Abstract
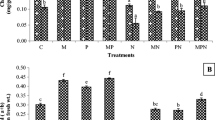
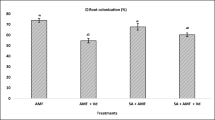
Cymbopogon citratus (lemongrass) is an important medicinal and aromatic plant containing citral-rich essential oil, of which the quality and quantity may be affected by nematode infection. Research has shown that arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) may act as nematode biocontrol agents and improve the chemical composition of plants. Three experiments were conducted to assess the effects of AMF inoculation on vegetative growth, essential oil composition, induction of defense-related proteins, and control of Pratylenchus brachyurus in C. citratus. Seedlings were transplanted into pots inoculated with one of two AMF species (Rhizophagus clarus or Claroideoglomus etunicatum). At 30 days after AMF inoculation, plants were inoculated with P. brachyurus. Evaluations were performed at 75 days after nematode inoculation. Although both AMF treatments led to effective root colonization (> 84%), fungus inoculation was not effective in reducing P. brachyurus population density. Nevertheless, C. etunicatum promoted an increase in shoot weight, and AMF treatments contributed to preserving essential oil composition in nematode-infected plants. In addition, both AMF treatments enhanced polyphenol oxidase activity and R. clarus increased peroxidase activity after nematode inoculation.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are either available within the paper or from the authors upon request.
References
Ajayi EO, Sadimenko AP, Afolayan AJ (2016) GC–MS evaluation of Cymbopogon citratus (DC) Stapf oil obtained using modified hydrodistillation and microwave extraction methods. Food Chem 209:262–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.04.071
Antunes PM, Lehmann A, Hart MM, Baumecker M, Rillig MC (2012) Long-term effects of soil nutrient deficiency on arbuscular mycorrhizal communities. Funct Ecol 26:532–540. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2011.01953.x
Barbosa LCA, Pereira UA, Martinazzo AP, Maltha CRÁ, Teixeira RR, Melo EDC (2008) Evaluation of the chemical composition of Brazilian commercial Cymbopogon citratus (DC) Stapf samples. Molecules 13:1864–1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13081864
Baum C, El-Tohamy W, Gruda N (2015) Increasing the productivity and product quality of vegetable crops using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: a review. Sci Hortic 187:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.03.002
Boneti JIS, Ferraz S (1981) Modificação do método de Hussey e Barker para extração de ovos de Meloidogyne exigua de raízes de cafeeiro. Fitopatol Bras 6:553
Borges CV, Minatel IO, Gomez-Gomez HA, Lima GPP (2017) Medicinal plants: influence of environmental factors on the content of secondary metabolites. In: Ghorbanpour M, Varma A (eds) Medicinal plants and environmental challenges. Springer, Cham, pp 259–277
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Brito ODC, Hernandes I, Ferreira JCA, Cardoso MR, Alberton O, Dias-Arieira CR (2018) Association between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Pratylenchus brachyurus in maize crop. Chil J Agric Res 78:521–527. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-58392018000400521
Cameron DD, Neal AL, Van Wees SC, Ton J (2013) Mycorrhiza-induced resistance: more than the sum of its parts? Trends Plant Sci 18:539–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.06.004
Campos MAS (2020) Bioprotection by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in plants infected with Meloidogyne nematodes: a sustainable alternative. Crop Prot 135:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2020.105203
Ceustermans A, Van Hemelrijck W, Van Campenhout J, Bylemans D (2018) Efeito de fungos micorrízicos arbusculares na infestação de Pratylenchus penetrans em mudas de macieira em casa de vegetação. Pathogens 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens7040076
Choshali AH, Rezaee S, Jamali S, Reza H, Rejali F (2019) Quantitative changes of chitinase and ß-1,3-glucanase in cucumber roots pre-colonized by VAM fungus against Meloidogyne incognita. Pak J Nematol 37:149–149
Copetta A, Lingua G, Berta G (2006) Effects of three AM fungi on growth distribution of glandular hairs and essential oil production in Ocimum basilicum L. var. Genovese. Mycorrhiza 16(7):485–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-006-0065-6
De La Peña E, Echeverría SR, Van der Putten WH, Freitas H, Moens M (2006) Mechanism of control of root-feeding nematodes by mycorrhizal fungi in the dune grass Ammophila arenaria. New Phytol 169:829–840. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01602.x
