Abstract
Epigenetic modification occurring in RNA has become the hotspot of the field. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation is the most abundant RNA internal modification mainly occurring at the consensus motif DR (m6A) CH (D = A/G/U, R = A/G, H = A/C/U) in the 3’-UTR particularly the region near stop codons. The life cycle of m6A methylation includes “writers,” “erasers,” and “readers”, which are responsible for the addition, removal, and recognition of m6A, respectively. m6A modification has been reported changing RNA secondary structure or modulating the stability, localization, transport, and translation of mRNAs to play crucial roles in various physiological and pathological conditions. Liver, as the largest metabolic and digestive organ, modulates vital physiological functions, and its dysfunction gives rise to the occurrence of various diseases. Despite the advanced intervening measures, mortality due to liver diseases is continuously high. Recent studies have explored the roles of m6A RNA methylation in the pathogenesis of liver diseases, providing new insights for studying the molecular mechanism of liver diseases. In the review, we extensively summarize the life cycle of m6A methylation, as well as its function and relevant mechanisms in liver fibrosis (LF), nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), hepatitis virus infection, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and eventually we explore the potential of m6A as a treatment option for these liver diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–6.
Saneyoshi M, Harada F, Nishimura S. Isolation and characterization of N6-methyladenosine from Escherichia coli valine transfer RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;190:264–73.
Iwanami Y, Brown GM. Methylated bases of ribosomal ribonucleic acid from HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968;126:8–15.
Yang Y, Fan X, Mao M, et al. Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N(6)-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 2017;27:626–41.
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, et al. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149:1635–46.
Bokar JA, Shambaugh ME, Polayes D, et al. Purification and cDNA cloning of the AdoMet-binding subunit of the human mRNA (N6-adenosine)-methyltransferase. RNA. 1997;3:1233–47.
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, et al. A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10:93–5.
Wang P, Doxtader KA, Nam Y. Structural basis for cooperative function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 methyltransferases. Mol Cell. 2016;63:306–17.
Ping XL, Sun BF, Wang L, et al. Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res. 2014;24:177–89.
Warda AS, Kretschmer J, Hackert P, et al. Human METTL16 is a N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) methyltransferase that targets pre-mRNAs and various non-coding RNAs. EMBO Rep. 2017;18:2004–14.
Ma H, Wang X, Cai J, et al. N(6-)methyladenosine methyltransferase ZCCHC4 mediates ribosomal RNA methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:88–94.
van Tran N, Ernst FGM, Hawley BR, et al. The human 18S rRNA m6A methyltransferase METTL5 is stabilized by TRMT112. Nucl Acids Res. 2019;47:7719–33.
Peng H, Chen B, Wei W, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) in 18S rRNA promotes fatty acid metabolism and oncogenic transformation. Nat Metab. 2022;4:1041–54.
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7:885–7.
Linder B, Grozhik AV, Olarerin-George AO, et al. Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat Methods. 2015;12:767–72.
Wei J, Liu F, Lu Z, et al. Differential m(6)A, m(6)Am, and m(1)A demethylation mediated by FTO in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. Mol Cell. 2018;71(973–85): e5.
Fu Y, Jia G, Pang X, et al. FTO-mediated formation of N6-hydroxymethyladenosine and N6-formyladenosine in mammalian RNA. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1798.
Wang T, Kong S, Tao M, et al. The potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in Cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:88.
Huang H, Weng H, Chen J. m(6)A modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: roles and therapeutic implications in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2020;37:270–88.
Shi H, Wei J, He C. Where, when, and how: context-dependent functions of RNA methylation writers, readers, and erasers. Mol Cell. 2019;74:640–50.
Liu T, Wei Q, Jin J, et al. The m6A reader YTHDF1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via augmenting EIF3C translation. Nucl Acids Res. 2020;48:3816–31.
Zhuang M, Li X, Zhu J, et al. The m6A reader YTHDF1 regulates axon guidance through translational control of Robo3.1 expression. Nuc Acids Res. 2019;47:4765–77.
