Abstract
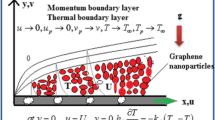
This research contemplates the flow and heat transport of MHD rheological Eyring–Powell fluid embedded with dust and graphene nanoparticles (GP) in an ethylene–glycol (EG) mixture in the presence of nonlinear convection, Cattaneo–Christov heat flux, and thermal radiation. Primarily existing PDEs (fluid and dust phase) are transferred to non-dimensional form by invoking similarity transformations then solved numerically through RKF-45 method. The graphene particles are significantly used in energy transmission in aerospace, power and propulsion generation etc. Through graphical illustrations, velocity and temperature profiles (fluid and dust phases) converse for various prominent parameters. The results of friction factor and heat transfer rate are presented and analyzed. Validation of the present result is made with the existing data. Results demonstrate that increasing nonlinear convection parameter has an inverse relationship with the Nusselt number and the velocity in the dust and fluid phases. This may happen due to the domination of unsteadiness in the flow.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- u, v :
-
Velocity components of fluid phase in x, y directions (m/s)
- \(u_{p} ,v_{p}\) :
-
Velocity components of particle phase in \(x,y\) directions
- g:
-
Acceleration due to gravity (\({\text{m/s}}^{ 2}\))
- \(\upsilon\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity (m2/s)
- \(f,f^{\prime}\) :
-
Dimensionless velocities of fluid phase
- \(F,F^{\prime}\) :
-
Dimensionless velocities of particle phase
- T :
-
Temperature of the fluid (K)
- \(T_{p}\) :
-
Temperature of the dust particle (K)
- \(k_{f}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity (w/mk)
- P :
-
Pressure
- A :
-
Unsteadiness parameter
- \(a\) :
-
Spherical radius of the dust particles
- N :
-
Number density of particles
- r :
-
Radius of the particles
- \(m\) :
-
Mass concentration of dust particles
- \(l\) :
-
Mass concentration of particles
- \(a\) :
-
Spherical radius of the dust particles
- \(\zeta\) :
-
Similarity variable
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Electrical conductivity (Siemens)
- \(\beta_{T}\) :
-
Fluid particle interaction parameter for temperature
- \(\beta_{\upsilon }\) :
-
Fluid particle interaction parameter for velocity
- \(\sigma^{*}\) :
-
Stefan-Boltzmann constant (Wm/K4)
- \(k^{ + }\) :
-
Mean absorption coefficient
- \(k_{\infty }\) :
-
Fluid free stream conductivity
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Conductivity variation parameter
- \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature (K)
- \(\theta_{p}\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature for the particle (K)
- \(\phi\) :
-
Nano particle volume fraction
- \(\phi_{d}\) :
-
Nano dust particle volume fraction
- \(\rho_{nf}\) :
-
Density of the nanofluid (kg/m3)
- \(\rho_{f}\) :
-
Density of the base fluid (kg/m3)
- \(\rho_{s}\) :
-
Density of the nanoparticles (kg/m3)
- \(\mu_{f}\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity of the base fluid (Ns/m2)
- \(\mu_{\text{nf}}\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity of the nanofluid (Ns/m2)
- \(c_{pf}\) :
-
Specific heat capacity at constant pressure of the fluid (J/kg K)
- \(c_{mf}\) :
-
Specific heat capacity at constant pressure of the dust particles (\({\text{J/kg\, K}}\))
- \(k_{nf}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity (W/m K)
- \((\rho c_{p} )_{nf}\) :
-
Effective heat capacity (Kg/m3 K)
- \((\rho c_{p} )_{p}\) :
-
Effective heat capacity of the particle medium (Kg/m3 K)
- \(\tau_{v}\) :
-
Relaxation time of the dust particles
- \(\alpha_{nf}\) :
-
Diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- \(\nu_{nf}\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity (\({\text{m}}^{ 2} / {\text{s}}\))
- \(\varGamma\) :
-
Dimensionless fluid parameter
- \(\delta\) :
-
Dimensionless fluid parameter
- \(\Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(Ec\) :
-
Eckert number
- \(R\) :
-
Radiation parameter
- \(\varLambda\) :
-
Thermal relaxation time
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Specific heat ratio
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Buoyancy parameter
- \(Gr_{x}\) :
-
Local Grashoff number
- \(\text{Re}_{x}\) :
-
Local Reynolds number
- \(\lambda_{1}\) :
-
Nonlinear convection parameter
- \(M\) :
-
Magnetic parameter
- \(C_{f}\) :
-
Skin friction coefficient
- \(Nu_{x}\) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- \(\text{Re}_{x}\) :
-
Local Reynolds number
- f :
-
Fluid
- w :
-
Condition at the wall
- ∞:
-
Condition at the free stream
- nf :
-
Nanofluid
References
Abbas N, Saleem S, Nadeem S, Alderremy AA, Khan AU (2018) On stagnation point flow of a micro polar nanofluid past a circular cylinder with velocity and thermal slip. Results Phys 9:1224–1232
Acharya N, Das K, Kundu PK (2017) Cattaneo-Christov intensity of magnetized upper-convected maxwell Nanoßuid flow over an inclined stretchingsheet: a generalised fourier and FickÕs perspective. Int J Mech Sci. 130:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.05.043
Ardahaie SS, Amiri AJ, Amouei A, Hosseinzadeh K, Ganji DD (2018) Investigating the effect of adding nanoparticles to the blood flow in presence of magnetic field in a porous blood arterial. Inf Med Unlocked 10:71–81
Babu N, Neeraja G, Raju CSK (2017) Radiated two-phase (Blasius and Sakiadis) flow in a suspension of graphene nanoparticles with heat source or sink. J Nanofluids 6:1046–1053
Balazadeh N, Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD, Li Z (2018) Semi analytical analysis for transient Eyring–Powell squeezing flow in a stretching channel due to magnetic field using DTM. J Mol Liq 260:30–36
Buongiorno J, Hu LW (2005) Nanofluid coolants for advanced nuclear power plants. Proc ICAPP 5:15–19
Cattaneo C (1948) Sulla conduzione del calore. Atti Sem Mat Fis Univ Modena Reggio Emilia 3:83–101
Choi SUS, Eastman JA (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Pub Fed 231:99–106
Christov Cl (2009) On frame indifferent formulation of the Maxwell–Cattaneo model of finite—speed heat conduction. Mech Res Commun 36:481–486
Dogonchi AS, Hatami M, Hosseinzadeh K, Domairry G (2015) Non-spherical particles sedimentation in an incompressible Newtonian medium by Padé approximation. Powder Technol 278:248–256
Fourier JBJ (1822) Theorie analytique de la chaleur. Didot, Paris, pp 499–508
Ghadikolaei SS, Yassari M, Sadeghi H, Hosseinzadeh K, Ganji DD (2017a) Investigation on thermophysical properties of TiO2–Cu/H2O hybrid nanofluid transport dependent on shape factor in MHD stagnation point flow. Powder Technol 322:428–438
Ghadikolaei SS, Hosseinzadeh K, Ganji DD (2017b) Analysis of unsteady MHD Eyring–Powell squeezing flow in stretching channel with considering thermal radiation and Joule heating effect using AGM. Case stud therm Eng 10:579–594
Ghadikolaei SS, Hosseinzadeh K, Yassari M, Sadeghi H, Ganji DD (2017c) Boundary layer analysis of micropolar dusty fluid with TiO2 nanoparticles in a porous medium under the effect of magnetic field and thermal radiation over a stretching sheet. J Mol Liq 244:374–389
Ghadikolaei SS, Hosseinzadeh K, Ganji DD (2018a) Investigation on three dimensional squeezing flow of mixture base fluid (ethylene glycol-water) suspended by hybrid nanoparticle (Fe3O4–Ag) dependent on shape factor. J Mol Liq 262:376–388