Dos Anjos ÉCT, Cavalcante UMT, Gonçalves DMC, Pedrosa EMR, dos Santos VF, Maia LC (2010) Interactions between an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (Scutellospora heterogama) and the root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) on sweet passion fruit (Passiflora alata). Braz Arch Biol Technol 53:801–809. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132010000400008
Duangmal K, Apenten RKO (1999) A comparative study of poliphenoloxidases from taro (Colocasia esculenta) e potato (Solanum tuberosum var. Romano). Food Chem 64:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00127-7
Elsen A, Beeterens R, Swenne R, De Waele D (2003) Effects of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and two plant-parasitic nematodes on Musa genotypes differing in root morphology. Biol Fertil Soils 38:367–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-003-0669-3
Elsen A, Gervacio D, Swennen R, De Waele D (2008) AMF-induced biocontrol against plant parasitic nematodes in Musa sp.: a systemic effect. Mycorrhiza 18:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-008-0173-6
Favoreto L, Meyer MC, Dias-Arieira CR, Machado ACZ, Santiago DC, Ribeiro NR (2019) Diagnosis and management of nematodes in soybean crop. Informe Agropecuario 40:18–29
Ferraz LCCB, Brown DJF (2016) Principais nematoides endoparasitas migradores: nematoides das lesões radiculares e nematoides cavernícolas. In: Ferraz LCCB, Brown DJF (eds) Nematologia de plantas: fundamentos e importância. Norma Editora, Manaus, pp 151–165
Ferreira DF (2014) Sisvar: a guide for its bootstrap procedure in multiple comparisons. Cienc Agrotec 38:109–112
Fontana A, Reichelt M, Hempel S, Gershenzon J, Unsicker SB (2009) The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on direct and indirect defense metabolites of Plantago lanceolata L. J Chem Ecol 35:833–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-009-9654-0
Frew A, Powell JR, Glauser G, Bennett AE, Johnson SN (2018) Mycorrhizal fungi enhance nutrient uptake but disarm defences in plant roots, promoting plant-parasitic nematode populations. Soil Biol Biochem 126:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.08.019
Ganjewala D, Kumar S, Luthra R (2009) An account of cloned genes of methyl-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants. Curr Issues Mol Biol 11:35–45
Gomes EC, Negrelle RRB (2015) Proposals and recommendations for qualification of the production chain of lemon grass (Cymbopogon citratus) (DC.) Stapf (Poaceae). Rev Bras Plant Med 17:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1590/1983-084X/10_077
Gomes EC, Negrelle RRB, Doni Filho L (2007) Caracterização da produção de capim-limão no estado do Paraná, Brasil. Sci Agrar 8:385–390. https://doi.org/10.5380/rsa.v8i4.9885
Gough EC, Owen KJ, Zwart RS, Thompson JP (2020) A systematic review of the effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on root-lesion nematodes, Pratylenchus spp. Front Plant Sci 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00923
Gupta R, Tiwari S, Saikia SK, Shukla V, Singh R, Singh SP et al (2015) Exploitation of microbes for enhancing bacoside content and reduction of Meloidogyne incognita infestation in Bacopa monnieri L. Protoplasma 252:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0657-5
Haiyan L, Runjin L, Yanjie L, Huairui S, Yu L (2003) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and heterodera glycines on enzyme activity in soybean roots. Mycosystema 22:613–619
Hajra N, Shahina F, Firoza K, Maria R (2015) Damage induced by root-knot nematodes and its alleviation by vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in roots of Luffa cylindrica. Pak J Nematol 33:71–78
Hammer EC, Pallon J, Wallander H, Olsson PA (2011) Tit for tat? A mycorrhizal fungus accumulates phosphorus under low plant carbon availability. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 76:236–244. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01043.x
Hao Z, Fayolle L, Van Tuinen D, Chatagnier O, Li X, Gianinazzi S, Gianinazzi-Pearson V (2012) Local and systemic mycorrhiza-induced protection against the ectoparasitic nematode Xiphinema index involves priming of defence gene responses in grapevine. J Exp Bot 63:3657–3672. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers046
Hosseini A, Gharaghani A (2015) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and nutrient uptake of apple rootstocks in calcareous soil. Int J Hort Sci Technol 2:173–185
Hussey RS, Barker KRA (1973) Comparison of methods colleting inocula of Meloidogyne spp. including a new technique. Plant Dis Rep 57:1025–1028
Jenkins WR (1964) A rapid centrifugal-flotation technique for separating nematodes from soil. Plant Dis Rep 48:692