Zhou J, Wan J, Gao X, et al. Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation directs translational control of heat shock response. Nature. 2015;526:591–4.
Du H, Zhao Y, He J, et al. YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12626.
Shi H, Wang X, Lu Z, et al. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N(6)-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 2017;27:315–28.
Li A, Chen YS, Ping XL, et al. Cytoplasmic m(6)A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Res. 2017;27:444–7.
Roundtree IA, Luo GZ, Zhang Z, et al. YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N(6)-methyladenosine methylated mRNAs. Elife. 2017;6.
Mao Y, Dong L, Liu XM, et al. m(6)A in mRNA coding regions promotes translation via the RNA helicase-containing YTHDC2. Nat Commun. 2019;10:5332.
Liu N, Dai Q, Zheng G, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent RNA structural switches regulate RNA-protein interactions. Nature. 2015;518:560–4.
Zhou KI, Shi H, Lyu R, et al. Regulation of co-transcriptional pre-mRNA splicing by m(6)A through the low-complexity protein hnRNPG. Mol Cell. 2019;76(70–81): e9.
Alarcon CR, Goodarzi H, Lee H, et al. HNRNPA2B1 is a mediator of m(6)A-dependent nuclear RNA processing events. Cell. 2015;162:1299–308.
Meyer KD, Patil DP, Zhou J, et al. 5’ UTR m(6)A promotes cap-independent translation. Cell. 2015;163:999–1010.
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, et al. Recognition of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:285–95.
He PC, He C. m(6) A RNA methylation: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential. EMBO J. 2021;40: e105977.
Friedman SL. Liver fibrosis—from bench to bedside. J Hepatol. 2003;38(Suppl 1):S38-53.
Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:209–18.
Cui Z, Huang N, Liu L, et al. Dynamic analysis of m6A methylation spectroscopy during progression and reversal of hepatic fibrosis. Epigenomics. 2020;12:1707–23.
Fan C, Ma Y, Chen S, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the transcriptome-wide m6A methylation modification difference in liver fibrosis mice by high-throughput m6A sequencing. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 767051.
Wang Y, Zhao Y, Wang Z, et al. Peroxiredoxin 3 inhibits acetaminophen-induced liver pyroptosis through the regulation of mitochondrial ROS. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 652782.
Geng Y, Wang Y, Sun R, et al. Carnosol alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis through targeting of PRDX3. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021;432: 115758.
Sun R, Tian X, Li Y, et al. The m6A reader YTHDF3-mediated PRDX3 translation alleviates liver fibrosis. Redox Biol. 2022;54: 102378.
Yang JJ, Wang J, Yang Y, et al. ALKBH5 ameliorated liver fibrosis and suppressed HSCs activation via triggering PTCH1 activation in an m(6)A dependent manner. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;922: 174900.
Shen M, Guo M, Li Y, et al. m(6)A methylation is required for dihydroartemisinin to alleviate liver fibrosis by inducing ferroptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;182:246–59.
Shen M, Li Y, Wang Y, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modification regulates ferroptosis through autophagy signaling pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Redox Biol. 2021;47: 102151.
Zhao T, Qi J, Liu T, et al. N6-methyladenosine modification participates in the progression of hepatitis B virus-related liver fibrosis by regulating immune cell infiltration. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9: 821710.
Shu B, Zhou YX, Li H, et al. The METTL3/MALAT1/PTBP1/USP8/TAK1 axis promotes pyroptosis and M1 polarization of macrophages and contributes to liver fibrosis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7:368.
Luo Y, Zhang Z, Xiang L, et al. Analysis of N6-methyladenosine methylation modification in fructose-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12: 780617.
Zhong X, Yu J, Frazier K, et al. Circadian clock regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism by modulation of m(6)A mRNA methylation. Cell Rep. 2018;25(1816–28): e4.
