Abstract
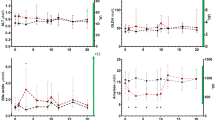
Five clinically healthy 1-year-old female sheep were used for this study. The animals were dewormed by albendazole orally and ivermectin subcutaneously. Prior to injection of the gentamicin (0 h), blood, urine, and fecal samples were taken to determine baseline values of calcium, phosphorus, and parathormone. Gentamicin was administrated intravenously (jugular vein) at a dose rate of 2.2 mg kg−1 body weight with 100 cm3 normal saline solutions every 12 h up to 5 days. To evaluate the effects of gentamicin on blood, urine, and fecal parameters, samples were collected based on 1/2 half life of gentamicin (1 h after injection of gentamicin) and delivered to laboratory. Blood calcium and blood phosphorus increased significantly (P < 0.05) at 72, 84, 96, 120, 108, 168, and 216 h and 84, 96, 120, 108, 168, 216, and 264 h, respectively. Urine calcium increased significantly (P < 0.05) at 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 120, 108, 168, and 216 h and urine phosphorus increased but levels did not reach significance. Blood parathormone levels showed a general elevation over the course of the study but a significant increase only occurred at 108 h after injection of gentamicin. Fecal calcium and phosphorus declined significantly (P < 0.05) at 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, and 120 h and 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, and 120 h, respectively, after injection of gentamicin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams HR (2001) Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutic. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 841–855
Bennett WM (1989) Editorial review: mechanisms of aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 16:1–6. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.1989.tb01901.x
Bennett WM, Pulliam JP, Porter GA, Houghton DC (1985) Modification of experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity by selective parathyroidectomy. Am J Physiol 49(6 Pt 2):832–835
Bertolaso L, Bindini D, Previati M, Falgione D, Lanzoni I, Parmeggiani A, Vitali C, Corbacella E, Capitani S, Martini A (2003) Gentamicin-induced cytotoxicity involves protein kinase C activation, glutathione extrusion and malondialdehyde production in an immortalized cell line from the organ of corti. Audiol Neurootol 8(1):38–48
Brinker KR, Bulger RE, Dobyan DC, Stacey TR, Southern PM, Henrich WL, Cronin RE (1981) Effect of potassium depletion on gentamicin nephrotoxicity. J Lab Clin Med 98:292–301
Chahwala SB, Harpur ES (1983) Gentamicin induced hypercalciuria in the rat. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 53:358–362
Chiu PY, Leung HY, Ko KM (2008) Schisandrin B enhances renal mitochondrial antioxidant status, functional and structural integrity, and protects against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 31:602–605. doi:10.1248/bpb.31.602
Crawford LM, Campbell DL, Harvey T (1977) Hypocalcemic effect of aminoglycoside antibiotics in the dairy cow. Can J Comp Med 41(3):251–256
Elliott WC, Newman N, Madan A, Jones DB (2000) Gentamicin effects on urinary electrolyte excretion in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 67(1):16–21. doi:10.1067/mcp. 2000.103864
Elliott WC, Patchin DS, Jones DB (1987) Effect of parathyroid hormone activity on gentamicin nephrotoxicity. J Lab Clin Med 109(1):48–54
Friedman PA, Gesek FA (1994) Hormone-responsive calcium entry in distal convoluted tubules. J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1396–1404
Geor RJ (2007) Acute renal failure in horses. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract 23:577–591. doi:10.1016/j.cveq.2007.09.007
Giapros VI, Cholevas VI, Andronikou SK (2004) Acute effects of gentamicin on urinary electrolyte excretion in neonates. Pediatr Nephrol 19(3):322–325. doi:10.1007/s00467-003-1381-0
Hacew S (1990) Pathogenic factors in aminoglycoside-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 51:241–259. doi:10.1016/0378-4274(90)90067-V
Harpur ES, Fathalla SAK, Phipps DJ (1985) Increased urinary excrition of calcium and magnesium is an early manifestation of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in the rat. In: Bach PH (ed) Renal heterogeneity and target cell toxicity. Wiley, Chichester, pp 349–352
Hyduk SJ, Chan JR, Duffy ST, Chen M, Peterson MD, Waddell TK, Digby GC, Szaszi K, Kapus A, Cybulsky MI (2007) Phospholipase C, calcium, and calmodulin are critical for alpha 4 beta 1 integrin affinity up-regulation and monocyte arrest triggered by chemoattractants. Blood 109:176. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-01-029199
Jackson GL, Sendelbach DM, Stehel EK, Baum M, Manning MD, Engle WD (2003) Association of hypocalcemia with a change in gentamicin administration in neonates. Pediatr Nephrol 18(7):653–656
Lee WK, Jang SB, Cha SH, Lee JH, Lee KH, Kim J, Jo YH, Endou H (2002) Different sensitivity to nephrotoxic agents and osmotic stress in proximal tubular and collecting duct cell lines derived from transgenic mice. Toxicol In Vitro 16:55–62. doi:10.1016/S0887-2333(01)00097-2
Melvin J, William O (1996) In: Swenson MJ, Reece WO (eds) Duke's physiology of domestic animals. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, Chapter 29 and 34, pp 554–557, 646–647. ISBN 0-8014-2804-1
Oliveira JFP, Cipullo JP, Burdmann EA (2006) Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg 21:444–452. doi:10.1590/S1678-97412006000400015
Parsons PP, Garland HO, Harpur ES (2000) Localization of the nephron site of gentamicin-induced hypercalciuria in the rat: a micropuncture study. Br J Pharmacol 130(2):441–449. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0703329
Pittinger C, Adamson R (1972) Antibiotic blockade of neuromuscular function. Annu Rev Pharmacol 12:169–184. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.12.040172.001125
Sandoval RM, Reilly JP, Running W, Campos SB, Santos JR, Phillips CL, Molitoris BA (2006) A non-nephrotoxic gentamicin congener that retains antimicrobial efficacy. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2697. doi:10.1681/ASN.2005101124
Schmitz DG (2007) Toxins affecting the urinary system. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract 23:677–690. doi:10.1016/j.cveq.2007.09.001
Tulkens PM (1989) Nephrotoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Toxicol Lett 364:223–228
Ward DT, Yau SK, Mee AP, Mawer EB, Miler CA, Garland H, Riccardi D (2001) Functional, molecular, and biochemical characterization of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:779–790
Acknowledgment
The authors greatly appreciate the support of this research by the Shahrekord University of Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafari Dehkordi, A., Mirzaei, A. The effects of therapeutic dose of gentamicin on calcium and parathormone in sheep. Comp Clin Pathol 18, 371–375 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-009-0818-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-009-0818-7