Abstract
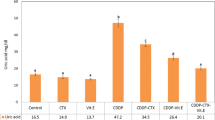
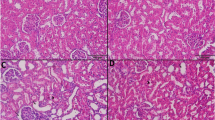
Nephrotoxicity is usually thought of as a common invariable consequence of hemodynamic toxicity whose effects, including oliguria and dysuria, has largely limited the clinical use of cisplatin. In this study, we investigated the protective effects of low and high dose of vitamin C against cisplatin-induced rat nephrotoxicity. Hence, 50 adult male Swiss albino rats were randomly divided into five equal groups to receive a corresponding dose of either normal saline as control, vitamin C (600 mg/kg/BW, i.v.), or cisplatin alone (7 mg/kg/BW, i.p.) or in combination with vitamin C at low dose (200 mg/kg/BW, i.v.) and high dose (600 mg/kg/BW, i.v.) for 9 days. Daily administration of cisplatin at a dose of 7 mg/kg/BW resulted in a significant increase in oxidative stress in renal tissues and plasma and a concomitant decrease in the creatinine clearance and renal blood flow as a result of early hemodynamic toxicity. Histopathological examination revealed acute tubular necrosis with hyaline cast formation triggered by cisplatin over 9 days of experiment. Further biochemical studies showed protecting effects of supplemented vitamin C at a high dose, illustrated by slowdown in the urinary enzyme activity, a significant decrease in plasma lipid peroxidation, and an increased tissue superoxide dismutase activity with recovery in the glomerular hemodynamicity and the ATPase activity up to 50 % when compared to controls and rats receiving low-dose. In high-dose animals, normal glomerular and tubular function on recovery from toxic renal failure led us to conclude that antioxidant property of vitamin C increases with dose, and, therefore, high dose of vitamin C prevents both functional and histological renal changes induced by cisplatin in rats, more efficient than low dose of the vitamin.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajith TA, Usha S, Nivitha V (2007) Ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol protect anticancer drug cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in mice: a comparative study. Clin Chim Acta 375:82–86
Antunes LM, Darin JD, Bianchi MD (2000) Protective effects of vitamin C against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and lipid peroxidation in adult rats: a dose-dependent study. Pharmacol Res 41:405–411
Appenroth D, Frob S, Kersten L, Splinter FK, Winnefeld K (1997) Protective effects of vitamin E and C on cisplatin nephrotoxicity in developing rats. Arch Toxicol 71:677–683
Arivarasu NA, Priyamvada S, Mahmood R (2011) Oral administration of caffeic acid ameliorates the effect of cisplatin on brush border membrane enzymes and antioxidant system in rat intestine. Exp Toxicol Pathol. doi:10.1016/j.etp.2011.05.004
Bernheim F, Bernheim ML, Wilbur KM (1948) The reaction between thiobarbituric acid and the oxidation products of certain lipides. J Biol Chem 174:257–264
Bidadkosh A, Derakhshanfar A, Rastegar A, Yazdani S (2011) Antioxidant preserving effects of l-arginine at reducing the hemodynamic toxicity of gentamicin-induced rat nephrotoxicity: pathological and biochemical findings. Comp Clin Pathol 20:1–6
Brun C (1951) A rapid method for the determination of para-aminohippuric acid in kidney function tests. J Lab Clin Med 37:955–958
Cross JM, Donald AE, Nuttall SL, Deanfield JE, Woolfson RG, Macallister RJ (2003) Vitamin C improves resistance but not conduit artery endothelial function in patients with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 63:1433–1442
De Martinis BS, Bianchi MD (2001) Effect of vitamin C supplementation against cisplatin-induced toxicity and oxidative DNA damage in rats. Pharmacol Res 44:317–320
Edwards BD, Chalmers RJ, O'Driscoll JB, Mitchell DM, Smith RJ, Lawson RS, Testa HJ, Ballardie FW (1994) Angiotensin II as a risk factor for cyclosporin nephrotoxicity in patients with psoriasis. Clin Nephrol 41:350–356
El-Beshbishy HA, Bahashwan SA, Aly HA, Fakher HA (2011) Abrogation of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice by alpha lipoic acid through ameliorating oxidative stress and enhancing gene expression of antioxidant enzymes. Eur J Pharmacol 668:278–284
Ghaznavi R, Kadkhodaee M (2007) Comparative effects of selective and non-selective nitric oxide synthase inhibition in gentamicin-induced rat nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 81:453–457
Hamers FP, Brakkee JH, Cavalletti E, Tedeschi M, Marmonti L, Pezzoni G, Neijt JP, Gispen WH (1993) Reduced glutathione protects against cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Cancer Res 53:544–549
