Abstract
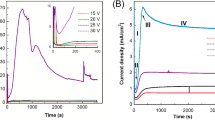
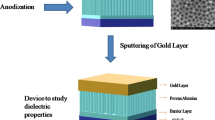
Nanoporous anodic alumina were fabricated by using aqueous oxalic acid electrolyte via the simple and convenient electrochemical anodization method. The pore formation resulted from the interaction of surface aluminum with the prepared electrolyte of 0.3M oxalic acid having pH value less than 5. The phase purity and the morphology of the prepared porous alumina were studied by using X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy respectively. Before pore widening, aluminum oxide nanopores of average pore size ~ 40 nm were obtained. However, after pore widening, nanopores of average pore size ~ 64 nm were obtained. For proper understanding of the formation of porous alumina nanopores, formation mechanism was discussed in detail by using current density–time spectra.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
An YY, Wang J, Zhou WM, Jin HX, Li JF, Wang CW (2018) The preparation of high quality alumina defective photonic crystals and their application of photoluminescence enhancement. Superlattices Microstruct 119:1–8
Ateş S, Baran E (2018) The nanoporous anodic alumina oxide formed by two-step anodization. Thin Solid Films 648:94–102
Bocchetta P, Santamaria M, Di Quarto F (2008) Electrosynthesis of Ce–Co mixed oxide nanotubes with high aspect ratio and tunable composition. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 11:K27–K30
Brevnov DA, Barela MJ, Brooks MJ, López GP, Atanassov PB (2004) Fabrication of anisotropic super hydrophobic/hydrophilic nanoporous membranes by plasma polymerization of C 4 F 8 on anodic aluminum oxide. J Electrochem Soc 151(8):B484–B489
Chahrour KM, Ahmed NM, Hashim MR, Elfadill NG, Maryam W, Ahmad MA, Bououdina M (2015) Effects of the voltage and time of anodization on modulation of the pore dimensions of AAO films for nanomaterials synthesis. Superlattices Microstruct 88:489–500
Chen W, Wu JS, Xia XH (2008) Porous anodic alumina with continuously manipulated pore/cell size. ACS Nano 2(5):959–965
Dar FA, Shah MA (2018a) Low temperature fabrication of Al2O3 nanostrips and their enhanced dielectric property. Mater Res Express 5(1):015048
Dar FA, Shah MA (2018b) Structural, morphological and dielectric properties of Li-doped Al2O3. Appl Phys A 124(7):513
Diggle JW, Downie TC, Goulding CW (1969) Anodic oxide films on aluminum. Chem Rev 69(3):365–405
Ding GQ, Zheng MJ, Xu WL, Shen WZ (2005) Fabrication of controllable free-standing ultrathin porous alumina membranes. Nanotechnology 16(8):1285
Domanska MM, Stepniowski WJ, Salerno M (2018) Effect of inter-electrode separation in the fabrication of nanoporous alumina by anodization. J Electroanal Chem 823:47–53
Garcia-Vergara SJ, Iglesias-Rubianes L, Blanco-Pinzon CE, Skeldon P, Thompson GE, Campestrini P (2006) Mechanical instability and pore generation in anodic alumina. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A: mathematical, physical and engineering sciences, vol 462, no 2072. The Royal Society, London, pp 2345–2358
Jani AMM, Losic D, Voelcker NH (2013) Nanoporous anodic aluminium oxide: advances in surface engineering and emerging applications. Prog Mater Sci 58(5):636–704
Kasi AK, Kasi JK, Bokhari M (2018) Fabrication of mechanically stable AAO membrane with improved fluid permeation properties. Microelectron Eng 187:95–100
Lee W, Park SJ (2014) Porous anodic aluminum oxide: anodization and templated synthesis of functional nanostructures. Chem Rev 114(15):7487–7556
Lillo M, Losic D (2009a) Ion-beam pore opening of porous anodic alumina: the formation of single nanopore and nanopore arrays. Mater Lett 63(3–4):457–460
Lillo M, Losic D (2009b) Pore opening detection for controlled dissolution of barrier oxide layer and fabrication of nanoporous alumina with through-hole morphology. J Membr Sci 327(1–2):11–17
Macias G, Hernández-Eguía LP, Ferré-Borrull J, Pallares J, Marsal LF (2013) Gold-coated ordered nanoporous anodic alumina bilayers for future label-free interferometric biosensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(16):8093–8098
Masuda H, Fukuda K (1995) Ordered metal nanohole arrays made by a two-step replication of honeycomb structures of anodic alumina. Science 268(5216):1466–1468
Masuda H, Satoh M (1996) Fabrication of gold nanodot array using anodic porous alumina as an evaporation mask. Jpn J Appl Phys 35(1B):L126