Jenkins WR (1969) Nematodes associated with lemon grass in Guatemala. In: Symposium on tropical nematology, proceedings, Puerto, pp 80–83
Jones JT, Haegeman A, Danchin EGJ, Gaur HS, Helder-J JMGK, Kikuchi T, Manzanilla-Lopez R, Palomares-Rius JE, Wesemael WML, Perry RN (2013) Top 10 plant parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 14:946–961. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12057
Jung SC, Martinez-Medina A, Lopez-Raez JA, Pozo MJ (2012) Mycorrhiza-induced resistance and priming of plant defenses. J Chem Ecol 38:651–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-012-0134-6
Kapoor R, Chaudhary V, Bhatnagar AK (2007) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza and phosphorus application on artemisinin concentration in Artemisia annua L. Mycorrhiza 17:581–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-007-0135-4
Kapoor R, Anand G, Gupta P, Mandal S (2017) Insight into the mechanisms of enhanced production of valuable terpenoids by arbuscular mycorrhiza. Phytochem Rev 16:677–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-016-9486-9
Khaosaad T, García-Garrido JM, Steinkellner S, Vierheilig H (2007) Take-all disease is systemically reduced in roots of mycorrhizal barley plants. Soil Biol Biochem 39:727–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.09.014
Koffi MC, Vos C, Draye X, Declerck S (2013) Effects of Rhizophagus irregularis MUCL 41833 on the reproduction of Radopholus similis in banana plantlets grown under in vitro culture conditions. Mycorrhiza 23:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-012-0467-6
Lermen C, Morelli F, Gazim ZC, da Silva AP, Gonçalves JE, Dragunski DC, Alberton O (2015) Essential oil content and chemical composition of Cymbopogon citratus inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under different levels of lead. Ind Crop Prod 76:734–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.07.009
Li JF, He XH, Li H, Zheng WJ, Liu JF, Wang MY (2015) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increase growth and phenolics synthesis in Poncirus trifoliata under iron deficiency. Sci Hortic 183:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.12.015
López-Ráez JA, Flors V, García JM, Pozo MJ (2010) AM symbiosis alters phenolic acid content in tomato roots. Plant Signal Behav 5:1138–1140. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.5.9.12659
Lusso MFG, Pascholati SF (1999) Activity and isoenzymatic pattern of soluble peroxidases in maize tissues after mechanical injury or fungal inoculation. Summa Phytopathol 25:244–249
Majewska E, Kozlowska M, Gruszczynska-Sekowska E, Kowalska D, Tarnowska K (2019) Lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) essential oil: extraction, composition, bioactivity and uses for food preservation-a review. Pol J Food Nutr Sci 69:327–341. https://doi.org/10.31883/pjfns/113152
Mandal S, Upadhyay S, Wajid S, Ram M, Jain DC, Singh VP, Abdin MZ, Kapoor R (2015) Arbuscular mycorrhiza increase artemisinin accumulation in Artemisia annua by higher expression of key biosynthesis genes via enhanced jasmonic acid levels. Mycorrhiza 25:345–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-014-0614-3
McGonigle TP, Miller MH, Evans DG, Fairchild GL, Swan JA (1990) A new method which gives an objective measure of colonization of roots by vesicular—arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 115:495–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1990.tb00476.x
Medeiros HA, Resende RS, Ferreira FC, Freitas LG, Rodrigues FA (2015) Induction of resistance in tomato against Meloidogyne javanica by Pochonia chlamydosporia. Nematoda 2:1–7. https://doi.org/10.4322/nematoda.10015
Minton MM, Barber NA, Gordon LL (2016) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on herbivory defense in two Solanum (Solanaceae) species. Plant Ecol Evol 149:157–164. https://doi.org/10.5091/plecevo.2016.1176
Morone-Fortunato I, Avato P (2008) Plant development and synthesis of essential oils in micropropagated and mycorrhiza inoculated plants of Origanum vulgare L. ssp. hirtum (Link) Ietswaart. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 93:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-008-9353-5
Ngadze E, Icishahayo D, Coutinho TA, Van der Waals JE (2012) Role of polyphenol oxidase, peroxidase, phenylalanine ammonia lyase, chlorogenic acid, and total soluble phenols in resistance of potatoes to soft rot. Plant Dis 96:186–192. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-02-11-0149
Oostenbrink R (1966) Major characteristics of the relation between nematodes and plants. Meded Land Bouwhogeschool 66:1–46
