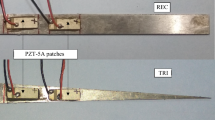
Abstract
Energy harvesting has experienced significant attention from researchers globally. This is due to the quest to power remote sensors and portable devices with power requirements of tens to hundreds of μW. Hence, ambient vibration energy has the potential to provide such power demands. Thus, cantilever beams with piezoelectric materials have been utilized to transduce mechanical energy in vibrating bodies to electrical energy. However, the challenge is to develop energy harvesters that can harvest sufficient amount of energy needed to power wireless sensor nodes at wide frequency bandwidth. In this article, piezoelectric energy harvester (PEH) beams with coupled magnets are proposed to address this issue. With macro fiber composite as the piezoelectric transducer, mathematical models of different system configurations having magnetic couplings are derived based on the continuum based model. Simulations of the system dynamics are done using numerical integration technique in MATLAB software to study the influence of magnetic interactions in generating power and frequency bandwidth due to base excitations at low frequency range. Experimental results comparing conventional system and the proposed piezoelectric beam configurations with coupled magnets are also presented. Finally, the optimal beam separation distance between the magnetic oscillator and PEH is presented in this work.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton SR, Sodano HA (2007) A review of power harvesting using piezoelectric materials (2003–2006). Smart Mater Struct 16:R1
Challa VR, Prasad MG, Shi Y, Fisher FT (2008) A vibration energy harvesting device with bidirectional resonance frequency tunability. Smart Mater Struct 17:015035. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/17/01/015035
Cook-Chennault K, Thambi N, Sastry A (2008) Powering MEMS portable devices—a review of non-regenerative and regenerative power supply systems with special emphasis on piezoelectric energy harvesting systems. Smart Mater Struct 17:043001
Cottone F, Vocca H, Gammaitoni L (2009) Nonlinear energy harvesting. Phys Rev Lett 102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.080601
Erturk A, Inman DJ (2011) Piezoelectric energy harvesting. Wiley, London
Erturk A, Hoffmann J, Inman DJ (2009) A piezomagnetoelastic structure for broadband vibration energy harvesting. Appl Phys Lett 94. doi:10.1063/1.3159815
Liao Y, Sodano HA (2009) Optimal parameters and power characteristics of piezoelectric energy harvesters with an RC circuit. Smart Mater Struct 18:045011
Lin J-T, Lee B, Alphenaar B (2010) The magnetic coupling of a piezoelectric cantilever for enhanced energy harvesting efficiency. Smart Mater Struct 19:045012
Muthalif AGA, Nordin NHD (2015) Optimal piezoelectric beam shape for single and broadband vibration energy harvesting: modeling, simulation and experimental results. Mech Syst Signal Process 54–55:417–426. doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.07.014
Qing O, Xiaoqi C, Gutschmidt S, Wood A, Leigh N (2010) A two-mass cantilever beam model for vibration energy harvesting applications. In: Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), 2010 IEEE conference, pp 301–306. doi:10.1109/COASE.2010.5584730
Roundy S (2005) On the effectiveness of vibration-based energy harvesting. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 16:809–823
Saadon S, Sidek O (2011) A review of vibration-based MEMS piezoelectric energy harvesters. Energy Convers Manag 52:500–504
Stanton SC, McGehee CC, Mann BP (2009) Reversible hysteresis for broadband magnetopiezoelastic energy harvesting. Appl Phys Lett 95:174103. doi:10.1063/1.3253710
Tang L, Yang Y (2012) A nonlinear piezoelectric energy harvester with magnetic oscillator. Appl Phys Lett 101:094102. doi:10.1063/1.4748794
Tang L, Yang Y, Soh CK (2012) Improving functionality of vibration energy harvesters using magnets. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 23:1433–1449. doi:10.1177/1045389x12443016
Tang L, Yang Y, Soh C (2013) Broadband vibration energy harvesting techniques. In: Elvin N, Erturk A (eds) Advances in energy harvesting methods, Springer, New York, pp 17–61. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-5705-3_2
Timoshenko S, Woinowsky-Krieger S, Woinowsky-Krieger S (1959) Theory of plates and shells, vol 2. McGraw-hill, New York
Twiefel J, Westermann H (2013) Survey on broadband techniques for vibration energy harvesting. J Intell Mater Syst Struct. doi:10.1177/1045389x13476149
Vokoun D, Beleggia M, Heller L, Šittner P (2009) Magnetostatic interactions and forces between cylindrical permanent magnets. J Magn Magn Mater 321:3758–3763. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.07.030
Yang Y, Tang L (2009) Equivalent circuit modeling of piezoelectric energy harvesters. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 20:2223–2235. doi:10.1177/1045389x09351757
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, D.S., Muthalif, A.G.A., Nordin, N.H.D. et al. Comparative study of conventional and magnetically coupled piezoelectric energy harvester to optimize output voltage and bandwidth. Microsyst Technol 23, 2663–2674 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3066-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3066-1