Feng Y, Dong H, Sun B, et al. METTL3/METTL14 Transactivation and m(6)A-dependent TGF-beta1 translation in activated kupffer cells. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12:839–56.
Kang H, Zhang Z, Yu L, et al. FTO reduces mitochondria and promotes hepatic fat accumulation through RNA demethylation. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:5676–85.
Guo J, Ren W, Li A, et al. Fat mass and obesity-associated gene enhances oxidative stress and lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:1004–9.
Hu Y, Feng Y, Zhang L, et al. GR-mediated FTO transactivation induces lipid accumulation in hepatocytes via demethylation of m(6)A on lipogenic mRNAs. RNA Biol. 2020;17:930–42.
Li Y, Zhang Q, Cui G, et al. m(6)A regulates liver metabolic disorders and hepatogenous diabetes. Genom Proteom Bioinform. 2020;18:371–83.
Qin Y, Li B, Arumugam S, et al. m(6)A mRNA methylation-directed myeloid cell activation controls progression of NAFLD and obesity. Cell Rep. 2021;37: 109968.
Zhou B, Liu C, Xu L, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine reader protein YT521-B homology domain-containing 2 suppresses liver steatosis by regulation of mRNA stability of lipogenic genes. Hepatology. 2021;73:91–103.
Peneau C, Imbeaud S, La Bella T, et al. Hepatitis B virus integrations promote local and distant oncogenic driver alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2022;71:616–26.
Li TY, Yang Y, Zhou G, et al. Immune suppression in chronic hepatitis B infection associated liver disease: a review. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25:3527–37.
Kim GW, Siddiqui A. Hepatitis B virus X protein recruits methyltransferases to affect cotranscriptional N6-methyladenosine modification of viral/host RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118.
Kim GW, Imam H, Siddiqui A. The RNA binding proteins YTHDC1 and FMRP regulate the nuclear export of N(6)-methyladenosine-modified hepatitis B virus transcripts and affect the viral life cycle. J Virol. 2021;95: e0009721.
Imam H, Khan M, Gokhale NS, et al. N6-methyladenosine modification of hepatitis B virus RNA differentially regulates the viral life cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:8829–34.
Kim GW, Moon JS, Siddiqui A. N6-methyladenosine modification of the 5' epsilon structure of the HBV pregenome RNA regulates its encapsidation by the viral core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022;119.
Kim GW, Siddiqui A. Hepatitis B virus X protein expression is tightly regulated by N6-methyladenosine modification of its mRNA. J Virol. 2022;96: e0165521.
Kim GW, Imam H, Khan M, et al. HBV-induced increased N6 methyladenosine modification of PTEN RNA affects innate immunity and contributes to HCC. Hepatology. 2021;73:533–47.
Kim GW, Imam H, Khan M, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modification of hepatitis B and C viral RNAs attenuates host innate immunity via RIG-I signaling. J Biol Chem. 2020;295:13123–33.
Imam H, Kim GW, Mir SA, et al. Interferon-stimulated gene 20 (ISG20) selectively degrades N6-methyladenosine modified Hepatitis B Virus transcripts. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16: e1008338.
Qu S, Jin L, Huang H, et al. A positive-feedback loop between HBx and ALKBH5 promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis. BMC Cancer. 2021;21:686.
Tao L, Li D, Mu S, et al. LncRNA MAPKAPK5_AS1 facilitates cell proliferation in hepatitis B virus -related hepatocellular carcinoma. Lab Invest. 2022;102:494–504.
Rao X, Lai L, Li X, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modification of circular RNA circ-ARL3 facilitates Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma via sponging miR-1305. IUBMB Life. 2021;73:408–17.
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology. 2018;67:2254–70.
Lin X, Chai G, Wu Y, et al. RNA m(6)A methylation regulates the epithelial mesenchymal transition of cancer cells and translation of Snail. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2065.
