Abstract
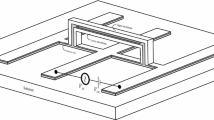
The fabrication and testing of a parallel plate MEMS electrostatic micro-actuator is reported. The device consists of stationary bulk silicon and movable membrane chips with three spring-like x-beam configurations fabricated from a silicon on insulator (SOI) wafer. A SU-8 photoresist layer was deposited on the stationary chip to act as a spacer since its thickness determines the electrostatic force that can be applied. This in turn has an effect on the displacement of the micro-actuator. We investigated the effects of the applied voltage on the displacement of movable x-beam membranes for different arm designs with similar surface areas. We achieved maximum stable displacements of 8.75 µm and 9.89 µm for spacer thicknesses of 28 µm and 33 µm at 95 VDC and 128 VDC, respectively, for a serpentine arm design. Beyond these voltages, we found the displacement of the micro-actuator tended to be non-uniform and unstable. We also estimated the mechanical stiffness constants of our x-beam designs from the snap-in conditions. Our estimates for various spacer thicknesses were within 5% of one another.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams TM, Layton RA (2010) Introductory MEMS fabrication and applications. Springer, Berlin, p 173
Balakrisnan B, Nacev A, Burke JM, Dasguptal A, Smela E (2012) Design of compliant meanders for applications in MEMS actuators, and flexible electronics. Smart Mater Struct 3669:149
Born M, Wolf E (1993) Principles of optics, 6th edn. Pergamon, Oxford, p 325
Busta H, Amantea R, Furst D, Chen JM, Turowski M, Mueller C (2001) A MEMS shield structure for controlling pull-in forces and obtaining increased pull-in voltages. J Micromech Micro Eng 11:720
Chuang WC, Lee HL, Chang PZ, Hu YC (2010) Review on the modeling of electrostatic MEMS. Sensors 10:6149
Elliot RS (1999) Electromagnetics: history, theory, and applications, 1st edn. Wiley-IEEE Press, Hoboken
Hernandez G (1988) Fabry-Perot interferometers. Cambridge University Press, London, p 46
Hung ES, Senturia SD (1999) Extending the travel range of analog-tuned electrostatic actuators. J Microelectromech Syst 8:497
Lishchynska M, O’mahony C, Slattery O, Behan R (2006) Spring constant models for analysis and design of MEMS plates on straight or meander tethers. Sensor Lett 4:200
Sam Jebar Kumar J, Amoatey Tetteh E, Paul Braineard E (2014) A study of why electrostatic actuation is preferred and a simulation of an electrostatically actuated cantilever beam for MEMS applications. I J Eng Sci Emerg Technol 6:441
Seeger J, Boser B (2003) Charge control of parallel-plate electrostatic actuators and the tip-in instability. J Microelectromech Syst 12:656
Shiyun X, Yugang S, Chunsen T, Long C (2015) Research on Meander-type coupled structure of capacitively coupled power transfer system. WSEAS Transact Circuits Syst 14:247
Tachi S, Tsujimoto K, Ninomiya K, Suzuki K, Okudaira S (1987) Low temperature reactive ion etching and microwave plasma etching of silicon. Appl Phys Lett 52:616
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge EPIR Technologies, Inc. for funding this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Admassu, D., Durowade, T., Velicu, S. et al. Estimation of the mechanical stiffness constant of MEMS-based parallel-plate micro-actuators. Microsyst Technol 27, 2751–2759 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05022-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05022-1