Abstract
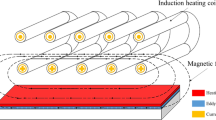
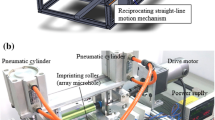
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is a polymer that is both elastic and cost-effective, making it an ideal material for replication molds when creating delicate microstructures. Its surface microstructure is durable, and the replication process is straightforward and fast. However, as the mold is soft, no extensive research has been conducted to prove it is suitable for rolling embossing. Moreover, PDMS is an insulator with high thermal resistance, making it difficult to heat uniformly for embossing. Typically, external heat sources are used to heat PDMS molds indirectly. We developed a double-sided mold with magnetic powder embedded inside PDMS to overcome these challenges and increase hardness and heating efficiency. Our study addresses the air-gap issue when roller embossing convex microlens arrays on polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) polymer. Ultimately, this research also realized a double-sided PDMS mold for simultaneous double-sided embossing of two pieces of PMMA convex and concave microlens arrays on a roller, improving the microstructure's replication fidelity.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Chang J-H, Yang S-Y (2003) Gas pressurized hot embossing for transcription of micro-features. Microsyst Technol 10:76–80
Chang J-H, Yang S-Y (2005) Development of fluid-based heating and pressing systems for micro hot embossing. Microsyst Technol 11:396–403
Chang J-H, Cheng F-H, Chao C-C, Weng Y-C, Yang S-Y (2005) Direct imprinting using soft mold and gas pressure for large area and curved surfaces. J Vac Sci Technol A 23:1687
Chang C-Y, Yang S-Y, Chu M-H (2007) Rapid fabrication of ultraviolet-cured polymer microlens arrays by soft roller stamping process. Microeng 84:355–361
Goral VN, Hsieh Y-C, Petzold ON, Faris RA, Yuen P-K (2010) Hot embossing of plastic microfluidic devices using poly(dimethylsiloxane) molds. J Micromech Microeng 21:017002
Heyderman L-J, Schift H, David C, Gobrecht J, Schweizer T (2000) Flow behaviour of thin polymer films used for hot embossing lithography. Microeng 54:229–245
Hoffmann JE, Bedner K, Clemens H, Degen R, Dhum C, Giro F, Kirsch U, Schmitt M, Saumer M (2008) The influence of the electroplating parameters on the conditions of deposited nickel-iron coatings. Mater Sci Eng Technol 39:209–216
Hsu M-H, Tsai Y-Y, Yang S-Y (2022) Induction heating ferromagnetic particles embedded PDMS mold for microstructure embossing. J Phys Commun 6:025002
Hsu M-H, Tsai Y-Y, He J-W, Yang S-Y (2023) Induction heating of dual magnetic particles embedded PDMS molds for roller embossing applications. Microsyst Technol 29:405–415
Hu C-N, Hsieh H-T, Su G-D (2011) Fabrication of microlens arrays by a rolling process with soft polydimethylsiloxane molds. J Micromech Microeng 21:065013
Jiang L-T, Huang T-C, Chiu C-R, Chang C-Y, Yang S-Y (2007) Fabrication of plastic microlens arrays using hybrid extrusion rolling embossing with a metallic cylinder mold fabricated using dry film resist. Opt Express 15:12088–12094
Kim K, Park S, Lee J-B, Manohara H, Desta Y, Murphy M, Ahn C-H (2002) Rapid replication of polymeric and metallic high aspect ratio microstructures using PDMS and LIGA technology. Microsyst Technol 9:5–10
Kim M, Moon B-U, Hidrovo CH (2013) Enhancement of the thermo-mechanical properties of PDMS molds for the hot embossing of PMMA microfluidic devices. J Micromech Microeng 23:095024
Kuo C-C, Wang Y-J (2014) Development of a micro-hot-embossing mold with high replication fidelity using surface modification. Mater Manuf 29:1101–1110
Liu Y, Zhang P, Deng Y et al (2014) Polymeric microlens array fabricated with PDMS mold-based hot embossing. J Micromech Microeng 24:095028
Miranda I et al (2022) Properties and Applications of PDMS for Biomedical Engineering: A Review. J Funct Biomater 13:2
Moore S, Gomez J, Lek D, Youa BH, Kimc N, Song I-H (2016) Experimental study of polymer microlens fabrication using partial-filling hot embossing technique. Microeng 162:57–62
Narasimhan J, Papautsky I (2004) Polymer embossing tools for rapid prototyping of plastic microfluidic devices. J Micromech Microeng 14:96–103
Nilsson D, Jensen S, Menon A (2003) Fabrication of silicon molds for polymer optics. J Micromech Microeng 13:S57–S61
Velten T, Bauerfeld F, Schuck H, Scherbaum S, Landesberger C, Bock K (2011) Roll-to-roll hot embossing of microstructures. Microsyst Technol 17:619–627
Yang S-Y, Cheng F-S, Xu S-W, Huang P-H, Huang T-C (2008) Fabrication of microlens arrays using UV micro-stamping with soft roller and gas-pressurized platform. Microeng 85:603–609
Yeo LP, Ng SH, Wang Z-F, Wang Z-P, Rooij NF (2009) Micro-fabrication of polymeric devices using hot roller embossing. Microeng 86:933–936
Acknowledgements
Thank Wei-Cheng for helping to install the initial roller embossing apparatus and providing the valuable experience of roller embossing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, MH., Tsai, YY., He, JW. et al. A double-sided PDMS mold for double-sided embossing by rollers. Microsyst Technol 30, 47–54 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-023-05554-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-023-05554-2