Abstract
Nephrotoxicity is a common adverse effect of treatment with cisplatin (CDDP). This study was performed to evaluate the antioxidant and nephroprotective efficacy of ceftriaxone (CTX) and vitamin E (Vit.E), alone and in combination against CDDP-induced acute renal injury. Fifty-six male albino rats were equally divided into seven groups, receiving (I) normal saline, (II) CTX (100 mg/kg, intraperitoneal [i.p] injection), (III) Vit.E (100 mg/kg orally), (IV) CDDP (5 mg/kg i.p injection), (V) CDDP plus CTX, (VI) CDDP plus Vit.E, and (VII) CDDP plus CTX in combination with Vit.E. All treatments were administered daily for 10 days except CDDP, which was given as a single dose at the sixth day of the study. Compared to normal control rats, CDDP-injected rats showed significantly (p < 0.05) higher serum levels of renal injury biomarkers (uric acid, urea, and creatinine) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), as well as increased renal tissue concentrations of malondialdehyde, nitric oxide, and TNF-α. Moreover, CDDP administration was associated with significantly lower (p < 0.05) renal tissue levels of reduced glutathione and activities of endogenous antioxidant enzymes (glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase) and total antioxidant capacity. All these alterations were significantly ameliorated in CDDP-injected rats, receiving CTX and/or Vit.E, compared to rats receiving CDDP alone. Interestingly, the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects were more marked in the CTX-Vit.E combination group, compared to groups receiving either drug alone. In conclusion, CTX and Vit.E (especially in combination) could counteract the nephrotoxic effect of CDDP, probably through their antioxidant activities.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
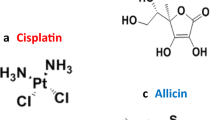
- CDDP:
-
cis-diamminedichloroplatinum II
- CTX:
-
Ceftriaxone
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TAC:
-
Total antioxidant capacity
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- Vit.E:
-
Vitamin E
References
Abdel-Daim MM, El-Ghoneimy A (2015) Synergistic protective effects of ceftriaxone and ascorbic acid against subacute deltamethrin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Ren Fail 37:297–304
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Anacona JR, Osorio I (2008) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of copper (II) complexes with sulphathiazole and cephalosporin ligands. Transit Met Chem 33:517–521
Arany I, Safirstein RL (2003) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol 23:460–464
Arreola-Mendoza L, Reyes JL, Melendez E, Martín D, Namorado MC, Sanchez E, Del Razo LM (2006) Alpha-tocopherol protects against the renal damage caused by potassium dichromate. Toxicology 218:237–246
Azzi A, Ricciarelli R, Zingg J-M (2002) Non-antioxidant molecular functions of α-tocopherol (vitamin E). FEBS Lett 519:8–10
Babior BM (2004) NADPH oxidase is a membrane-bound enzyme which has the ability to generate high levels of O2•- in response to stimulus. Curr Opin Immunol 16:42–47
Baliga R, Ueda N, Walker PD, Shah SV (1997) Oxidant mechanisms in toxic acute renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis 29:465–477
Beauchamp D, Thériault G, Grenier L, Gourde P, Perron S, Bergeron Y, Fontaine L, Bergeron MG (1994) Ceftriaxone protects against tobramycin nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:750–756
Bertram KA (2009) Basic and clinical pharmacology, Eleventh edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Burton G, Joyce A, Ingold K (1982) First proof that vitamin E is major lipid-soluble, chain-breaking antioxidant in human blood plasma. Lancet 320:327
Coulombe J, Favreau L (1963) A new simple semimicro method for colorimetric determination of urea. Clin Chem 9:102–108
Dasari S, Tchounwou PB (2014) Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 740:364–378
de Oliveira ML, Antunes LMG, Francescato HDC, Bianchi MLP (2003) The effects of oral glutamine on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol Res 47:517–522
