Abstract
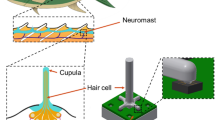
Biomimetics is a promising field of research in which natural processes and structures are transferred to technical applications. The lateral line is a critical component of the fish sensory system and plays an important role in many behaviors by providing hydrodynamic information about the surrounding fluid. It is believed that the artificial lateral line flow sensors (ALLFS) are advantageous for underwater applications. This paper reviews the morphology and biophysics of the lateral line, especially theoretical models of lateral line, including biomechanical model, frequency response and time domain response of lateral line. Also, this paper reviews some efforts to mimic lateral line system in recent years. In order to capture the recent research status, this paper reviews the design and fabrication of ALLFS based on different sensing principles. Further researches to develop ALLFS and their underwater applications are also discussed in this paper.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulsadda AT, Tan X (2011) Underwater source localization using an IPMC-based artificial lateral line. Robotics and automation (ICRA). Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, pp 447–452
Abdulsadda AT, Tan X (2012) An artificial lateral line system using IPMC sensor arrays. Int J Smart Nano Mater. doi:10.1080/19475411.2011.650233
Asadnia M, Kottapalli Ajay Giri Prakash, Shen Zhiyuan, Miao Jianmin, Triantafyllou Michael (2013) Flexible and surface-mountable piezoelectric sensor arrays for underwater sensing in marine vehicles. IEEE Sens J 13(10):3918–3925
Batchelor GK (1967) Basic developments in fluid dynamics. J Fluid Mech 28:822–824
Beckmann M, Eros T, Schmitz A, Bleckmann H (2010) Number and distribution of superficial neuromasts in twelve common European cypriniform fishes and their relationship to habitat occurrence. Int Rev Hydrobiol 95:273–284
Bleckmann H, Mogdans Joachim, Coombs SL (2014) Flow sensing in air and water. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Chen J, Fan ZF, Zou J, Engel J, Liu C (2003) Two-dimensional micromachined flow sensor array for fluid mechanics studies. J Aerosp Eng 16:85–97
Chen N, Chen J, Engel J, Pandya S, Tucker C, Liu C (2006) Development and characterization of high-sensitivity bioinspired artificial haircell sensor The 12th Solid State Sensors, Actuator, and Microsystems Workshop, Hilton Head, South Carolina, 4–8 Jun
Chen NN, Tucker C, Engel JM, Yang YC, Pandya S, Liu C (2007) Design and characterization of artificial haircell sensor for flow sensing with ultrahigh velocity and angular sensitivity. J Microelectromech Syst 16:999–1014
Chenyang X, Shang C, Wendong Z, Binzhen Z, Guojun Z, Hui Q (2007) Design, fabrication, and preliminary characterization of a novel MEMS bionic vector hydrophone. Microelectron J 38:1021–1026
Coombs S, Braun CB (2003) Information processing by the lateral line system. In: Collin SP, Marshall NJ (eds) Sensory processing in aquatic environments. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 122–138
Dagamseh AMK, Lammerink TSJ, Bruinink CM, Wiegerink RJ, Krijnen GJM (2009) Dipole source localisation using bio-mimetic flow-sensor arrays. Procedia Chem 1:891–894
Dagamseh AMK, Lammerink TSJ, Kolster ML, Bruinink CM, Wiegerink RJ, Krijnen GJM (2010) Dipole-source localization using biomimetic flow-sensor arrays positioned as lateral-line system. Sens Actuators A 162:355–360
Dagamseh AMK, Lammerink TSJ, Sanders R, Wiegerink RJ, Krijnen GJM (2011) Towards high-resolution flow cameras made of artificial hair flow-sensors for flow pattern recognition Mems: IEEE 24th International conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, pp 648–651
Dinklo T (2005) Mechano- and electrophysiological studies on cochlear hair cells and superficial lateral line cupulae. Doctoral dissertation, University of Groningen
Dusek J, Kottapalli AGP, Woo ME, Asadnia M, Miao J, Lang JH, Triantafyllou MS (2013) Development and testing of bio-inspired microelectromechanical pressure sensor arrays for increased situational awareness for marine vehicles. Smart Mater Struct. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/22/1/014002
