Abstract
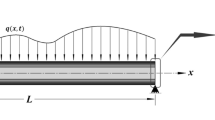
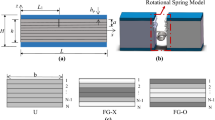
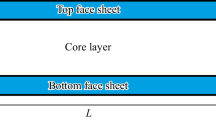
This paper investigates the static pull-in instability and free vibration of a multilayer functionally graded graphene nanoplatelet (GPL) reinforced composite (FG-GPLRC) micro-beam sandwiched between two copper layers subjected to a combined action of an electric voltage and a uniform temperature change based on Euler–Bernoulli beam theory. The GPL nanofillers are uniformly dispersed within each individual layer while its weight fraction changes from layer to layer in the multilayer FG-GPLRC micro-beam. The modified Halpin–Tsai model is used to predict the effective Young’s modulus while the rule of mixture is used to determine the effective Poisson’s ratio, mass density and thermal expansion coefficient. The static pull-in voltage and natural frequency of clamped–clamped micro-beams are obtained by employing Galerkin and iterative method. The effects of GPL distribution pattern, weight fraction, geometry and size as well as the geometry of the beam, the temperature change and the total number of layers on the static and dynamic characteristics of the micro-beams are discussed in detail.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam H (1997) Carbon fibre in automotive applications. Mater Des 18(4–6):349–355
Baradaran S, Moghaddam E, Basirun WJ, Mehrali M, Sookhakian M, Hamdi M, Nakhaei Moghaddam MR, Alias Y (2014) Mechanical properties and biomedical applications of a nanotube hydroxyapatite-reduced graphene oxide composite. Carbon 69:32–45
Bartoluccia SF, Paras J, Rafiee MA, Rafiee J, Lee S, Kapoor D, Koratkar N (2011) Graphene–aluminum nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng A 528:7933–7937
Bellucci S, Balasubramanian C, Micciulla F, Rinaldi G (2007) CNT composites for aerospace applications. J Exp Nanosci 2(3):193–206
Chen D, Yang J, Kitipornchai S (2017) Nonlinear vibration and postbuckling of functionally graded graphene reinforced porous nanocomposite beams. Compos Sci Technol 142:235–245
Chu K, Jia CC, Li WS (2012) Effective thermal conductivity of graphene-based composites. Appl Phys Lett 101:121916
Gauvin F, Robert M (2015) Durability study of vinylester/silicate nanocomposites for civil engineering applications. Polym Degrad Stab 121:359–368
Ji XY, Cao YP, Feng XQ (2010) Micromechanics prediction of the effective elastic moduli of graphene sheet-reinforced polymer nanocomposites. Modell Simul Mater Sci Eng 18(4):045005
Jia XL, Yang J, Kitipornchai S (2010) Characterization of FGM micro-switches under electrostatic and Casimir forces. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 10:012178
Jia XL, Yang J, Kitipornchai S, Lim CW (2012) Pull-in instability and free vibration of electrically actuated poly-SiGe graded micro-beams with a curved ground electrode. Appl Math Model 36:1875–1884
Jia XL, Zhang SM, Ke LL, Yang J, Kitipornchai S (2014) Thermal effect on the pull-in instability of functionally graded micro-beams subjected to electrical actuation. Compos Struct 116:136–146
Jia XL, Ke LL, Feng CB, Yang J, Kitipornchai S (2015) Size effect on the free vibration of geometrically nonlinear functionally graded micro-beams under electrical actuation and temperature change. Compos Struct 133:1137–1148
Kaneria AJ, Sharma DS, Trivedi RR (2013) Static analysis of electrostatically actuated micro cantilever beam. Procedia Eng 51:776–780
King JA, Klimek DR, Miskioglu I, Odegard GM (2013) Mechanical properties of graphene nanoplatelet/epoxy composites. J Appl Polym Sci 128(6):4217–4223
Krylov S, Maimon R (2004) Pull-in dynamics of an elastic beam actuated by continuously distributed electrostatic force. J Vib Acoust 126:332–342
Li Y, Zhang H, Porwal H, Huang ZH, Bilotti E, Peijs T (2017) Mechanical, electrical and thermal properties of in situ exfoliated graphene/epoxy nanocomposites. Compos Part A 95:229–236
Mestrom RMC, Fey RHB, Phan KL, Nijmeijer H (2010) Simulations and experiments of hardening and softening resonances in a clamped–clamped beam MEMS resonator. Sens Actuators A 162:225–234