Ghadikolaei SS, Hosseinzadeh K, Yassari M, Sadeghi H, Ganji DD (2018b) Analytical and numerical solution of non-Newtonian second-grade fluid flow on a stretching sheet. Therm Sci Eng Prog 5:309–316
Ghadikolaei SS, Hosseinzadeh K, Ganji DD, Jafari B (2018c) Nonlinear thermal radiation effect on magneto Casson nanofluid flow with Joule heating effect over an inclined porous stretching sheet. Case Stud Therm Eng 12:176–187
Ghadikolaei SS, Hosseinzadeh K, Ganji DD, Hatami M (2018d) Fe3O4–(CH2OH)2 nanofluid analysis in a porous medium under MHD radiative boundary layer and dusty fluid. J Mol Liq 258:172–185
Gireesha BJ, Chamkha AJ, Manjunatha S, Bagewadi CS (2013) Mixed convective flow of a dusty fluid over a vertical stretching sheet with non-uniform heat source/sink and radiation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 23:598–612. https://doi.org/10.1108/09615531311323764
Hatami M, Sheikholeslami M, Hosseini M, Ganji DD (2014a) Analytical investigation of MHD nanofluid flow in non-parallel walls. J Mol Liq 194:251–259
Hatami M, Hosseinzadeh K, Domairry G, Behnamfar MT (2014b) Numerical study of MHD two-phase Couette flow analysis for fluid-particle suspension between moving parallel plates. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45(5):2238–2245
Hosseinzadeh K, Amiri AJ, Ardahaie SS, Ganji DD (2017) Effect of variable lorentz forces on nanofluid flow in movable parallel plates utilizing analytical method. Case stud therm Eng 10:595–610
Hosseinzadeh K, Afsharpanah F, Zamani S, Gholinia M, Ganji DD (2018a) A numerical investigation on ethylene glycol-titanium dioxide nanofluid convective flow over a stretching sheet in presence of heat generation/absorption. Case Stud Therm Eng 12:228–236
Hosseinzadeh K, Alizadeh M, Ganji DD (2018b) Hydrothermal analysis on MHD squeezing nanofluid flow in parallel plates by analytical method. Int J Mech Materials Eng 13(1):4
Jayachandra Babu M, Sandeep N, Raju CSK (2015) Heat and mass transfer in MHD Eyring–Powell nanofluid flow due to cone in porous medium. Int J Eng Res Afr 19:57–74. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/JERA.19.57
Jayachandra Babu M, Sandeep N, Saleem S (2017) Free convective MHD Cattaneo-Christov flow over three different geometries with thermophoresis and Brownian motion. Alex Eng J 56(4):659–669
Khan JA, Mustafa M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2015) Numerical study of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model for viscoelastic flow due to an exponentially stretching surface. Plos One 10(9):e0137363
Krishnamurthy MR, Gireesha BJ, Gorla RSR, Prasannakumara BC (2016) Suspended particle effect on slip flow and melting heat transfer of nanofluid over a stretching sheet embedded in a porous medium in the presence of nonlinear therm radiation. J Nanofluids 5:502–510
Kumar R, Sood S (2015) Nonlinear convection stagnation point heat transfer and MHD fluid flow in porous medium towards a permeable shrinking sheet arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06109
Makinde OD (2013) Computational modelling of nanofluids flow over a convectively heated unsteady stretching sheet. Current Nanosci 9:673–678
Mamatha SU, Raju CSK (2017) Cattaneo–Christov on heat and mass transfer of unsteady Eyring Powell dusty nanofluid over sheet with heat and mass flux conditions. Inf Med Unlocked. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2017.06.001
Mamatha SU, Mahesha, Raju CSK (2017) Multiple slips magnetohydrodynamic carreau dustynano fluid over a stretched surface with cattaneo-christov heat flux. J Nanofluids 6(6):1074–1081. https://doi.org/10.1166/jon.2017.1408
Nadeem S, Saleem S (2014) Mixed convection flow of Eyring–Powell fluid along a rotating cone. Results Phys 4:54–62
