Abstract:
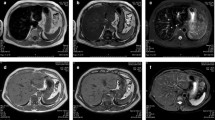
We describe liver fibrosis caused by iron overload after a long history of blood transfusion in a patient with chronic renal failure. Pertinent laboratory data were: serum (s)-Fe 148 μg/dl; unsaturated iron binding capacity (UIBC) 14 μg/dl; s-ferritin 9350 ng/ml; human leukocyte antigen (HLA) A2, A24, B39, B55, Cw1, Cw7. Computed tomography revealed a high density in the liver, and laparoscopy revealed a brown liver. Liver histology showed bridging fibrosis from portal tracts. A heavy iron deposit was seen in Kupffer cells as well as in hepatocytes surrounded by fibrosis around the portal tracts. Immunocytochemistry revealed α-smooth muscle actin in many stellate cells distributed along the fibrotic area, and electron microscopy revealed infiltrating myofibroblastic stellate cells coexisting with collagen fibers around degenerated hepatocytes containing iron deposits. The findings are consistent with the notion that stellate cells play an important role in liver fibrogenesis in both genetic and transfusional iron overload hemochromatosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received Aug. 15, 1997; accepted Feb. 27, 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harada, Y., Iwai, M., Kakusui, M. et al. Activated hepatic stellate cells participate in liver fibrosis in a patient with transfusional iron overload. J Gastroenterol 33, 751–754 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350050168
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350050168