Montazeri A, Rafii-Tabar H (2011) Multiscale modeling of graphene- and nanotube-based reinforced polymer nanocomposites. Phys Lett A 375(45):4034–4040
Peng JS, Yang L, Luo GB, Yang J (2014a) Nonlinear electro-dynamic analysis of micro-actuators: effect of material nonlinearity. Appl Math Model 38:2781–2790
Peng JS, Yang L, Yang J (2014b) Dynamic pull-in instability of a micro-actuator made from nonlinear elasticity materials. Smart Mater Struct 23:065023
Peng JS, Yang L, Yang J (2017a) Size effect on the dynamic analysis of electrostatically actuated micro-actuators. Microsyst Technol 23:1247–1254
Peng JS, Yang L, Lin F, Yang J (2017b) Dynamic analysis of size-dependent microbeams with nonlinear elasticity under electrical actuation. Appl Math Model 43:441–453
Rafiee MA, Rafiee J, Wang Z, Song H, Yu ZZ, Koratkar N (2009) Enhanced mechanical properties of nanocomposites at low graphene content. ACS Nano 3(12):3884–3890
Shen HS, Lin F, Xiang Y (2017) Nonlinear bending and thermal postbuckling of functionally graded graphene-reinforced composite laminated beams resting on elastic foundations. Eng Struct 140:89–97
Song M, Kitipornchai S, Yang J (2017) Free and forced vibrations of functionally graded polymer composite plates reinforced with graphene nanoplatelets. Compos Struct 159:579–588
Wang S, Tambraparni M, Qiu JJ, Tipton J, Dean D (2009) Thermal expansion of graphene composites. Macromolecules 42:5251–5255
Wang Y, Yu J, Dai W, Song Y, Wang D, Zeng L, Jiang N (2015a) Enhanced thermal and electrical properties of epoxy composites reinforced with graphene nanoplatelets. Polym Compos 36(3):556–565
Wang F, Drzal LT, Qin Y, Huang Z (2015b) Mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of graphene nanoplatelet/epoxy composites. J Mater Sci 50(3):1082–1093
Wu H, Drzal LT (2014) Effect of graphene nanoplatelets on coefficient of thermal expansion of polyetherimide composite. Mater Chem Phys 146:26–36
Wu HL, Yang J, Kitipornchai S (2017) Dynamic instability of functionally graded multilayer graphene nano-composite beams in thermal environment. Compos Struct 162:244–254
Yang B, Yang J, Kitipornchai S (2016) Thermoelastic analysis of functionally graded graphene reinforced rectangular plates based on 3D elasticity. Meccanica 52(10):1–18
Yang J, Wu HL, Kitipornchai S (2017a) Buckling and postbuckling of functionally graded multilayer graphene platelet-reinforced composite beams. Compos Struct 161:111–118
Yang L, Fang F, Peng JS, Yang J (2017b) Dynamic pull-in instability of a thermoelectromechanically loaded micro-beam based on “symmetric stress” gradient elasticity theory. Int J Struct Stab Dyn 17(10):1750117
Younis MI, Abdel-Rahman EM, Nayfeh AH (2003) A reduced-order model for electrically actuated microbeam-based MEMS. J Microelectromech Syst 12:672–680
Yu L, Park JS, Lim YS, Lee CS, Shin K, Moon HJ, Yang CM, Lee YS, Han JH (2013) Carbon hybrid fillers composed of carbon nanotubes directly grown on graphene nanoplatelets for effective thermal conductivity in epoxy composites. Nanotechnology 24:155604
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a research grant from the Science Foundation, the Education Department of Sichuan Province, China [Project No. 16ZB0433]. The authors are grateful for this financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work has not been published previously and it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere. If accepted, it will not be published elsewhere in the same form, in English or in any other language, including electronically without the written consent of the copyright-holder.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Peng, J., Fang, F. et al. Static pull-in instability and free vibration of functionally graded graphene nanoplatelet reinforced micro-sandwich beams under thermo-electrical actuation. Microsyst Technol 25, 3599–3608 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04359-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04359-6