Abstract
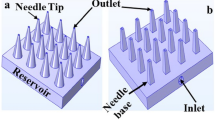
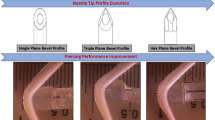
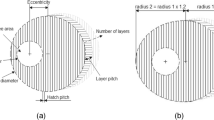
Hypodermic injections give the best results in terms of drug administration efficiency, but benefit from a negative image among patients due to the fear of pain linked to needles. Transdermal drug delivery (TDD) has thus been greatly developed in the past ten years in order to be able to by-pass the skin protective layers in a minimally invasive way. With the advent of micro electro mechanical systems, opportunities have appeared, particularly in the area of microneedles. In this paper we present a new design of hollow polymeric microneedles aimed at being used for TDD by allowing injection of a liquid in the non-innerve part of the dermis. The design has been studied in order to be able to manufacture these microneedles arrays using techniques that may be applicable to industrial production at low cost. The envisioned microfabrication processes and their stacking are presented which involve injection micromolding and excimer laser ablation. Microneedles are also numerically characterized in terms of mechanics and microfluidics showing that the design also involves interesting features in terms of needles resistance and microfluidic. Due to the innovative double-molding technique, the micro-needles are indeed emptied leaving a cavity. An outlet channel on the side of the needle allows fluid flowing out of the needles. The characteristics of this outlet channel contribute to flow homogenization when several needles are placed in an array pattern. This microneedle design thus combines interesting characteristics in terms of ease of fabrication at large scale, mechanical resistance and fluid dynamics.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Qallaf B, Das DB (2008) Optimization of square microneedle arrays for increasing drug pereability in skin. Chem Eng Sci 63:2523–2535
Bodhale D, Nisar A, Afzulpurkar N (2010) Structural and microfluidic analysis of hollow side-open polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 8:373–392
Burton S, Ng CY, Moeckly C, Brandwein D, Gilbert T, Johnson N, Brown K, Alston T, Prochnow G, Siebenaler K, Hansen K (2011) Rapid intradermal delivery of liquid formulations using a hollow microstructured array. Pharm Res 28:31–40
Davidson A, Al-Qallaf B, Das DB (2008) Transdermal drug delivery by coated microneedles: Geometry effects on effective skin thickness and drug permeability. Chem Eng Res Des 86:1196–1206
Davis S, Landis B, Adams Z, Allen M, Prausnitz M (2004) Insertion of microneedles into skin: measurement and prediction of insertion force and needel fracture force. J Biomech 37:1157–1163
Frick T (2003) Resistance forces acting on suture needles. J Biomech 34:1335–1340
Gardeniers HJ, Luttge R, Berenschot EJ, Boer M, Yeshurun S, Hefetz M, van’t Oever R, van den Berg A (2003) Silicon micromachined hollow microneedles or transdermal liquid transport. J Microelectromech Syst 12(6):855–862
Giboz J, Copponnex T, Mele P (2007) Microinjection molding of thermoplastic polymers: a review. J Micromech Microeng 17:R96–R109
Gill H, Prausnitz M (2007) Coated microneedles for transdermal delivery. J Control Release 117:227–237
Griss P, Stemme G (2003) Side-opened out-of-plane microneedles for microfluidic transdermal liquid transfer. J Microelectromech Syst 12(3):296–301
Gupta J, Felner E, Prausnitz M (2009) Minimally invasive insulin delivery in subjects with type 1 diabetes using hollow microneedls. Diabetes Technol Ther 11(6):329–337
Henry S, McAllister D, Allen M, Prausnitz M (1998) Microfabricated miconeedles: a new approach to transdermal drug delivery. J Pharm Sci 87(8):922–925
Ji J, Tay F, Miao J (2006) Microfabricated hollow microneedle array using icp etcher. J Phys Conf Ser 34:1132–1136
Jiang J, Moore J, Edelhauser H, Prausnitz M (2009) Intrascleral drug delivery to the eye usinh hollow microneedles. Pharm Res 26(2):395–403
Khumpuang S, Maeda R, Sugiyama S (2003) Design and fabrication of a coupled microneedle array and insertion guide array for safe penetration through skin. In: Proceedings of 2003 international symposium on micromechatronics and human science
Kim K, Lee JB (2007) High aspect ratio tapered hollow metallic microneedles arrays with microfluidic interconnector. Microsyst Technol 13:231–235
Kim M, Hwang YY, Kyung JB, Park JH (2010) Novel treatment of fecal incontinece using microneedle and topical application of phenylephrine. In: Proceedings of the first international conference on microneedles, Atlanta
Lhernould MS, Delchambre A, Rgnier S, Lambert P (2007) Electrostatic forces in micromanipulations: review of analytical models and simulations including roughness. Appl Surf Sci 253:6203–6210
Martanto W (2005) Microinjection into skin using microneedles. Ph.D. thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology
Matteucci M, Fanetti M, Casella M, Gramatica F, Gavioli L, Tormen M, Grenci G, De Angelis F, Di Fabrizio E (2009) Poly vinyl alcohol re-usable masters for microneedle replication. Microelectron Eng 86:752–756
McAllister D, Wang P, Davis S, Park JH, Canatella P, Allen M, Prausnitz M (2003) Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecule and nanoparticles: Fabrication methods and transport studies. In: National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol 100, pp 13755–13760
Moon S, Lee S (2005) A novel fabrication method of a microneedle array using inclined deep X-ray exposure. J Micromech Microeng 15:903–911
Mukerjee E, Collins S, Isseroff R, Smith R (2004) Microneedle array for transdermal biological fluid extraction and in situ analysis. Sens Actuators A114:267–275
Roxhed N, Griss P, Stemme G (2008a) Membrane-sealed hollow microneedles and related administration schemes for transdermal drug delivery. Biomed Microdevices 10:271–279
Roxhed N, Samel B, Nordquist L, Griss P, Stemme G (2008b) Painless drug delivery through microneedle-based transdermal patches featuring active infusion. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(3):1063–1071
Sammoura F, Kang J, Heo YM, Jung T, Lin L (2007) Polymer microneedle fabrication using a microinjection molding technique. Microsyst Technol 13:517–522
Stoeber B, Liepmann D (2005) Arrays of hollow out-of-plane microneedles for drug delivery. J Microelectromech Syst 14(3):472–479
Sullivan S, Koutsonanos D, Martin M, Lee J, Zarnitsyn V, Choi S, Murthy N, Compans R, Skountzou I, Prausnitz MR (2010) Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for influenza vaccination. Nat Med 16:915–920
Teo A, Shearwood C, Ng K, Lu J, Moochhala S (2006) Transdermal microneedles for drug delivery applications. Mater Sci Eng B132:151–154
Acknowledgments
This work has been possible thanks to the support of the Walloon Region and SIRRIS research center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sausse Lhernould, M., Delchambre, A. Innovative design of hollow polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Microsyst Technol 17, 1675 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-011-1355-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-011-1355-2