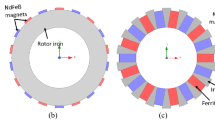
Abstract
For miniature spindle motors design and their applications, the output torque is one of the most important characteristics and it is necessary to improve the output torque of miniature spindle motors in keeping with consumer preferences. Accordingly, this paper is aimed to overcome this problem and propose a novel electromagnetic structure design to improve the output torque of the spindle motor for miniature cooling fans and modern consumer electronic products. In contrast to one phase DC brushless motor with only one axial air gap or radial air gap inside its electromagnetic structure, the proposed one phase DC brushless motor comprises simultaneously one axial air gap and radial air gap inside its electromagnetic structure. This paper utilizes commercial software MagNet to numerically verify the proposed one phase DC brushless motor. The simulation results show that compared to the conventional one phase DC brushless motors with only one axial air gap or radial air gap, the proposed one phase DC brushless motor can improve the output torque obviously. In other words, the novel electromagnetic structure of the proposed one phase DC brushless motor can enhance the operation efficiency. As a result, the results presented in this study show that the proposed one phase DC brushless motor provides potential solution for both existing and emerging miniature spindle motor applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry KF (2003) Analysis and performance comparison of a tooth wound brushless CPU cooling fan motor. Proc Electr Insul Conf Electr Manuf Coil Wind Technol Conf 2003:379–386
Chen WC, Tzou YY (2011) Current-mode sensorless control of single-phase brushless DC fan motors. IEEE PEDS 2011:659–663
Chen CY, Liu CS, Li YC (2015) Design and characterization of miniature fluid dynamic bearing using novel multi-step elliptical grooves. Microsyst Technol 21:91–100
Chuang CJ, Yang CM, Ho CL (2006) Stator device of a motor and fabrication method thereof. US Pat 7038352:B1
Grimes R, Davies M (2002) The effect of fan operating point and location on temperature distribution in electronic systems. In: The 8th Intersociety conference on thermal and thermomechanical phenomena in electronic systems, pp 677–684
Grimes R, Walsh E, Walsh P (2010) Active cooling of a mobile phone handset. Appl Therm Eng 30:2363–2369
Huang WS, Lin KC, Chou CH, Tsai MS (2003) Motor structure. US Patent 6509666:B1
Huang WS, Lin KC, Tsai MS, Chou CH (2004) Motor structure. US Patent 6703757:B2
Kordik JA (1992) High pole density three phase motor. US Patent 5164622:A
Lin SC, Chang CJ, Hsieh MY (2013) Performance enhancement of a small centrifugal cooling fan. Appl Mech Mater 284–287:878–882
Liu CS, Lin PD (2008) Analysis and validations of fluid dynamic bearing for spindle motors of high-density optical disc players. Jpn J Appl Phys 47:8101–8105
Liu CS, Chuo YC, Lin PH, Tsai MC, Chang YH, Horng JB (2007) Effects of the fluid dynamic bearing design on rotational precision of a spindle motor. IEEE Trans Magn 43:790–792
Liu CS, Lin PD, Tsai MC (2009) A miniature spindle motor with fluid dynamic bearings for portable storage device applications. Microsyst Technol 15:1001–1007
Murai Y, Kawase Y, Ohashi K (1989) Torque ripple improvement for brushless DC miniature motors. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 25:441–450
Ranjithkumar G, Prasad KNV (2012) Minimization of torque ripple content for BLDC motor by current controller using MLI. Procedia Eng 38:3113–3121
Rodriguez F, Emadi A (2007) A novel digital control technique for brushless DC motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 54:2365–2373
Song XQ, Zheng MQ, Zang KM, Sun FC, Sun DF (2001) The new digital control method for improving the electromagnetic torque of BLDCM. J Beijing Inst Technol 21:185–191
Sun L, Fang Q, Shang J (2007) Drive of single-phase brushless DC motors based on torque analysis. IEEE Trans Magn 43:46–50
Tan RHG, Goh YH, Wong YQ, Mok VH (2009) Energy efficient cooling fan for PC chassis. CITISIA 2009:177–181
Vinson WD, Franz JP, Jarrah Y (2014) Cooling fan for electronic device. USA Patent 8647077:B2
Wang DG, Muller PK (2000) Improving cooling efficiency by increasing fan power usage. Microelectron J 31:765–771
Wang CC, Yao YD, Liang KY, Huang CC, Chang YC (2012) Development of a miniature fan motor. J Appl Phys 111:07E718-1–07E718-3
Wibel W, Maikowske S, Brandner JJ (2015) Novel microstructured evaporation device. Microsyst Technol 21:549–560
Yoo JH, Hong JI, Cao W (2000) Piezoelectric ceramic bimorph coupled to thin metal plate as cooling fan for electronic devices. Sen Actuators A 79:8–12
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided to this study by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Grant No. NSC 102-2221-E-194-023 and the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under Grant No. MOST 103-2221-E-194-006-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, CS., Chang, YH. Development of novel spindle motor with dual air gaps to improve output torque. Microsyst Technol 23, 371–379 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2685-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2685-2