Abstract
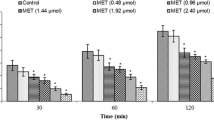
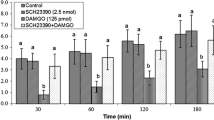
Purine nucleotides play different roles in many physiological functions of the central nervous system. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of the central purine molecule ATP, an agonist of P2 receptors, for the first time, in the regulation of feeding behavior in broilers. Different doses of ATP (2.5, 25, and 50 μg) and its antagonist pyridoxal-phosphate-6-azophenyl-2′, 4′-disulphonic acid (PPADS) (50 μg), ATP (50 μg) plus PPADS (50 μg), and the solvent were injected intracerebroventricularly (ICV) to broilers. ATP increased food intake. PPADS reduced food intake. Concurrent injection of ATP and PPADS reduced food intake too. The present study suggests that ATP and P2 receptors are included in the regulation of food intake in neonate birds.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Verkhratsky A, Zimmermann H (2009) Purinergic signalling in the nervous system: an overview. Trends Neurosci 32:19–29
Belcher S, Zsarnovszky A, Crawford P, Hemani H, Spurling L, Kirley T (2006) Immunolocalization of ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 3 in rat brain: implications for modulation of multiple homeostatic systems including feeding and sleep–wake behaviors. Neuroscience 137:1331–1346
Bowser DN, Khakh BS (2007) Vesicular ATP is the predominant cause of intercellular calcium waves in astrocytes. J Gen Physiol 129:485–491
Burnstock G (2006) Historical review: ATP as a neurotransmitter. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:166–176
Burnstock G (2007) Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev 87:659–797
Burnstock G, Krügel U, Abbracchio MP, Illes P (2011) Purinergic signalling: from normal behaviour to pathological brain function. Prog Neurobiol 95:229–274
Collden G, Mangano C, Meister B (2010) P2X2 purinoreceptor protein in hypothalamic neurons associated with the regulation of food intake. Neuroscience 171:62–78
Florenzano F, Viscomi MT, Mercaldo V, Longone P, Bernardi G, Bagni C, Molinari M, Carrive P (2006) P2X2R purinergic receptor subunit mRNA and protein are expressed by all hypothalamic hypocretin/orexin neurons. J Comp Neurol 498:58–67
Furuse M (2002) Central regulation of food intake in the neonatal chick. Anim Sci J 73:83–94
Jonaidi H, Rasooli R (2013) Effect of central enterostatin on fat intake in neonatal chicks. Neurosci Lett 533:60–64
Kato F, Kawamura M, Shigetomi E, Tanaka J-i, Inoue K (2004) ATP-and adenosine-mediated signaling in the central nervous system: synaptic purinoceptors: the stage for ATP to play its “dual-role”. J Pharmacol Sci 94:107–111
Kittner H, Franke H, Harsch JI, El-Ashmawy IM, Seidel B, Krügel U, Illes P (2006) Enhanced food intake after stimulation of hypothalamic P2Y1 receptors in rats: modulation of feeding behaviour by extracellular nucleotides. Eur J Neurosci 24:2049–2056
Kogure K, Alonso OF (1978) A pictorial representation of endogenous brain ATP by a bioluminescent method. Brain Res 154:273–284
Morton G, Cummings D, Baskin D, Barsh G, Schwartz M (2006) Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 443:289–295
Motaghi S, Jonaidi H, Jadidi J (2017) Study of illness anorexia in birds by concentrating on roles of central and peripheral cyclooxygenases-1 and cyclooxygenases-2. Comp Clin Pathol 26:377–383
Pankratov YV, Lalo UV, Krishtal OA (2002) Role for P2X receptors in long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 22:8363–8369
Richards M, Proszkowiec-Weglarz M (2007) Mechanisms regulating feed intake, energy expenditure, and body weight in poultry. Poult Sci 86:1478–1490
Saito E-S, Kaiya H, Tachibana T, Tomonaga S, Denbow DM, Kangawa K, Furuse M (2005) Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on food intake is mediated by the corticotropin-releasing factor system in neonatal chicks. Regul Pept 125:201–208
Seidel B, Bigl M, Franke H, Kittner H, Kiess W, Illes P, Krügel U (2006) Expression of purinergic receptors in the hypothalamus of the rat is modified by reduced food availability. Brain Res 1089:143–152
Wollmann G, Acuna-Goycolea C, van den Pol AN (2005) Direct excitation of hypocretin/orexin cells by extracellular ATP at P2X receptors. J Neurophysiol 94:2195–2206
Funding
This research was financially supported by Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman Research Council under annual grant of corresponding author (No. 1393).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in this study involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution at which the studies were conducted.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motaghi, S., Jonaidi, H., Gooshki, S.N. et al. The central role of ATP in controlling broiler’s food intake. Comp Clin Pathol 28, 599–602 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2882-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2882-3