Naikoo GA, Dar RA, Khan F (2014) Hierarchically macro/mesostructured porous copper oxide: facile synthesis, characterization, catalytic performance and electrochemical study of mesoporous copper oxide monoliths. J Mater Chem A 2(30):11792–11798
Naikoo GA, Dar RA, Thomas M, Sheikh MUD, Khan F (2015) Hierarchically porous metallic silver monoliths: facile synthesis, characterization and its evaluation as an electrode material for supercapacitors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26(4):2403–2410
Najma B, Kasi AK, Kasi JK, Akbar A, Bokhari SMA, Stroe IR (2018) ZnO/AAO photocatalytic membranes for efficient water disinfection: synthesis, characterization and antibacterial assay. Appl Surf Sci 448:104–114
Ono S, Masuko N (2003) Evaluation of pore diameter of anodic porous films formed on aluminum. Surf Coat Technol 169:139–142
Patermarakis G (1998) Development of a theory for the determination of the composition of the anodizing solution inside the pores during the growth of porous anodic Al2O3 films on aluminium by a transport phenomenon analysis. J Electroanal Chem 447(1–2):25–41
Patermarakis G (2009) The origin of nucleation and development of porous nanostructure of anodic alumina films. J Electroanal Chem 635(1):39–50
Poinern GEJ, Ali N, Fawcett D (2011) Progress in nano-engineered anodic aluminum oxide membrane development. Materials 4(3):487–526
Romero V, Vega V, García J, Prida VM, Hernando B, Benavente J (2012) Ionic transport across tailored nanoporous anodic alumina membranes. J Colloid Interface Sci 376(1):40–46
Shawaqfeh AT, Baltus RE (1999) Fabrication and characterization of single layer and multi-layer anodic alumina membranes. J Membr Sci 157(2):147–158
Song M, Zhou X, He X, Cao H, Liu J, Qiu H, Jin Z (2018) Distance dependent fluorescence enhancement of silver nanowires deposited on AAO. Opt Mater 83:241–244
Stępniowski WJ, Bojar Z (2011) Synthesis of anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) at relatively high temperatures. Study of the influence of anodization conditions on the alumina structural features. Surf Coat Technol 206(2–3):265–272
Sulka GD (2008) Highly ordered anodic porous alumina formation by self-organized anodizing. Nanostruct Mater Electrochem 1:1–116
Vorozhtsova M, Drbohlavova J, Hubalek J (2011) Chemical microsensors with ordered nanostructures. In: Microsensors. https://doi.org/10.5772/18066
Vrublevsky I, Jagminas A, Schreckenbach J, Goedel WA (2007) Electronic properties of electrolyte/anodic alumina junction during porous anodizing. Appl Surf Sci 253(10):4680–4687
Wang Q, Long Y, Sun B (2013) Fabrication of highly ordered porous anodic alumina membrane with ultra-large pore intervals in ethylene glycol-modified citric acid solution. J Porous Mater 20(4):785–788
Wu L, Zhang H, Qin F, Bai X, Ji Z, Huang D (2017) Performance enhancement of pc-Si solar cells through combination of anti-reflection and light-trapping: functions of AAO nano-grating. Opt Commun 385:205–212
Zaraska L, Sulka GD, Jaskuła M (2010a) The effect of n-alcohols on porous anodic alumina formed by self-organized two-step anodizing of aluminum in phosphoric acid. Surf Coat Technol 204(11):1729–1737
Zaraska L, Sulka GD, Szeremeta J, Jaskuła M (2010b) Porous anodic alumina formed by anodization of aluminum alloy (AA1050) and high purity aluminum. ElectrochimicaActa 55(14):4377–4386
Zaraska L, Stępniowski WJ, Ciepiela E, Sulka GD (2013) The effect of anodizing temperature on structural features and hexagonal arrangement of nanopores in alumina synthesized by two-step anodizing in oxalic acid. Thin Solid Films 534:155–161
Zaraska L, Stępniowski WJ, Jaskuła M, Sulka GD (2014) Analysis of nanopore arrangement of porous alumina layers formed by anodizing in oxalic acid at relatively high temperatures. Appl Surf Sci 305:650–657
Zhang R, Jiang K, Ding G (2010) Surface morphology control on porous anodic alumina in phosphoric acid. Thin Solid Films 518(14):3797–3800
Zhao Y, Chen M, Zhang Y, Xu T, Liu W (2005) A facile approach to formation of through-hole porous anodic aluminum oxide film. Mater Lett 59(1):40–43
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly thankful to NIT Srinagar, IIT Kanpur, and Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, for providing experimental facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mir, M.A., Shah, M.A. & Ganai, P.A. Effect of Etching on Nanoporous Anodic Alumina. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 43, 2651–2655 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-019-00708-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-019-00708-2