion in dairy goats.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to institutional regulations, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abou Akkada A, Bartley E, Berube R, Fina L (1968) Simple method to remove completely ciliate protozoa of adult ruminants. Appl Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/am.16.10.1475-1477
Abdelmawla SMS (2008) Natural saponin plant extract without or with fresh baker’s yeast in lactating buffaloe cows rations impact on nutrients digestibility, milk production, composition, and some blood serum parameters. J Agric Sci Mansoura Univ. https://doi.org/10.21608/jappmu.2008.217998
Alonso AN (1979) Diagnostic analysis of rumen fluid. The Veterinary clinics of North America. Large Animal Practice 1(2):363-376. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0196-9846(17)30189-1
Aliah ZM, Rashidah S, Jinap S, Anis S, Meor H, Intan HI (2019) Chemical and mineral composition of raw goat milk as affected by breed varieties available in Malaysia. Int J Food Prop 22:815–824. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2019.1610431
Ankrah P, Loerch S, Kampman K, Dehority B (1990) Effects of defaunation on in situ dry matter and nitrogen disappearance in steers and growth of lambs. J Anim Sci 68(10):3330–3336. https://doi.org/10.2527/1990.68103330x
Azab ME, Abdel –Maksoud HA (1999) Changes in some haematological and biochemical parameters during pregnancy and post-partum periods in female Baladi goats. Small Rum Res 34:77–85
Balikci E, Yildiz A, Gurdogan F (2007) Blood metabolite concentrations during pregnancy and post-partum in Akkaraman ewes. Rum Res 67:247–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SMALLRUMRES.2005.10.011
Bani-Ismail ZA, Al-Majali AM, Amireh F, Al-Rawashdeh OF (2008) Metabolic profile in goat does in late pregnancy with and without subclinical pregnancy toxemia. Vet Clin Pathol 37:434–437. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-165x.2008.00076.x
Bird SH, Leng RA (1978) The effects of defaunation of the rumen on the growth rates of cattle on low protein high energy diets. Brit J Nutr 40:163–167. https://doi.org/10.1079/BJN19780108
Bird SH, Romulo B, Leng RA (1994) Effects of lucerne supplementation and defaunation on feed intake, digestibility, N retention and productivity of sheep fed straw based diets. Anim Feed Sci Technol 45(2):119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-8401(94)90020-5
Carnicella D, Dario M, Caribe-Ayres MC, Laudadio V, Dario C (2008) The effect of diet, parity, year and number of kids on milk yield and milk composition in Maltese goat. Small Rumin Res 77(1):71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2008.02.006
Chandramoni TC, Haque N, Lal M, Jadhao S, Khan M (2002) Energy balance in faunated and defaunated sheep on a ration high in concentrate to roughage (good quality) ratio. Pak J Nutr 1(1):31–33. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2002.31.33
Chilliard Y, Ferlay A, Rouel J, Lamberet G (2003) A review of nutritional and physiological factors affecting goat milk lipid synthesis and lipolysis. J Dairy Sci 86:1751–1770. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(03)73761-8
Ciappesoni G, Pribyl J, Milerski M, Mares V (2004) Factors affecting goat milk yield and its composition. Czech J Anim Sci 49(11):465–473. https://www.agriculturejournals.cz/pdfs/cjs/2004/11/01.pdf
Coleman GS (1975) The interrelationship between rumen ciliate protozoa and bacteria. In: McDonald IW, Warner ACI (eds) Digestion and metabolism in the ruminant. University of New England Publishing Unit, Armidale, pp 149–164
Colin GP (2021) Compositional and functional characteristics of goat milk and relevance as a base for infant formula. J Food Sci 86:2. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15574
Eadie JM, Oxford A (1957) A simple and safe procedure for the removal of holotrich ciliates from the rumen of an adult fistulated sheep. Nature 179:4557–4485. https://doi.org/10.1038/179485a0
Eryavuz A, Dündar Y, Ozdemir M, Aslan R, Tekerli M (2003) Effects of urea and sulfur on performance of faunate and defaunate Ramlic lambs, and some rumen and blood parameters. Anim Feed Sci Technol 109(1–4):35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-8401(03)00201-3
Fahmy WG, Bahaa AO, Murphy MR, Nombekela SW, Corley RN, Zhu JS (1998) Effect of defaunation and amino acid supplementation on growth and amino acid balance in growing sheep. Ann Zootech 44:364
Finlay BJ, Esteban G, Clarke KG (1994) Some rumen ciliates have endosymbiotic methanogens. FEMS Microbiol Lett 117:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06758.x
Fox PF, Uniacke-Lowe T, McSweeney PL, O’Mahony JA (2015) Salts of milk, In: Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry. Springer, Cham, pp 241–270. http://students.aiu.edu/submissions/profiles/resources/onlineBook/U7Y2y8_Dairy_Chemistry_and_Biochemistry.pdf
Gupta AR, Putra RC, Saini M, Swarup D (2007) Haematology and serum biochemistry of Chital (Axis axis) and barking deer (Muntiacus muntjak) reared in semi-captivity. Vet Res Comm 31:801–808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-006-0095-8
Hegarty RS (1999) Reducing rumen methane emissions through elimination of rumen protozoa. Aust J Agric Res 50:1321–1327. https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201302935576
Hsu J, Fahey J.r, Berger L, Mackie RI, Merchen NR, (1991) Manipulation of nitrogen digestion by sheep using defaunation and various nitrogen supplementation regimens. J Anim Sci 69(3):1290–1299. https://doi.org/10.2527/1991.6931290x
