Abstract
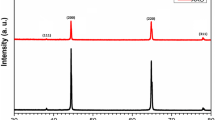
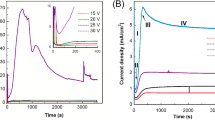
Most anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) or porous anodic aluminum (PAA) films were fabricated using the potentiostatic method from high-purity (99.999%) aluminum films at low temperatures of 0–10°C to avoid dissolution effects at room temperature (RT). In this article, the fabrication of AAO or PAA film from commercial purity (99%) aluminum at RT has been investigated using hybrid pulse anodization under different oxalic acid concentration and process duration. The effect of acid concentration and anodization duration on the formation of AAO size and morphology has been studied. Both pore diameter and oxide layer thickness of AAO films were examined via SEM images and found that both increased with increasing oxalic concentration and anodization duration. In addition, the pore distribution was more concentrated at high electrolytic concentration and anodization duration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung CK, Chang WT (2006) Effect of pulse frequency on the morphology and nanoindentation property of electroplated nickel films. Microsyst Technol 13:537–541
Chung CK, Chang WT (2009) Effect of pulse frequency and current density on anomalous composition and nanomechanical property of electrodeposited Ni–Co films. Thin Solid Films 517:4800–4804
Chung CK, Zhou RX, Liu TY, Chang WT (2009) Hybrid pulse anodization for the fabrication of porous anodic alumina films from commercial purity (99%) aluminum at room temperature. Nanotechnology. 20:055301
David HC (2001) Nanowires begin to shine. Nature 409:2–33
Fan DH, Wing GQ, Shen WZ, Zheng MJ (2007) Adsorption and diffusion of light alkanes on nanoporous faujasite catalysts investigated by molecular dynamics simulations. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 100:154–159
Favier F, Walter EC, Zach MP, Benter T, Penner RM (2001) Hydrogen sensors and switches from electrodeposited palldium mesowire arrays. Science 293:2227–2231
Lo D, Budiman RA (2007) Fabrication and characterization of porous anodic alumina films from impure aluminum foils. J Electrochem Soc 154:C60–C66
Manalis S, Babcock K, Massie J, Elings V, Dugas M (1995) Submicron studies of recording media using thin-film magnetic scanning probes. Appl Phys Lett 66:585–2587
Masuda H, Fukuda K (1995) Ordered metal nanohole arrays made by a two-step replication of honetcomb structure of anodic alumina. Science 268:1466–1468
Masuda H, Hasegwa F (1997) Self-ordering of cell arrangement of anodic porous alumina formed in sulfuric acid solution. J Electrochem Soc 144:127–130
Nielsch K, Müller F, Li AP, Gösele U (2000) Uniform nickel deposition into ordered alumina pores by pulsed electrodeposition. Adv Mater 12:582–586
Nielsch K, Choi J, Schwirn K, Wehrspohn RB, Golsele U (2002) Self-ordering regimes of porous alumina: the 10% porosity rule. Am Chem Soc 2:677–680
Ssito M, Kirihara M, Taniguchi T, Miyagi M (1989) Micropolarizer made of the anodized alumina film. Appl Phys Lett 55:607–609
Tian YT, Meng GW, Gao T, Sun SH, Xie T, Peng XS, Ye CH, Zhang LD (2004) Alumina nanowire arrays standing on a porous anodic alumina membrane. Nanotechnology 15:189–191
Yin AJ, Li J, Jian W, Bennett AJ, Xua JM (2001) Fabrication of highly ordered metallic nanowire arrays by electrodeposition. Appl Phys Lett 79:1039–1041
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, CK., Liu, T.Y. & Chang, W.T. Effect of oxalic acid concentration on the formation of anodic aluminum oxide using pulse anodization at room temperature. Microsyst Technol 16, 1451–1456 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-009-0944-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-009-0944-9