Deng J, Kohda Y, Chiao H, Wang Y, Hu X, Hewitt SM, Miyaji T, Mcleroy P, Nibhanupudy B, Li S (2001) Interleukin-10 inhibits ischemic and cisplatin-induced acute renal injury. Kidney Int 60:2118–2128
Dwivedi VK, Bhatanagar A, Chaudhary M (2012) Protective role of ceftriaxone plus sulbactam with VRP1034 on oxidative stress, hematological and enzymatic parameters in cadmium toxicity induced rat model. Interdiscip Toxicol 5:192–200
Ellie WR, Rolfes SR (2011) In: Williams P (ed) Understanding nutrition, Twelfth edn. Wadsworth, Cengage Learning, California
Goldstein RS, Mayor GH (1983) The nephrotoxicity of cisplatin. Life Sci 32:685–690
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Gunduz O, Oltulu C, Buldum D, Guven R, Ulugol A (2011) Anti-allodynic and anti-hyperalgesic effects of ceftriaxone in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett 491:23–25
Hanigan MH, Devarajan P (2003) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: molecular mechanisms. Cancer Ther 1:47
Hassan HA, Edrees GM, El-Gamel EM, El-sayed EA (2014) Amelioration of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by grape seed extract and fish oil is mediated by lowering oxidative stress and DNA damage. Cytotechnology 66:419–429
Ibrahim A, Eldaim MAA, Abdel-Daim MM (2016) Nephroprotective effect of bee honey and royal jelly against subchronic cisplatin toxicity in rats. Cytotechnology 68:1039–1048
Jamieson ER, Lippard SJ (1999) Structure, recognition, and processing of cisplatin− DNA adducts. Chem Rev 99:2467–2498
Kalkanis JG, Whitworth C, Rybak LP (2004) Vitamin E reduces cisplatin ototoxicity. Laryngoscope 114:538–542
Kawai Y, Satoh T, Hibi D, Ohno Y, Kohda Y, Miura K, Gemba M (2009) The effect of antioxidant on development of fibrosis by cisplatin in rats. J Pharmacol Sci 111:433–439
Koracevic D, Koracevic G, Djordjevic V, Andrejevic S, Cosic V (2001) Method for the measurement of antioxidant activity in human fluids. J Clin Pathol 54:356–361
Kruidering M, Van De Water B, De Heer E, Mulder GJ, Nagelkerke JF (1997) Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in porcine proximal tubular cells: mitochondrial dysfunction by inhibition of complexes I to IV of the respiratory chain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:638–649
Lausen K (1972) Creatinine assay in the presence of protein with LKB 8600 reaction rate Analyser. Clin Chim Acta 38:475–476
Leonetti C, Biroccio A, Gabellini C, Scarsella M, Maresca V, Flori E, Bove L, Pace A, Stoppacciaro A, Zupi G (2003) α-Tocopherol protects against cisplatin-induced toxicity without interfering with antitumor efficacy. Int J Cancer 104:243–250
Liu H, Baliga R (2003) Cytochrome P450 2E1 null mice provide novel protection against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and apoptosis. Kidney Int 63:1687–1696
Mehany HA, Abo-youssef AM, Ahmed LA, Arafa E-SA, El-Latif HAA (2013) Protective effect of vitamin E and atorvastatin against potassium dichromate-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 2:96–102
Mihara M, Uchiyama M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2010) Mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins 2:2490–2518
Nazıroǧlu M, Karaoğlu A, Aksoy AO (2004) Selenium and high dose vitamin E administration protects cisplatin-induced oxidative damage to renal, liver and lens tissues in rats. Toxicology 195:221–230
Nishikimi M, Appaji N, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
O’Dwyer PJ, Stevenson JP, Johnson SW (1999) Clinical status of cisplatin, carboplatin, and other platinum-based antitumor drugs. In: Cisplatin, B. L. (Ed.), Cisplatin: chemistry and biochemistry of a leading anticancer drug, 31–69
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Palipoch S, Punsawad C, Koomhin P, Suwannalert P (2014) Hepatoprotective effect of curcumin and alpha-tocopherol against cisplatin-induced oxidative stress. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:111
Park MS, De Leon M, Devarajan P (2002) Cisplatin induces apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells via activation of mitochondrial pathways. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:858–865