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA (2004) Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films, Source Sci. N Ser Gene Expr Genes Action 306:666–669. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1102896
Powell RE, Eyring H (1944) Mechanisms for the relaxation theory of viscosity. Nature 154:427–428. https://doi.org/10.1038/154427a0
Qayyum S, Hayat T, Shehzad SA, Alsaedi A (2017) Nonlinear convective flow of Powell-Erying magneto nanofluid with Newtonian heating. Results Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.08.001
Rahimi J, Ganji DD, Khaki M, Hosseinzadeh K (2016) Solution of the boundary layer flow of an Eyring–Powell non-Newtonian fluid over a linear stretching sheet by collocation method. Alex Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2016.11.006
Raju CSK, Sandeep N (2017) MHD slip flow of a dissipative Casson fluid over a moving geometry with heat source/sink: a numerical study. Acta Astronaut 133:436–443
Raju CSK, Sandeep N, Jayachandra Babu M, Sugunamma V (2016a) Dual solutions for three-dimensional MHD flow of a nanofluid over a nonlinearly permeable stretching sheet. Alex Eng J 55:151–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2015.12.017
Raju CSK, Sandeep N, Saleem S (2016b) Effects of induced magnetic field and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions on stagnation flow of a Casson fluid. Eng Sci Technol 19(2):875–887
Raju CSK, Sandeep N, Malvandi A (2016c) Free convective heat transfer of MHD Cu-kerosene nanofluid over a cone with temperature dependent viscosity. Acta Astronaut 129:419–428
Raju CSK, Sekhar KR, Ibrahim SM, Lorenzini G, Reddy GV, Lorenzini E (2017a) Variable viscosity on unsteady dissipative Carreau fluid over a truncated cone filled with titanium alloy nanoparticles. Contin Mech Thermodyn 29(3):699–713
Raju CSK, Sanjeevi P, Raju MC, Ibrahim SM, Lorenzini G, Lorenzini E (2017b) The flow of magnetohydrodynamic Maxwell nanofluid over a cylinder with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Contin Mech Thermodyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-017-0580-z
Raju CSK, Saleem S, Mamatha SU (2018a) Iqtadar Hussain, heat and mass transport phenomena of radiated slender body of three revolutions with saturated porous: Buongiorno’s model. Int J Therm Sci 132:309–315
Raju CSK, Naik M, Upadhya MS, Saleem S (2018b) Nonlinear unsteady convection on micro and nanofluids with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux. Results Phys 9:779–786
Saleem S, Nadeem S, Rashidi MM, Raju CSK (2018) An optimal analysis of radiated nanomaterial flow with viscous dissipation and heat source. Microsyst Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3996
Shaw S, Kameswaran PK, Sibanda P (2016) Effects of slip on nonlinear convection in nanofluid flow on stretching surfaces. Bound Value Probl. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13661-015-0506-2
Upadhya SM, Raju CSK, Saleem S, Alderremy AA (2018) Modified fourier heat flux on MHD flow over stretched cylinder filled with Dust, Graphene and silver nanoparticles. Results Phys 9:1377–1385
Yu W, Xie H, Bao D (2010) Enhanced thermal conductivities of nanofluids containing graphene oxide nanosheets. Nanotechnology 21(5):055705
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to express their gratitude to King Khalid University, Abha 61413, Saudi Arabia for providing administrative and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raju, C.S.K., Saleem, S., Al-Qarni, M.M. et al. Unsteady nonlinear convection on Eyring–Powell radiated flow with suspended graphene and dust particles. Microsyst Technol 25, 1321–1331 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4076-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4076-y