Abstract
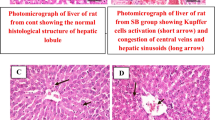
Acalypha wilkesiana is a member of the spurge family, genus Acalypha, that is widely used in folklore medicine. The aim of this study was to screen aqueous leaf extract of A. wilkesiana for toxic effects in vitro and in vivo. We examined the phytochemical profile, cytotoxic effects on baby hamster kidney cell line (BHK-21), and oral subacute toxicity of A. wilkesiana leaf decoction in rats. Rats were given 0, 300, 600, and 1200 mg/kg body weight of A. wilkesiana leaf extract, daily, orally for 14 days. The phytochemical profile showed the presence of flavonoids, saponin, cardiac glycosides, and tannins. It caused apoptosis in BHK-21 cell line at concentrations of 0, 25, 50, 100, and 200 μg/ml. There was significant increase in the levels of serum AST, ALT, creatinine, urea, Na+, K+, and Cl− levels in all the test groups compared to the control. Histology of the liver revealed centrilobular degeneration and necrosis with sinusoidal dilatation as well as polymorphonuclear and mononuclear infiltration. The kidney showed severe glomerular and tubular degeneration and necrosis with hemorrhage at all doses administered. We conclude that the plant was toxic at the doses tested in vitro and in vivo, and care should be exercised in its use in herbal medicine.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anokwuru CP, Sinisi A, Samie A, Taglialatela-Scafat O (2015) Antibacterial and antioxidant constituents of Acalypha wilkesiana. Nat Prod Res 29(12):1180–1183
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2013) Natural products: a continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830(6):3670–3695
Din WM, Chu J, Clarke G, Jin KT, Bradshaw TD, Fry JR, Wiart C (2013) Antioxidant and cytoprotective effects of an ethanol extract of Acalypha wilkesiana var. macafeana from Malaysia. Nat Prod Commun 8(3):375–380
Francis G, Kerem Z, Makkar PSH, Becker K (2002) The biological action of saponins in animal systems: a review. Br J Nutr 88(6):587–605
Freshney RI (2010) Culture of animal cells: a manual of basic technique and specialized applications, 6th edn
Gotep JG, Agada GOA, Gbise DS, Chollom S (2010) Antibacterial activity of ethanolic extract of Acalypha wilkesiana leaves growing in Jos, Plateau State, Nigeria. Malays J Microbiol 6(2):69–74
Gowda S, Desai PB, Hull VV, Math AAK, Vernekar SN, Kulkarni SS (2009) A review on laboratory liver function tests. Pan Afr Med J 3:17
Ikewuchi JC, Ikewuchi CC (2010) Hypocholesterolaemic effect of aqueous extract of Acalypha wilkesiana ‘Godseffiana’ Muell Arg on rats fed egg yolk supplemented diet: implications for cardiovascular risk management. Res J Sci Technol 2(4):78–81
Iniaghe OM, Oyewo EB, Egharevba O (2012) Hyponatremic effect of aqueous leaf extract of Acalypha wilkesiana in male wistar rats. Eur J Med Plants 2(4):348–355
Kanji S, MacLean RD (2012) Cardiac glycoside toxicity: more than 200 years and counting. Crit Care Clin 28(4):527–535
Kingsley O, Marshall AA (2014) Serum aminotransferase activities and bilirubin levels in salt loaded experimental rabbits treated with aqueous and ethanol extracts of Acalypha wilkesiana. J Exp Clin Biosci 2:37–41
Ogundaini AO (2005) From greens into medicine: taking a lead from nature. An inaugural lecture delivered at Oduduwa Hall, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Ile-Ife, Nigeria: OAU Press. (Inaugural Lecture Series, No. 176)
Olukunle JO, Adenubi OT, Biobaku KT, Sogebi EA (2015a) Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of methanol extract and fractions of Acalypha wilkesiana leaves. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 26(2):181–184
Olukunle JO, Jacobs EB, Ajayi OL, Biobaku KT, Abatan MO (2015b) Toxicological evaluation of the aqueous extract of Acalypha wilkesiana in Wistar albino rats. J Complement Integr Med 12(1):53–56
Omonkhua AA, Onoagbe IO (2008) Effects of Irvingia grandifolia, Urena lobata and Carica papaya on the oxidative status of normal rabbits. Internet J Nutr Wellnes. 6(2), ISSN, 1937–8297.
Pietta PG (2000) Flavonoids as antioxidants. J Nat Prod 63(7):1035–1042
Prakash Gupta RK, Pradeepa, Hanumanthappa M (2013) In vitro antioxidant and H+, K+-ATPase inhibition activities of Acalypha wilkesiana foliage extract. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 5(3):214–223
Santiago C, Lim K, Loh H, Ting KN (2015) Prevention of cell-surface attachment and reduction of penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a) level in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms by Acalypha wilkesiana. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:79
Sarwar GG, Wu XC, Cockell KA (2012) Impact of antinutritional factors in food proteins on the digestibility of protein and the bioavailability of amino acids and on protein quality. Br J Nutr 108:315–32
Seebaluck R, Gurib-Fakim A, Mahomoodally F (2015) Medicinal plants from the genus Acalypha (Euphorbiaceae)—a review of their ethnopharmacology and phytochemistry. J Ethnopharmacol 159:137–157
Sule OJ, Elekwa I, Ayalogu EO (2012) The protective nature of Acalypha wilkensiana leaves on CCL4-induced hepatotoxicity in wistar rats. J Pharm Biomed Sci. 14 (14)
Trease GE, Evans MD (1989) A textbook of pharmacognosy, 13th edn. Baillier, Trindal and Caussel, London, pp 144–148
Vijayarathna S, Sasidharan S (2012) Cytotoxicity of methanol extracts of Elaeis guineensis on MCF-7 and Vero cell lines. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(10):826–829
Acknowledgments
This research work was sponsored by the Africa Education Initiative (NEF), USA in partnership with the National Veterinary Research Institute, Vom, Nigeria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makoshi, M.S., Oladipo, O.O., Gotep, J.G. et al. Safety evaluation of Acalypha wilkesiana in albino rats and BHK-21 cell line. Comp Clin Pathol 25, 543–548 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-016-2224-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-016-2224-2