Perry TR, Schentag JJ (2001) Clinical use of ceftriaxone. Clin Pharmacokinet 40(9):685–694
Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2002) TNF-α mediates chemokine and cytokine expression and renal injury in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Clin Invest 110:835–842
Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2004) Inflammatory cytokines in acute renal failure. Kidney Int 66:S56–S61
Rothstein JD, Patel S, Regan MR, Haenggeli C, Huang YH, Bergles DE, Jin L, Hoberg MD, Vidensky S, Chung DS (2005) β-Lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 433:73–77
Siddik ZH (2003) Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 22:7265–7279
Stojiljkovic N, Ilic S, Veljkovic M, Todorovic J, Mladenovic M (2018) α-Tocopherol reduces morphological changes and oxidative stress during gentamicin-induced acute renal failure. Bull Exp Biol Med 164:442–445
Tahan G, Aytac E, Aytekin H, Gunduz F, Dogusoy G, Aydin S, Tahan V, Uzun H (2011) Vitamin E has a dual effect of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities in acetic acid–induced ulcerative colitis in rats. Can J Surg 54:333–338
Thadhani RP, Pascual M, Bonventre JV (1996) Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med 334:1448–1460
Townsend DM, Deng M, Zhang L, Lapus MG, Hanigan MH (2003) Metabolism of cisplatin to a nephrotoxin in proximal tubule cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1–10
Townsend DM, Tew KD, He L, King JB, Hanigan MH (2009) Role of glutathione S-transferase pi in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother 63:79–85
Traber MG, Stevens JF (2011) Vitamins C and E: beneficial effects from a mechanistic perspective. Free Radic Biol Med 51:1000–1013
Wang D, Lippard SJ (2005) Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:307–320
Wefers H, Sies H (1988) The protection by ascorbate and glutathione against microsomal lipid peroxidation is dependent on vitamin E. FEBS J 174:353–357
Weijl N, Elsendoorn T, Lentjes E, Hopman G, Wipkink-Bakker A, Zwinderman A, Cleton F, Osanto S (2004) Supplementation with antioxidant micronutrients and chemotherapy-induced toxicity in cancer patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Cancer 40:1713–1723
Whitehead T, Bevan E, Miano L, Leonardi A (1991) Defects in diagnostic kits for determination of urate in serum. Clin Chem 37:879–881
Yilmaz HR, Iraz M, Sogut S, Ozyurt H, Yildirim Z, Akyol O, Gergerlioglu S (2004) The effects of erdosteine on the activities of some metabolic enzymes during cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol Res 50:287–290
Yılmaz N, İlhan S, Nazıroğlu M, Oktar S, Nacar A, Arıca V, Tutanç M (2011) Ceftriaxone ameliorates cyclosporine A-induced oxidative nephrotoxicity in rat. Cell Biochem Funct 29:102–107
Yoshiyama Y, Yazaki T, Beauchamp D, KANKE M (1998) Protective effect of ceftriaxone against the nephrotoxicity of isepamicin administered once daily in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 21:520–523
Younan SM, Rashed LA (2013) Protective effect of vitamin E on nerve conduction and dorsal root ganglia against cisplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in rats. Med J Cairo Univ 81:145–157
Zamble DB, Lippard SJ (1995) Cisplatin and DNA repair in cancer chemotherapy. Trends Biochem Sci 20:435–439
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through Research Group no. RGP-018.
Funding
This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University, Saudi Arabia (Grant No: RGP-018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The Research Ethical Committee at Suez Canal University approved our experimental protocol (approval no. 20147). All animal stress conditions were taken into consideration and hardly avoided.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Daim, M.M., Aleya, L., El-Bialy, B.E. et al. The ameliorative effects of ceftriaxone and vitamin E against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 15248–15254 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04801-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04801-2



