Abstract
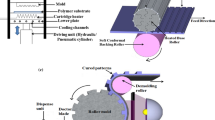
In this paper we present a new roll-to-roll embossing process allowing the replication of micro patterns with feature sizes down to 0.5 μm. The embossing process can be run in ‘continuous mode’ as well as in ‘discontinuous mode’. Continuous hot embossing is suitable for the continuous output of micro patterned structures. Discontinuous hot embossing has the advantage that it is not accompanied by waste produced during the initial hot embossing phase. This is because in ‘discontinuous mode’, embossing does not start before the foil has reached the target temperature. The foil rests between two parallel heating plates and foil movement and embossing starts only after the part of the foil resting between the heating plates has reached a thermal steady state. A new type of embossing master is used which is based on flexible silicon substrates. The embossing pattern with sub-μm topographic resolution is prepared on silicon wafers by state of the art lithography and dry etching techniques. The wafers are thinned down to a thickness of 40 μm, which guarantees the mechanical flexibility of the embossing masters. Up to 20 individual chips with a size of 20 × 20 mm² were assembled on a roller. Embossing experiments with COC foils showed a good replication of the silicon master structures in the foil. The maximum depth of the embossed holes was about 70% of the master height.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbucci R, Pasqui D, Wirsen A, Affrossman S, Curtis A, Tetta C (2003) Micro and nano-structured surfaces. J Mater Sci Mater Med 14:721–725
Clark P, Connelly P, Moores GR (1992) Cell guidance by micropatterned adhesiveness in vitro. J Cell Sci 103:287–292
Curtis A, Wilkinson C (1997) Topographical control of cells. Biomaterials 18:1573–1583
Landesberger C, Klink G, Schwinn G, Aschenbrenner R (2001) New dicing and thinning concept improves mechanical reliability of ultra thin silicon. Symposium and exhibition on advanced packaging materials. Georgia, Braselton
Landesberger C, Scherbaum S, Bock K (2007) Carrier techniques for thin wafer processing. In: Compound Semiconductor Mantech, ISBN 9781893580091. Conference on compound semiconductors manufacturing technology, Austin, May 2007
Lodish H, Berk A, Matsudaira P (2005) Molecular Cell Biology. 5th edn. Chap 1.1. Palgrave Macmillan, New York
Velten T, Schuck H, Richter M, Klink G, Bock K, Malek CK, Roth S, Scho H, Bolt PJ (2007) Microfluidics on foil: state of the art and new developments. In: Proceedings of IMechE, vol. 222. Part B: J Eng Manuf. http://journals.pepublishing.com/content/8w7l54p77815g325/
Velten T, Schuck H, Haberer W, Bauerfeld F (2010) Investigations on reel-to-reel hot embossing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47(1):73–80
Wanzenboeck H, Dominizi K, Erdösi D, Bertagnolli E (2006) Precision structured surfaces as functional carriers for in vitro cultures of living cells. In: Euspen Conference Proceedings, vol II. Baden bei Wien, Vienna, pp 377–380
Wood MA, Wilkinson CDW, Curtis ASG (2006) The effects of colloidal nanotopography on initial fibroblast adhesion and morphology. In: IEEE Transactions on Nanobiosience, vol 5(1), March 2006. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=1603530&tag=1
Yeo LP, Ng SH, Wang ZF, Xia HM, Wang ZP, Thang VS, Zhong ZW, de Rooij NF (2010) Investigation of hot roller embossing for microfluidic devices. J Micromech Microeng 20(1):015017
Acknowledgments
The work presented was funded by the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. The authors would like to thank Kai Mrosk for embossing experiments, Anna Ohlander for stamp embossing tests and Daniel Sauer and Thorsten Knoll for providing the AFM micrographs and the confocal microscope measurements, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velten, T., Bauerfeld, F., Schuck, H. et al. Roll-to-roll hot embossing of microstructures. Microsyst Technol 17, 619–627 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-010-1158-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-010-1158-x