Abstract
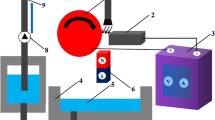
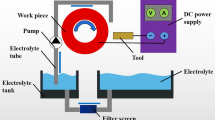
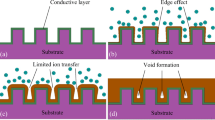
High-aspect-ratio (HAR) micro-electroforming is a significantly challengeable implementation to manufacture metallic microstructures and microparts mainly due to mass transportation limitation effect. In this paper, flow pattern and flow rate change characteristics within HAR micro-cavity during electroforming under magnetic field are investigated, and evaluations of the electroformed micro-sized HAR nickel features under the improved magnetohydrodynamic (MHD)-governed condition are carried out. It was found that, five electrolyte flow-pattern zones can be formed within the horizontally placed micro-cavity under the MHD condition and favorable mass transfer effects can be created when the current field applied is perpendicular to the gravity field; HAR (≥ 7) nickel microstructure with good surface quality and few plating defects can be produced at a relatively high current density (up to 11 A/dm2) under the combined actions of MHD-driven convection and external forced-convection; MHD-assisted nickel micro-electroforms have a higher microhardness, better surface morphologies and fewer defects than the ones obtained without the superimposition of the magnetic field. MHD-driven convection benefits the desirable implementation of HAR micro-electroforming processes.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaboubi O, Msellak K (2017) Magnetic field effects on the electrodeposition of CoNiMo alloys. Appl Surf Sci 396:375–383
Aaboubi O, Ali Omar AY, Franczak A et al (2015) Investigation of the electrodeposition kinetics of Ni–Mo alloys in the presence of magnetic field. J Electroanal Chem 737:226–234
Bund A, Ispas A, Mutschke G (2008) Magnetic field effects on electrochemical metal depositions. Sci Technol Adv Mater 9(2):024208
Devos O, Olivier A, Chopart JP et al (1998a) Magnetic field effects on nickel electrodeposition. J Electrochem Soc 145(2):401–405
Devos O, Aaboubi O, Chopart JP et al (1998b) Magnetic field effects on nickel electrodeposition ii. a steady-state and dynamic electrochemical study. J Electrochem Soc 145(12):4135–4139
Duch M, Esteve J, Gomez E et al (2002) Electrodeposited Co–Ni alloys for MEMS. J Micromech Microeng 12(4):400–405
Fahidy TZ (1983) Magnetoelectrolysis. J Appl Electrochem 13(5):553–563
Ganesh V, Vijayaraghavan D, Lakshminarayanan V (2005) Fine grain growth of nickel electrodeposit: effect of applied magnetic field during deposition. Appl Surf Sci 240(1–4):286–295
Gorobets OY, Gorobets VY, Derecha DO et al (2008) Nickel electrodeposition under influence of constant homogeneous and high-gradient magnetic field. J Phys Chem C 112(9):3373–3375
Griffiths SK, Nilson RH, Ting A et al (1998) Modeling electrodeposition for LIGA microdevice fabrication. Microsyst Techonol 4(2):98–101
Ispas A, Matsushima H, Plieth W et al (2007) Influence of a magnetic field on the electrodeposition of nickel–iron alloys. Electrochim Acta 52(8):2785–2795
Jia WP, Wu MH, Yang F (2012) Surface morphology and texture of nickel crystal micro-casting by electroforming under magnetic field. Adv Mater Res 535–537:450–454
Kołodziejczyk K, Miękoś E, Zieliński M et al (2018) Influence of constant magnetic field on electrodeposition of metals, alloys, conductive polymers, and organic reactions. J Solid State Electrochem 22(6):1629–1647
Krause A, Hamann C, Uhlemann M et al (2005) Influence of a magnetic field on the morphology of electrodeposited cobalt. J Magn Magn Mater 290–291:261–264
Liu G, Huang X, Xiong Y et al (2008) Fabricating HARMS by using megasonic assisted electroforming. Microsyst Technol 14(9–11):1223–1226
Lv YD (2012) Experimental research on micro-electroforming technology under a magnetic field. Master Dissertation. Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo (in Chinese)
Matsushima H, Nohira T, Mogi I et al (2004) Effects of magnetic fields on iron electrodeposition. Surf Coat Technol 179(2–3):245–251
Matsushima H, Bund A, Plieth W et al (2007) Copper electrodeposition in a magnetic field. Electrochim Acta 53(1):161–166
Ming PM, Zhu D, Hu YY et al (2009) Micro-electroforming under periodic vacuum-degassing and temperature-gradient conditions. Vacuum 83(9):1191–1199
Miura M, Oshikiri Y, Sugiyama A et al (2017) Magneto-dendrite effect: copper electrodeposition under high magnetic field. Sci Rep 7:45511
Weinmann M, Jung A, Natter H (2013) Magnetic field-assisted electroforming of complex geometries. J Solid State Electrochem 17(10):2721–2729
Weng FT (2005) A study of cathode agitation in ultrasonic-aided microelectroforming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25(9–10):909–912
Yamaguchi M, Tanimoto Y (2006) Magneto-science. In: Magneto-science: magnetic field effects on materials: fundamentals and applications, Springer series in materials science, vol 89. ISBN 978-3-540-37061-1. Kodansha Ltd., Springer, Berlin
Yu Y, Song Z, Ge H et al (2015) Effects of magnetic fields on the electrodeposition process of cobalt. Int J Electrochem Sci 10:4812–4819
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No .51475149], Program for Science & Technology Innovation Team in Universities of Henan Province (No. 15IRTSTHN013), Program for Science & Technology Innovation Team in Henan Polytechnic University (No. T2014-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, X., Ming, P. et al. Micro-electroforming high aspect ratio microstructures under magnetic field. Microsyst Technol 25, 1401–1411 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4090-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4090-0