Fan Z, Chen J, Zou J, Bullen D, Liu C, Delcomyn F (2002) Design and fabrication of artificial lateral line flow sensors. J Micromech Microeng 12:655–661
Fulford JM (2001) Accuracy and consistency of water-current meters. JAWRA J Am Water Resour Assoc 37(5):1215–1224
Gardiner JM, Atema J (2007) Sharks need the lateral line to locate odor sources: rheotaxis and eddy chemo taxis. J Exp Biol 210:1925–1934
Harris GG, van Bergeijk WA (1962) Evidence that the lateral-line organ responds to near field displacements of sound sources in water. J Acoust Soc Am 34:31–41
Izadi N, Krijnen Gijs JM (2012) Design and fabrication process for artificial lateral line sensors. In: Coombs S (ed) Frontiers in sensing from biology to engineering the lateral line. Springer, New York, pp 405–419
Izadi N, de Boer MJ, Berenschot JW, Krijnen GJM (2010) Fabrication of superficial neuromast inspired capacitive flow sensors. J Micromech Microeng. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/20/8/085041
Jing XM, Miao JM, Xu T, Norford L (2010a) Hair-like airflow sensing with piezoelectric vibrating diaphragm. In: proceeding sensors, 2010 IEEE, pp 1809–1812
Jing XM, Miao JM, Xu T, Olfatnia M, Norford L (2010b) Vibration characteristics of micromachined piezoelectric diaphragms with a standing beam subjected to airflow. Sens Actuators A 164:22–27
Kalmijn AJ (1988) Hydrodynamic and acoustic field detection. In: Atema J, Fay RR, Popper AN, Tavolga WN (eds) Sensory biology of aquatic animals. Springer, New York, pp 83–130
Kalmijn AJ (1989) Functional evolution of lateral line and inner ear sensory systems. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Springer, New York, pp 187–215
Kitzhofer J, Nonn T, Brücker C (2011) Generation and visualization of volumetric PIV data fields. Exp Fluids 51:1471–1492. doi:10.1007/s00348-011-1176-1
Klein A, Bleckmann H (2011) Determination of object position, vortex shedding frequency and flow velocity using artificial lateral line canals. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 2:276–283
Krijnen G, Lammerink T, Wiegerink R, Casas J (2007) Cricket inspired flow-sensor arrays. In: IEEE Sensors conference pp 539–546
Li Fei, Liu Weiting, Stefanini Cesare, Xin Fu, Dario Paolo (2010) A novel bioinspired PVDF micro/nano hair receptor for a robot sensing system. Sensors 10:994–1011
McConney ME, Chen N, Lu D, Hu HA, Coombs S, Liu C, Tsukruk VV (2008) Biologically inspired design of hydrogel-capped hair sensors for enhanced underwater flow detection. Soft Mater 5:292–295
McHenry MJ, Strother JA, van Netten SM (2008) Mechanical filtering by the boundary layer and fluid-structure interaction in the superficial neuromast of the fish lateral line system. J Comput Physiol A 194:795–810
Mogdans J, Bleckmann H (2012) Coping with flow: behavior, neurophysiology and modeling of the fish lateral line system. Biol Cybern 106(11–12):627–642
Nawi MNM, Abd Manaf A, Arshad MR, Sidek O (2011) Review of MEMS flow sensors based on artificial hair cell sensor Microsyst. Technol 17:1417–1426
Nguyen N, Jones D, Pandya S, Yang Y C, Chen NN, Tucker C, Liu C (2008) Biomimetic flow imaging with an artificial fish lateral line. In: Biosignals: Proc. First Int. Conf. on Bio-Inspired Systems and Signal Processing vol 2. pp 269–276
Nguyen N, Jones DL, Yang YC, Liu C (2011) Flow vision for autonomous underwater vehicles via an artificial lateral line. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process. doi:10.1155/2011/806406
Ozaki Y, Ohyama T, Yasuda T, Shimoyama I (2000) Air flow sensor modeled on wind receptor hairs of insects IEEE Int. Conf. MEMS pp 531–6
Pandya S, Yang Y, Jones DL, Engel J, Liu C (2006) Multisensor processing algorithms for underwater dipole localization and tracking using MEMS artificial lateral-line sensors. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process. doi:10.1155/ASP/2006/76593
Pandya S, Yang Y C, Liu C, Jones D L(2007) Biomimetic imaging of flow phenomena. IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing vol II, pp 933–936