Hanigan MH, Devarajan P (2003) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: molecular mechanisms. Cancer Ther 1:47–61
Hare RS (1950) Endogenous creatinine in serum and urine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 74:148–151
Kadkhodaee M, Khastar H, Faghihi M, Ghaznavi R, Zahmatkesh M (2005) Effects of co-supplementation of vitamins E and C on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rat. Exp Physiol 90:571–576
Kadkhodaee M, Khastar H, Arab HA, Ghaznavi R, Zahmatkesh M, Mahdavi-Mazdeh M (2007) Antioxidant vitamins preserve superoxide dismutase activities in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Transplant Proc 39:864–865
Kanter M, Coskun O, Armutcu F, Uz YH, Kizilay G (2005) Protective effects of vitamin C, alone or in combination with vitamin A, on endotoxin-induced oxidative renal tissue damage in rats. Tohoku J Exp Med 206:155–162
Kart A, Cigremis Y, Karaman M, Ozen H (2010) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) ameliorates cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity in rabbit. Exp Toxicol Pathol 62:45–52
Katayama R, Nagata S, Iida H, Yamagishi N, Yamashita T, Furuhama K (2011) Possible role of cysteine-S-conjugate beta-lyase in species differences in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 49:2053–2059
Kohn S, Fradis M, Podoshin L, Ben-David J, Zidan J, Robinson E (1997) Endothelial injury of capillaries in the stria vascularis of guinea pigs treated with cisplatin and gentamicin. Ultrastruct Pathol 21:289–299
Kumar Jana A, Agarwal S, Chatterjee SN (1986) Ultrasonic radiation induced lipid peroxidation in liposomal membrane. Radiat Environ Biophys 25:309–314
Launay-Vacher V, Rey JB, Isnard-Bagnis C, Deray G, Daouphars M (2008) Prevention of cisplatin nephrotoxicity: state of the art and recommendations from the European Society of Clinical Pharmacy Special Interest Group on Cancer Care. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61:903–909
Liao Y, Lu X, Lu C, Li G, Jin Y, Tang H (2008) Selection of agents for prevention of cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol Res 57:125–131
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Mitazaki S, Honma S, Suto M, Kato N, Hiraiwa K, Yoshida M, Abe S (2011) Interleukin-6 plays a protective role in development of cisplatin-induced acute renal failure through upregulation of anti-oxidative stress factors. Life Sci 88:1142–1148
Mukhopadhyay P, Horvath B, Zsengeller Z, Zielonka J, Tanchian G, Holovac E, Kechrid M, Patel V, Stillman IE, Parikh SM, Joseph J, Kalyanaraman B, Pacher P (2012) Mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants represent a promising approach for prevention of cisplatin-induced nephropathy. Free Radic Biol Med 52:497–506
Rossig L, Hoffmann J, Hugel B, Mallat Z, Haase A, Freyssinet JM, Tedgui A, Aicher A, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S (2001) Vitamin C inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis in congestive heart failure. Circulation 104:2182–2187
Wang Y, Mackenzie B, Tsukaguchi H, Weremowicz S, Morton CC, Hediger MA (2000) Human vitamin C (l-ascorbic acid) transporter SVCT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 267:488–494
Wenzel U, Nickel A, Kuntz S, Daniel H (2004) Ascorbic acid suppresses drug-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer cells by scavenging mitochondrial superoxide anions. Carcinogenesis 25:703–712
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K (2007) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci 334:115–124
Yokogoshi H, Mochizuki S, Takahata M, Quazi S, Yoshida A (1983) The hypercholesterolemic effect of caffeine-containing beverages and xanthine derivatives in rats. Nutr Rep Int 28:805–814
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Prof. A. Monabbati (Department of Pathology, Shiraz University of Medical Science) for his assistance in the reviewing of slides and Prof. A. Zakeri (Department of Physics, University of Science) for his kind cooperation in statistical analysis of the data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bidadkosh, A., Eini, F., Mohseni, M. et al. Vitamin C dose-dependently ameliorates renal hemodynamic toxicity of cisplatin in adult Swiss albino rats: a histopathologic and biochemical study. Comp Clin Pathol 23, 269–274 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-012-1606-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-012-1606-3