Abstract
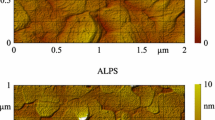
Ambient pressure plasma processes were applied for surface activation of semiconductor (Si, Ge and GaAs) and other wafers (glass) before direct wafer bonding for MEMS and engineered substrates. Surface properties of activated wafers were analysed. Caused by activation high bond energies were obtained for homogeneous (e.g. Si/Si) as well as for heterogeneous material combinations (for instance Si/Ge) after a subsequent low temperature annealing process at 200°C. The resulting bond energies are analogous or higher as obtained for low-pressure plasma activation processes. The advantages of the ambient pressure plasma processes are described; a technical solution is discussed demonstrating the low risk for contamination and radiation damage.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSOI:
-
Strained silicon-on-insulator
- SOI:
-
Silicon-on-insulator
- MEMS:
-
Micro-electro-mechanical-system
- CMOS:
-
Complementary metal oxide semiconductor
- GeOI:
-
Germanium-on-insulator
- AP:
-
Ambient pressure plasma
- LP:
-
Low-pressure plasma
- PE-CVD:
-
Plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition
- DBD:
-
Dielectric barrier discharge
- SAM:
-
Scanning acoustic microscopy
- AFM:
-
Atomic force microscopy
References
Alexe M, Dragoi V, Reiche M, Gösele U (2000) Electron Lett 36:677
Baravian G, Chaleix D, Choquet P, Nauche PL, Puech V, Rozoy M (1999) Surf Cat Technol 155:66
Eliasson B, Kogelschatz U (1991) Modelling and applications of silent discharge plasmas. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 19:309–323
Farrens SN, Dekker JR, Smith JK, Roberds BE (1995) J Electrochem Soc 142:3949
Kissinger G, Kissinger W (1993) Sens Actuators A36:149
Klages C-P, Eichler M (2002) Vakuum in Forschung Praxis 14:149
Niklaus F, Enoksson P, Griß P, Kälvesten E, Stemme G (2001) IEEE J Microelectromec Syst 10:525
Sanz-Velasco A (2002) The RDGT-integration of micromechanics and electronics by plasma assisted wafer bonding. PhD Thesis, Chalmers University, Göteborg
Steinkirchner J, Martini T, Reiche M, Kästner G, Gösele U (1995) Adv Mater 7:662
Thyen R, Höpfner K, Kläke N, Klages C-P (2000) In: Proceedings of the international symposium on high pressure and low temperature plasma chemistry (HAKONE VII), Greifswald
Weichel S, de Reus R, Lindahl M (1998) Sens Actuators A70:179
Wiegand M (2001) Effect of a plasma treatment on the properties of low-temperature wafer bonding of single-crystalline silicon. PhD Thesis, University of Halle
Wiegand M, Reiche M, Gösele U (2000) J Electrochem Soc 147:2734
Zucker O, Langheinrich W, Kulozik M, Goebel H (1993) Sens Actuators A36:227
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabriel, M., Johnson, B., Suss, R. et al. Wafer direct bonding with ambient pressure plasma activation. Microsyst Technol 12, 397–400 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-005-0044-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-005-0044-4