Peleshanko S, Julian MD (2007) Hydrogel-encapsulated microfabricated haircells mimicking fish cupula neuromast Adv. Mater 19:2903–2909
Pitcher T, Partridge B.L, Wardle C.S (1976) A blind fish can school Science 194: 963–965
Pohlmann K, Atema J, Breithaupt T (2004) The importance of the lateral line in nocturnal predation of piscivorous catfish. J Exp Biol 207:2971–2978
Qualtieri A, Rizzi F, Todaro MT, Passaseo A, Cingolani R, De Vittorio M (2011) Stress-driven AlN cantilever-based flow sensor for fish lateral line system. Microelectron Eng 88:2376–2378
Sebastian G, Wolfgang S (2009) The Micro-Pillar Shear-Stress Sensor MPS3 for Turbulent Flow. Sensors 9:2222–2251. doi:10.3390/s90402222
Schlichting H (1979a) Boundary-layer theory. Springer-Verlag, New York
Schlichting H (1979b) Boundary-layer theory. Springer-Verlag, New York
Song C, Aiyar AR, Kim SH, Allen MG (2011) Exploitation of aeroelastic effects for drift reduction, in an all-polymer air flow sensor. Sensors Actuators A 165:66–72
Stocking JB, Eberhardt WC, Shakhsheer YA, Calhoun BH, Paulus JR, Appleby M (2010) A capacitance-based whisker-like artificial sensor for fluid motion sensing. 2010 IEEE Sensors conference pp 2224–2229
Stokes GG (1851) On the effect if the internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums Trans. Camb. Phil. Soc. 9:8–106
Tao J, Yu X, Berilla J (2011a) Micropillar sensing element for bio-Inspired flow sensors 8th Int. Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring (Standford, CA) ed F Chang, pp 1732–9
Tao J, Yu X, Berilla J (2011b) Bio-inspired flow and acoustic sensor Proc. SPIE 8019:80190R–80210R
Van Baar JJ, Dijkstra M, Wiegerink RJ, Lammerink TSJ, Krijnen GJM, Humphrey JAC (2003) Fabrication of arrays of artificial hairs for complex flow pattern recognition. IEEE Sens Conf 1:332–336
van Netten SM (1991) Hydrodynamics of the excitation of the cupula in the fish canal lateral line. J Acoust Soc Am 89:310–319
Van Netten SM (2006) Hydrodynamic detection by cupulae in a lateral line canal: functional relations between physics and physiology. Biol Cybern 94:67–85
van Netten SM, McHenry MJ (2013) The biophysics of the fish lateral line. In: Coombs S (ed) The Lateral line. Springer, New York, pp 99–119
Van Trump WJ, McHenry MJ (2008) The morphology and mechanical sensitivity of lateral line receptors in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). J Exp Biol 211(13):2105–2115
Wang YH, Lee CY, Chiang CM (2007) A MEMS-based air flow sensor with a free-standing micro-cantilever structure. Sensors 7:2389–2401
Windsor SP, McHenry MJ (2009) The influence of viscous hydrodynamics on the fish lateral-line system Int. Comp Biol 49:691–701
Xue CY, Chen S, Zhang WD, Zhang BZ, Zhang GJ, Qiao H (2007) Design, fabrication, and preliminary characterization of a novel MEMS bionic vector hydrophone. Microelectron J 38:1021–1026
Xu Y, Kamran M (2014) Bioinspired hydrodynamic force feedforward for autonomous underwater vehicle control. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 19(4):1127–1137
Yang Y, Chen N, Tucker C, Engel JM, Pandya S, Liu C (2007) From artificial hair cell sensor to artificial lateral line system: development and application. In: Proc IEEE 20th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, MEMS (2007), Kobe, Japan, pp 577–580
Yang YN, Klein A, Bleckmann H, Liu C (2011a) Artificial lateral line canal for hydrodynamic detection. Appl Phys Lett 99:023701
Yang YC, Klein A, Bleckmann H, Liu C (2011b) Artificial lateral line canal for hydrodynamic detection. Appl Phys Lett 99:023701
Yu X, Tao J, Berilla J (2010) A bio-inspired flow sensor, Proc. SPIE 7646, Nanosensors, Biosensors, and Info-Tech Sensors and Systems 2010, 764618 (30 Mar 2010); doi:10.1117/12.849230
Zhang BZ, Qiao H, Chen S, Liu J, Zhang WD, Xiong JJ, Xue CY, Zhang GJ (2008) Modeling and characterization of a micromachined artificial hair cell vector hydrophone. Microsyst Technol 14:821–828
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shizhe, T. Underwater artificial lateral line flow sensors. Microsyst Technol 20, 2123–2136 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2350-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2350-1