Qiao K, Liu Y, Xu Z, et al. RNA m6A methylation promotes the formation of vasculogenic mimicry in hepatocellular carcinoma via Hippo pathway. Angiogenesis. 2021;24:83–96.
Xu H, Wang H, Zhao W, et al. SUMO1 modification of methyltransferase-like 3 promotes tumor progression via regulating Snail mRNA homeostasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics. 2020;10:5671–86.
Chen Y, Peng C, Chen J, et al. WTAP facilitates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic silencing of ETS1. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:127.
Chou J, Lin JH, Brenot A, et al. GATA3 suppresses metastasis and modulates the tumour microenvironment by regulating microRNA-29b expression. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15:201–13.
Lan T, Li H, Zhang D, et al. KIAA1429 contributes to liver cancer progression through N6-methyladenosine-dependent post-transcriptional modification of GATA3. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:186.
Liu X, Liu J, Xiao W, et al. SIRT1 Regulates N(6)-methyladenosine RNA modification in hepatocarcinogenesis by inducing RANBP2-dependent FTO SUMOylation. Hepatology. 2020;72:2029–50.
Chen Y, Zhao Y, Chen J, et al. ALKBH5 suppresses malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma via m(6)A-guided epigenetic inhibition of LYPD1. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:123.
Zhang C, Huang S, Zhuang H, et al. YTHDF2 promotes the liver cancer stem cell phenotype and cancer metastasis by regulating OCT4 expression via m6A RNA methylation. Oncogene. 2020;39:4507–18.
Zhong L, Liao D, Zhang M, et al. YTHDF2 suppresses cell proliferation and growth via destabilizing the EGFR mRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019;442:252–61.
Ma Y, Han CC, Li Y, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 inhibits IGF-1-induced proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by controlling bFGF and PDGF autocrine/paracrine loops. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;478:964–9.
Nguyen LH, Robinton DA, Seligson MT, et al. Lin28b is sufficient to drive liver cancer and necessary for its maintenance in murine models. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:248–61.
Ma JZ, Yang F, Zhou CC, et al. METTL14 suppresses the metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent primary MicroRNA processing. Hepatology. 2017;65:529–43.
Zuo X, Chen Z, Gao W, et al. M6A-mediated upregulation of LINC00958 increases lipogenesis and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:5.
Xia A, Yuan W, Wang Q, et al. The cancer-testis lncRNA lnc-CTHCC promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis by binding hnRNP K and activating YAP1 transcription. Nat Cancer. 2022;3:203–18.
Chen YT, Xiang D, Zhao XY, et al. Upregulation of lncRNA NIFK-AS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma by m(6)A methylation promotes disease progression and sorafenib resistance. Hum Cell. 2021;34:1800–11.
Peng L, Pan B, Zhang X, et al. Lipopolysaccharide facilitates immune escape of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via m6A modification of lncRNA MIR155HG to upregulate PD-L1 expression. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022.
Liang W, Wang Y, Zhang Q, et al. M(6)A-mediated upregulation of LINC00106 promotes stemness and metastasis properties of hepatocellular carcinoma via sponging Let7f. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 781867.
Dai YZ, Liu YD, Li J, et al. METTL16 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through downregulating RAB11B-AS1 in an m(6)A-dependent manner. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27:41.
Rong D, Wu F, Lu C, et al. m6A modification of circHPS5 and hepatocellular carcinoma progression through HMGA2 expression. Mol Ther Nucl Acids. 2021;26:637–48.
Du A, Li S, Zhou Y, et al. M6A-mediated upregulation of circMDK promotes tumorigenesis and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:109.
Liu H, Lan T, Li H, et al. Circular RNA circDLC1 inhibits MMP1-mediated liver cancer progression via interaction with HuR. Theranostics. 2021;11:1396–411.
Chen Y, Ling Z, Cai X, et al. Activation of YAP1 by N6-methyladenosine-modified circCPSF6 drives malignancy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2022;82:599–614.
