Abstract
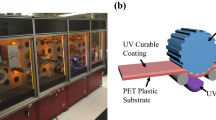
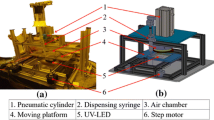
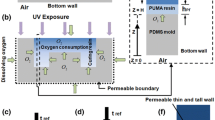
In ultraviolet (UV) embossing, a substrate with a coating of liquid or semi-solid UV curable resin mix is pressed against a patterned embossing mold. The resin mix is irradiated with UV before demolding of the hardened microstructures. UV embossing can be done at room temperature and low pressure. However, demolding of UV embossed high aspect ratio microstructures from a metallic mold is typically difficult since there is no differential thermal contraction between the mold and the embossing. Several factors have been identified to influence demolding of UV embossed microstructures: (1) Roughness of mold, (2) Taper angle of microstructures of mold, (3) Chemical interaction between mold and embossing, (4) Tensile and crosslinking shrinkage properties of the irradiated resin and (5) Uniformity of crosslinking process through the thickness of the molded microstructures. By controlling these five parameters, a microarray with an aspect ratio of 5 was demonstrated using a Formulation containing epoxy acrylate, Irgacure® 651, silicone acrylate and other acrylates. The embossed microstructures replicated the features of the mold very well. It was also shown that by controlling the amount of irradiation, the tensile modulus of the UV formulation increased whilst the elongation decreased. An optimum irradiation is needed for clean demolding from the mold without microcracking.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by a Strategic Development Scheme fund (SDS 15/2001) from the Nanyang Technological University. The authors also acknowledge the kind contributions of chemicals by UCB Chemicals, Sartomer, Henkel (Singapore), Dupont (Singapore) and Ciba Chemicals and a microstructured mold by Dr R. C. Liang of SiPix Imaging (CA, USA). The second author acknowledges the financial support of Nanyang Technological University through a Research Scholarship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan-Park, M., Neo, W. Ultraviolet embossing for patterning high aspect ratio polymeric microstructures. Microsystem Technologies 9, 501–506 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-002-0289-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-002-0289-0