Phillips JM, Hayman DS (1970) Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans Br Mycol Soc 55:157–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1536(70)80110-3
Pozo MJ, Azcón-Aguilar C (2007) Unraveling mycorrhiza-induced resistance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:393–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2007.05.004
Pozo MJ, Cordier C, Dumas-Gaudot E, Gianinazzi S, Barea JM, Azcón-Aguilar C (2002) Localized versus systemic effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on defence responses to Phytophthora infection in tomato plants. J Exp Bot 53:525–534. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.368.525
Rajeswara Rao BR, Adinarayana G, Kumar AN, Rajput DK, Syamasundar KV (2016) Chemical-profile variations in essential oils isolated from lemongrass (Cymbopogon flexuosus) biomass and condensate wastewater by re-distillation and solvent extraction techniques. J Essent Oil Res 28:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.2016.1167130
Ranitha M, Nour AH, Sulaiman ZA, Nour AH, Raj TS (2014) A Comparative Study of Lemongrass (Cymbopogon Citratus) Essential Oil Extracted by Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation (MAHD) and Conventional Hydrodistillation (HD) Method. Int J Chem Eng 5(2):104–108. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJCEA.2014.V5.360
Rodríguez-Echeverría S, De La Peña E, Moens M, Freitas H, Van Der Putten WH (2009) Can root-feeders alter the composition of AMF communities? Experimental evidence from the dune grass Ammophila arenaria. Basic Appl Ecol 10:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2008.01.004
Saikia SK, Tiwari S, Pandey R (2013) Rhizospheric biological weapons for growth enhancement and Meloidogyne incognita management in Withania somnifera cv. Poshita Biol Control 65:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2013.01.014
Sankaranarayanan C, Hari K (2020) Integration of arbuscular mycorrhizal and nematode antagonistic fungi for the biocontrol of root lesion nematode Pratylenchus zeae Graham, 1951 on sugarcane. Sugar Tech 1:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-020-00876-1
Schaarschmidt S, Kopka J, Ludwig-Müller J, Hause B (2007) Regulation of arbuscular mycorrhization by apoplastic invertases: enhanced invertase activity in the leaf apoplast affects the symbiotic interaction. Plant J 51:390–405. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03150.x
Schouteden N, De Waele D, Panis B, Vos CM (2015) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for the biocontrol of plant-parasitic nematodes: a review of the mechanisms involved. Front Microbiol 6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01280
Seymour NP, Edwards DG, Thompson JP (2019) A dual rescaled Mitscherlich model of the simultaneous savings in phosphorus and zinc fertiliser from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal colonisation of linseed (Linum usitatissimum L). Plant Soil 440:97–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04065-2
Shaikh MN, Suryawanshi YC, Mokat DN (2019) Volatile profiling and essential oil yield of Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf treated with rhizosphere fungi and some important fertilizers. J Essential Oil Bear Plants 22:477–483. https://doi.org/10.1080/0972060X.2019.1613933
Sharma IP, Sharma AK (2017) Physiological and biochemical changes in tomato cultivar PT-3 with dual inoculation of mycorrhiza and PGPR against root-knot nematode. Symbiosis 71:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-016-0423-x
Sidker MM, Vestergård M (2020) Impacts of root metabolites on soil nematodes. Front Plant Sci 10:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01792
Silva MTR, Calandrelli A, Rinaldi LK, Miamoto A, Moreno BP, da Costa WF, Silva C, Alberton O, Dias-Arieira CR (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizae maintain lemongrass citral levels and mitigate resistance despite root lesion nematode infection. Rhizosphere 19:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2021.100359
Smith SE, Jakobsen I, Gronlund M, Smith FA (2011) Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant phosphorus nutrition: interactions between pathways of phosphorus uptake in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots have important implications for understanding and manipulating plant phosphorus acquisition. Plant Physiol 156:1050–1057. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.174581
Talavera M, Itou K, Mizukubo T (2001) Reduction of nematode damage by root colonization with arbuscular mycorrhiza (Glomus spp.) in tomato-Meloidogyne incognita (Tylenchida: Meloidogynidae) and carrot-Pratylenchus penetrans (Tylenchida: Pratylenchidae) pathosystems. Appl Entomol Zool 36:387–392. https://doi.org/10.1303/aez.2001.387