Duan JL, Chen W, Xie JJ, et al. A novel peptide encoded by N6-methyladenosine modified circMAP3K4 prevents apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:93.
Wu A, Hu Y, Xu Y, et al. Methyltransferase-like 3-mediated m6A methylation of Hsa_circ_0058493 accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by binding to YTH domain-containing protein 1. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 762588.
Liu L, Gu M, Ma J, et al. CircGPR137B/miR-4739/FTO feedback loop suppresses tumorigenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:149.
Qu N, Bo X, Li B, et al. Role of N6-methyladenosine (m(6)A) methylation regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 755206.
Bo C, Li N, He L, et al. Long non-coding RNA ILF3-AS1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by stabilizing ILF3 mRNA in an m(6)A-dependent manner. Hum Cell. 2021;34:1843–54.
Chen F, Li M, Wang L. LncRNA CASC11 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via upregulation of UBE2T in a m(6)A-dependent manner. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 772671.
Chen J, Zhou X, Wu W, et al. FTO-dependent function of N6-methyladenosine is involved in the hepatoprotective effects of betaine on adolescent mice. J Physiol Biochem. 2015;71:405–13.
Dang Y, Hao S, Zhou W, et al. The traditional Chinese formulae Ling-gui-zhu-gan decoction alleviated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via inhibiting PPP1R3C mediated molecules. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19:8.
Liu T, Yang LL, Zou L, et al. Chinese medicine formula lingguizhugan decoction improves beta-oxidation and metabolism of fatty acid in high-fat-diet-induced rat model of fatty liver disease. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013: 429738.
Dang Y, Xu J, Yang Y, et al. Ling-gui-zhu-gan decoction alleviates hepatic steatosis through SOCS2 modification by N6-methyladenosine. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127: 109976.
Chen YW, Liu BW, Zhang YJ, et al. Preservation of basal AcSDKP attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced fibrosis in the rat liver. J Hepatol. 2010;53:528–36.
Wei A, Zhao F, Hao A, et al. N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline (AcSDKP) mitigates the liver fibrosis via WTAP/m(6)A/Ptch1 axis through Hedgehog pathway. Gene. 2022;813: 146125.
Lu N, Li X, Yu J, et al. Curcumin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic lipid metabolism disorder by modification of m(6) A RNA methylation in piglets. Lipids. 2018;53:53–63.
Peng S, Xiao W, Ju D, et al. Identification of entacapone as a chemical inhibitor of FTO mediating metabolic regulation through FOXO1. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11.
Chen B, Ye F, Yu L, et al. Development of cell-active N6-methyladenosine RNA demethylase FTO inhibitor. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:17963–71.
Li Q, Huang Y, Liu X, et al. Rhein inhibits AlkB repair enzymes and sensitizes cells to methylated DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:11083–93.
Su R, Dong L, Li C, et al. R-2HG exhibits anti-tumor activity by targeting FTO/m(6)A/MYC/CEBPA signaling. Cell. 2018;172(90–105): e23.
Huang Y, Su R, Sheng Y, et al. Small-molecule targeting of oncogenic FTO demethylase in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2019;35(677–91): e10.
Acknowledgements
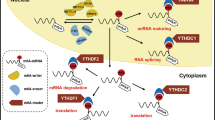
The study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81820108005, 82270551, 81900502), National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2020YFA0710803 and 2017YFA0105704) and Key R&D Program of Shaanxi (No. 2021ZDLSF02-07 and 2022ZDLSF03-03). The Fig. 2 was drawn by Figdraw website (www.figdraw.com).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LY, ST, XZ, and MZ contributed to collection of references and manuscript writing. XZ contributed to manuscript revisions. YH and YS contributed to determining the subject and manuscript revisions. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Tian, S., Zheng, X. et al. N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation in liver diseases: from mechanism to treatment. J Gastroenterol 58, 718–733 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-023-02008-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-023-02008-4