Abstract
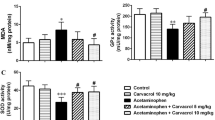
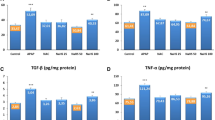
Acetaminophen as an analgesic and antipyretic drug can induce renal toxicity in high doses. Cimetidine as an H2-blocker can inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzymes and reduce the toxic effect of acetaminophen on renal tissue. Eighty rats in eight groups comprising normal control group, acetaminophen control group, cimetidine control group, and five different treatment groups (cimetidine was administrated at 0, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h after acetaminophen administration) were used. Acetaminophen was administered at a toxic of dose 3 g/kg orally, and cimetidine (12.5 mg/kg) was administrated by intraperitoneal route at different times after induction of toxicity. Creatinine and urea were measured, and pathologic lesions were determined. In treatment groups 3 and 6, the urea and creatinine concentration showed no significant difference from group 1. In other treatment groups, the urea and creatinine concentrations were increased significantly (p < 0.05). Histopathologic changes in group 6 were mild in comparison to other groups. We concluded that administration of cimetidine at least 2 h after acetaminophen toxicity can reduce renal lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blantz RC (1996) Acetaminophen: acute and chronic effects on renal function. Am J Kidney Dis 28(1):S3–S6
Bonkovsky HL, Kane RE, Jones DP, Galinsky RE, Banner B (1994) Acute hepatic and renal toxicity from low doses of acetaminophen in the absence of alcohol abuse or malnutrition: evidence for increased susceptibility to drug toxicity due to cardiopulmonary and renal insufficiency. Hepatology 19(5):1141–1148
Burkhart KK, Janco N, Kulig KW, Rumack BH (1995) Cimetidine as adjunctive treatment for acetaminophen overdose. Hum Exp Toxicol 14(3):299–304
Burtis CA, Ashwood ER (eds) (1994) Tietz textbook of clinical chemistry, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 735–888
Dahlin DC, Miwa GT, Lu AY, Nelson SD (1984) N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine: a cytochrome P-450-mediated oxidation product of acetaminophen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81:1327–1331
Duggin GG (1996) Combination analgesic-induced kidney disease: the Australian experience. Am J Kidney Dis 28(1 Suppl 1):S39–S47
Ferris EJ, Griffth JQ (1971) The rat in laboratory investigation, 2nd edn. Hafer Publishing Company, New York, pp 415–419
Flanagan RJ, Meredith TJ (1991) Use of N-acetylcysteine in clinical toxicology. Am J Med 91(3C):131S–139S
Greene W (1984) Drug interactions involving cimetidine–mechanisms, documentation, implications. Rev Drug Metab Drug Interact 5(1):25–51
Kaneko JJ (1989) Clinical biochemistry of domestic animals, 4th edn. Academic, New York, pp 352–357
Mann JM, Pierre-Louis M, Kragel PJ, Kragel AH, Roberts WC (1989) Cardiac consequences of massive acetaminophen overdose. Am J Cardiol 63(13):1018–1021
McMurtry RJ, Snodgrass WR, Mitchell JR (1978) Renal necrosis, glutathione depletion, and covalent binding after acetaminophen. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 46(1):87–100
Mitchell JR, Jollow DJ, Potter WZ, Davis DC, Gillette JR, Brodie BB (1973) Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. I. Role of drug metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 187:185–194
Newton JF, Bailie MB, Hook JB (1983) Acetaminophen nephrotoxicity in the rat. Renal metabolic activation in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 70(3):433–444
Potter WZ, Thorgeirsson SS, Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR (1974) Acetaminophen induced hepatic necrosis. V. Correlation of hepatic necrosis, covalent binding and glutathione depletion in hamsters. Pharmacology 12:129–143
Sajedianfard J, Khodakaram-Tafti A, Esmailpour H (2006) Therapeutic effect of cimetidine on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Comp Clin Pathol 15:55–57
Smilkstein MJ, Knapp GL, Kulig KW, Rumack BH (1988) Efficacy of oral N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose. Analysis of the national multicenter study (1976 to 1985). N Engl J Med 319(24):1557–1562
Speeg KV Jr, Mitchell MC, Maldonado AL (1985) Additive protection of cimetidine and N-acetylcysteine treatment against acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 234(3):550–554
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajedianfard, J., Khodakaram-Tafti, A. & Barati, A. Therapeutic effect of cimetidine on acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Comp Clin Pathol 16, 157–159 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-007-0680-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-007-0680-4