Huber TL (1971) Effect of acute indigestion on compartmental water volumes and osmolality in sheep. Am J Vet Res 32(6):887–890. https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/19721402432
Hungate RE (1966) The rumen and its microbes. Academic press New York, pp 533. https://www.elsevier.com/books/the-rumen-and-its-microbes/hungate/978-1-4832-3308-6
Mehta BM (2014) Chemical composition of milk and milk products, In. Handbook of food chemistry, Springer, pp: 1–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41609-5_31-1
Newbold CJ, De la Fuente G, Belanche A, Ramos-Morales E, McEwan N (2015) The role of ciliate protozoa in the rumen. Front Microbiol 6:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01313
Olafadehan O, Adewumi M, Okunade S (2014) Effects of feeding tannin-containing forage in varying proportion with concentrate on the voluntary intake, haematological and biochemical indices of goats. Trakia Journal of Sciences 12(1):73
Orpin C (1977) Studies on the defaunation of the ovine rumen using dioctyl sodium sulphosuccinate. J Appl Bacteriol 43(2):309–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00756.x
Pugh DG, Baird NN (2012) Sheep and goat medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences, pp. 621
SAS (2013) The SAS system for Windows, release 9.4. In Cary, North Carolina, USA: SAS Institute Inc
Saber M, Tayeb FM, Abdou OM, Abdel-Salam AB, Mousa SA (2020a) Impact of transfaunation of rumen ciliate cultures on physical examination, selected serum parameters and milk profile in defaunated lactating dairy goats. Int J Vet Sci 9(2):239–243. https://doi.org/10.37422/IJVS/20.012
Saber M, Tayeb, FM, Abdou OM, Abdel-Salam AB, Mousa SA (2020b) Effect of seasons and breeds on selected serum parameters and milk profile in clinically healthy lactating dairy goats in Egypt. Int J Vet Sci 9(2):244–248. https://doi.org/10.37422/IJVS/20.006
Santra A, Jakhmola RC (1998) Effect of defaunation on animal productivity. J Appl Him Res 14:103–116. https://doi.org/10.1080/09712119.1998.9706689
Santra A, Karim S (2000) Growth performance of faunated and defaunated Malpura weaner lambs. Anim Feed Sci Technol 86(3–4):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-8401(00)00161-9
Sokratis, S, Natalja P, Stig P, Ian G, Michael RF (2019) Comparative nutrient profiling of retail goat and cow milk. Nutrients Journal 11(10):2282. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102282
Son HN, Huyen DTN, Roger SH (2020) Defaunation and its impacts on ruminal fermentation, enteric methane production and animal productivity. Lives Res Rural Dev 32(4). http://www.lrrd.org/lrrd32/4/nghson32060.html
Tambuwal FM, Agale BM, Bangana A (2002) Haematological and biochemical values of apparently healthy Red Sokoto goats. Proc 27th Annual Confr Nig Soc Anim Prod (NSAP), FUT, Akure, Nigeria, pp. 50–55
Van’t Klooster A (1967) The state of Ca, Mg and some other minerals in the gut contents and faeces of ruminants in relation to their absorption. Nutr Abst and Rev 39:129–130
Williams AG, Coleman GS (1997) The rumen protozoa. In: Hobson PN, Stewart CS (eds) The rumen microbial ecosystem. Blackie Academic and Professional, London, UK, pp 73–139
Wright AG (2015) Rumen protozoa. Rumen microbiology: from evolution to revolution. Springer, New Delhi, pp 113–120
Yokus B, Cakir DU, Kanay Z, Toprak G, Uysal E (2006) Effects of seasonal and physiological variations on the serum chemistry, vitamins and thyroid hormone concentrations in sheep. J Vet Med A 53:271–276. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0442.2006.00831.x
Young DS, Friedman RB (2002) Effects of disease on clinical laboratory tests. In: Clin Chem 48(4):682–683. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/48.4.682a
Young WP (2010) Goat milk: composition, characteristics. In book: Encyclopedia of Animal Science, 2nd Edition, CRC PressEditors, pp. 537–540. https://doi.org/10.1081/E-EAS2-120045704
Zahraddeen D, Butswat ISR, Mbap ST (2007) Evaluation of some factors affecting milk composition of indigenous goats in Nigeria. Lives Res Rural Dev 19(11). http://www.lrrd.org/lrrd19/11/zahr19166.htm
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mahmoud Saber and Sabry Ahmed Mousa contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Ayah Badawi Abdel-Salam and Mahmoud Saber. Statistical analyses were performed by Hisham Ahmed Abdelrahman. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mahmoud Saber and Ayah Badawi Abdel-Salam. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. The manuscript was revised by Sabry Ahmed Mousa. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the declaration of Ethics of Animal Experiments Committee, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University (Date: 10/10/2019/ No: VetCU10102019084).
Informed consent
A documented consent approving serum and milk sample collection was carried out by head of Department of Medicine and Infectious Diseases, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University.
Consent for publication
A documented consent approving the publication was carried out by all authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saber, M., Abdel-Salam, A.B., Abdelrahman, H.A. et al. Influence of two defaunating agents and defaunation intervals on milk profile and selected serum parameters in lactating dairy goats in Egypt. Comp Clin Pathol 32, 925–939 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03503-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03503-z