Tiwari S, Pandey S, Chauhan PS, Pandey R (2017) Biocontrol agents in co-inoculation manages root knot nematode [Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid & White) Chitwood] and enhances essential oil content in Ocimum basilicum L. Ind Crop Prod 97:292–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.12.030
Torres-Avilez WM, Silva FS, Albuquerque UP (2018) Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf. In: Albuquerque UP, Patil U, Máthé A (eds) Medicinal and aromatic plants of South America. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 183–196
Umesha S (2006) Phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity in tomato seedlings and its relationship to bacterial canker disease resistance. Phytoparasitica 34:68–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02981341
Veresoglou SD, Rillig MC (2012) Suppression of fungal and nematode plant pathogens through arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Biol Lett 8:214–217. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2011.0874
Vierheilig H, Steinkellner S, Khaosaad T, Garcia-Garrido JM (2008) The biocontrol effect of mycorrhization on soilborne fungal pathogens and the autoregulation of the AM symbiosis: one mechanism, two effects? In: Varma A (ed) Mycorrhiza, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 305–307
Vogelsang R, Barz W (1993) Purification, characterization and differential hormonal regulation of a β-1,3-glucanase and chitinases from chickpea (Cicer arientinum L.). Planta 189:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201344
Vos C, Claerhout S, Mkandawire R, Panis B, De Waele D, Elsen A (2012a) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reduce root-knot nematode penetration through altered root exudation of their host. Plant Soil 354:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-1070-x
Vos C, Van Den Broucke D, Lombi FM, De Waele D, Elsen A (2012b) Mycorrhiza-induced resistance in banana acts on nematode host location and penetration. Soil Biol Biochem 47:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.12.027
Vos CM, Tesfehun AN, Panis B, Waele DD, Elsen A (2012c) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi induce systemic resistance in tomato against the sedentary nematode Meloidogyne incognita and the migratory nematode Pratylenchus penetrans. Appl Soil Ecol 61:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2012.04.007
Wang C, Li X, Zhou J, Wang G, Dong Y (2008) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and yield of cucumber plants. Commun Soil Sci Plant 39:499–509. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620701826738
Wuyts N, Swennen R, de Waele D (2006) Effects of plant phenylpropanoid pathway products and selected terpenoids and alkaloids on the behaviour of the plant-parasitic nematodes Radopholus similis, Pratylenchus penetrans and Meloidogyne incognita. Nematology 8:89–101. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854106776179953
Yen HY, Lin YC (2017) Green extraction of Cymbopogon citrus essential oil by solar energy. Ind Crop Prod 108:716–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.07.039
Zeng Y, Guo LP, Chen BD, Hao ZP, Wang JY, Huang LQ et al (2013) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis and active ingredients of medicinal plants: current research status and prospectives. Mycorrhiza 23:253–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-013-0484-0
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Odair Alberton (Paranaense University, Brazil) for providing the AMF.
Funding
This study was supported by a master’s scholarship to MTRS (Grant no. 132466/2019–8) and a research productivity grant to CRDA (Grant No. 303269/2020-0) from the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and by master’s and doctoral scholarships to AC (Grant No. 344568/2019-1), LKR (Grant No. 344503/2019-01), and AM (Grant No. 344530/2019-01) from the Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, MTRS and CRDA; Data curation, MTRS; Formal analysis, MTRS, AM, AC, LKR e CRDA; Funding acquisition, CRDA; Investigation, MTRS; Methodology, MTRS, CRDA, BPM and CS; Project administration, CRDA; Supervision, CRDA; Writing—original draft, MTRS; Writing—review and editing, MTRS, AM, AC, LKR, and CRDA.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues e Silva, M.T., Calandrelli, A., Miamoto, A. et al. Pre-inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi affects essential oil quality and the reproduction of root lesion nematode in Cymbopogon citratus. Mycorrhiza 31, 613–623 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-021-01045-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-021-01045-2