Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to investigate the association between the Oxygen Reserve index (ORi) and arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) during one-lung ventilation in patients who underwent non-cardiac thoracic surgery requiring one-lung ventilation.
Methods
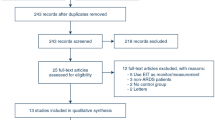
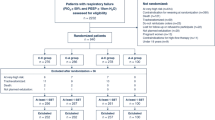
This retrospective study assessed the eligibility of 578 adult patients who underwent elective non-cardiac thoracic surgery requiring one-lung ventilation at a tertiary hospital, and their electronic medical records were reviewed. The ORi monitor was used in all patients during anesthesia, and arterial blood gas analysis was routinely performed 15 min after the initiation of one-lung ventilation. The primary endpoint was the association between ORi and PaO2 which were measured simultaneously during one-lung ventilation. We also investigated the risk factors for PaO2 less than 150 mmHg during one-lung ventilation.
Results
Total of 554 patient were included in the analysis. The ORi value measured 15 min after the start of one-lung ventilation was significantly associated with PaO2 in the linear regression model (r2 = 0.5752, P < 0.001), and 0.27 of the ORi value could distinguish PaO2 ≥ 150 mmHg (sensitivity 0.909, specificity 0.932). Risk factors for PaO2 < 150 mmHg during one-lung ventilation included a lower ORi, older age, higher body mass index, left-sided one-lung ventilation, and lower hemoglobin concentrations.
Conclusion
This study suggested that ORi could provide useful information on arterial oxygenation even during one-lung ventilation for non-cardiac thoracic surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Edmark L, Auner U, Lindbäck J, Enlund M, Hedenstierna G. Post-operative atelectasis - a randomised trial investigating a ventilatory strategy and low oxygen fraction during recovery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2014;58(6):681–8.
Yang M, Kim JA, Ahn HJ, Choi YS, Park M, Jeong H, Kim K, Lee NY. Continuous Titration of Inspired Oxygen Using Oxygen Reserve Index to Decrease Oxygen Exposure During One-lung Ventilation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesth Analg. 2022;135(1):91–9.
Ishida Y, Okada T, Kobayashi T, Uchino H. ORI™: A new indicator of oxygenation. J Anesth. 2021;35(5):734–40.
Scheeren TWL, Belda FJ, Perel A. The oxygen reserve index (ORI): A new tool to monitor oxygen therapy. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018;32(3):379–89.
Sagiroglu G, Baysal A, Karamustafaoglu YA. The use of oxygen reserve index in one-lung ventilation and its impact on peripheral oxygen saturation, perfusion index and pleth variability index. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021;21(1):319.
Alday E, Nieves JM, Planas A. Oxygen Reserve Index Predicts Hypoxemia During One-Lung Ventilation: An Observational Diagnostic Study. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020;34(2):417–22.
Koishi W, Kumagai M, Ogawa S, Hongo S, Suzuki K. Monitoring the Oxygen Reserve Index can contribute to the early detection of deterioration in blood oxygenation during one-lung ventilation. Minerva Anestesiol. 2018;84(9):1063–9.
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (strobe) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. 2007;370(9596):1453–7.
Guenoun T, Journois D, Silleran-Chassany J, Frappier J, D’Attellis N, Salem A, Safran D. Prediction of arterial oxygen tension during one-lung ventilation: Analysis of preoperative and intraoperative variables. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2002;16(2):199–203.
Applegate RL, Dorotta IL, Wells B, Juma D, Applegate PM. The Relationship Between Oxygen Reserve Index and Arterial Partial Pressure of Oxygen During Surgery. Anesth Analg. 2016;123(3):626.
Sylvester JT, Shimoda LA, Aaronson PI, Ward JP. Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Physiol Rev. 2012;92(1):367–520.
Cho YJ, Kim TK, Hong DM, Seo JH, Bahk JH, Jeon Y. Effect of desflurane-remifentanil vs. Propofol-remifentanil anesthesia on arterial oxygenation during one-lung ventilation for thoracoscopic surgery: a prospective randomized trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017;17(1):9.
Yao HY, Liu TJ, Lai HC. Risk factors for intraoperative hypoxemia during monopulmonary ventilation: an observational study. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2019;69(4):390–5.
Karzai W, Schwarzkopf K. Hypoxemia during one-lung ventilation: Prediction, prevention, and treatment. Anesthesiology. 2009;110(6):1402–11.
Vos JJ, Willems CH, van Amsterdam K, van den Berg JP, Spanjersberg R, Struys MM, Scheeren TW. Oxygen Reserve Index: Validation of a New Variable. Anesth Analg. 2019;129(2):409–15.
Cheng H-W, Yeh C-Y, Chang M-Y, Ting C-K, Chang P-L. How early warning with the Oxygen Reserve Index (ORI™) can improve the detection of desaturation during induction of general anesthesia? J Clin Monit Comput. 2022;36(5):1379–85.
Yoshida K, Isosu T, Noji Y, Ebana H, Honda J, Sanbe N, Obara S, Murakawa M. Adjustment of Oxygen Reserve Index (ORI™) to avoid excessive hyperoxia during general anesthesia. J Clin Monit Comput. 2020;34:509–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Bang, Y.J., Seong, Y. & Jeong, H. Association between Oxygen Reserve index and arterial partial pressure of oxygen during one-lung ventilation: a retrospective cohort study. J Anesth 37, 938–944 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-023-03259-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-023-03259-4