Abstract
Background
Inhibitors of nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway have shown potential anti-tumor activities. However, it is not fully elucidated in gastric cancer.
Methods
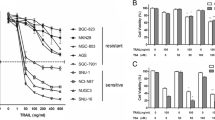
Firstly, we screened the inhibitory effect of pharmacologic NF-κB inhibitors on cell viability of human gastric cancer cells via CCK-8 assay. Next, cell apoptosis, cell cycle distribution, and mitochondrial membrane potential after BAY 11-7082 treatment were detected by annexin V staining, propidium iodide staining, TUNEL, and JC-1 assays in human gastric cancer HGC-27 cells. Expression of regulatory factors for apoptosis and cell cycle were measured by western blot. Finally, human gastric cancer xenograft model was established to verify the anti-tumor effects of BAY 11-7082 in vivo. Cellular apoptosis and growth inhibition in subcutaneous tumor section were detected by TUNEL and immunohistochemistry assays.
Results
BAY 11-7082 exhibited rapid and potent anti-tumor effects on gastric cancer cells in vitro within a panel of NF-κB inhibitors. BAY 11-7082 induced rapid apoptosis in HGC-27 cells through activating the mitochondrial pathway, as well as down-regulation of Bcl-2 and up-regulation of Bax. BAY 11-7082 also induced S phase arrest through suppressing Cyclin A and CDK-2 expression. Xenograft model confirmed the anti-tumor effects of BAY 11-7082 on apoptosis induction and growth inhibition in vivo.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrated that BAY 11-7082 presented the most rapid and potent anti-tumor effects within a panel of NF-κB inhibitors, and could induce cellular apoptosis and block cell cycle progression both in vitro and in vivo, thus providing basis for clinical application of BAY 11-7082 in gastric cancer cases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29.
Washington K. 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual: stomach. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:3077–9.
Oshima T, Masuda M. Molecular targeted agents for gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer. Surg Today. 2012;42:313–27.
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F, Karin M. NF-kappaB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev. 2012;246:379–400.
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR, Li ZW. NF-kappaB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:301–10.
Perkins ND. The diverse and complex roles of NF-kappaB subunits in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:121–32.
Ghosh S, Karin M. Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 2002;109(Suppl):S81–96.
Kanarek N, Ben-Neriah Y. Regulation of NF-kappaB by ubiquitination and degradation of the IkappaBs. Immunol Rev. 2012;246:77–94.
Nakanishi C, Toi M. Nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitors as sensitizers to anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:297–309.
Sasaki N, Morisaki T, Hashizume K, Yao T, Tsuneyoshi M, Noshiro H, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB p65 (RelA) transcription factor is constitutively activated in human gastric carcinoma tissue. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:4136–42.
Wu L, Pu Z, Feng J, Li G, Zheng Z, Shen W. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and enhanced activity of NF-kappaB in gastric carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2008;97:439–44.
Kang MJ, Ryu BK, Lee MG, Han J, Lee JH, Ha TK, et al. NF-kappaB activates transcription of the RNA-binding factor HuR, via PI3 K-AKT signaling, to promote gastric tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:2030–42, 2042.e1–3.
Liu CA, Wang MJ, Chi CW, Wu CW, Chen JY. Rho/Rhotekin-mediated NF-kappaB activation confers resistance to apoptosis. Oncogene. 2004;23:8731–42.
Sakamoto K, Hikiba Y, Nakagawa H, Hayakawa Y, Yanai A, Akanuma M, et al. Inhibitor of kappaB kinase beta regulates gastric carcinogenesis via interleukin-1alpha expression. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(226–238):e226.
Matsumoto Y, Marusawa H, Kinoshita K, Endo Y, Kou T, Morisawa T, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection triggers aberrant expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase in gastric epithelium. Nat Med. 2007;13:470–6.
Liu X, Wang X, Zhang J, Lam EK, Shin VY, Cheng AS, et al. Warburg effect revisited: an epigenetic link between glycolysis and gastric carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2010;29:442–50.
Cho SJ, Park JW, Kang JS, Kim WH, Juhnn YS, Lee JS, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB dependency of doxorubicin sensitivity in gastric cancer cells is determined by manganese superoxide dismutase expression. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:1117–24.
Zanotto-Filho A, Braganhol E, Schroder R, de Souza LH, Dalmolin RJ, Pasquali MA, et al. NFkappaB inhibitors induce cell death in glioblastomas. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;81:412–24.
Meng Z, Lou S, Tan J, Xu K, Jia Q, Zheng W. Nuclear factor-kappa B inhibition can enhance apoptosis of differentiated thyroid cancer cells induced by 131I. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e33597.
Nakabayashi H, Shimizu K. Involvement of Akt/NF-kappaB pathway in antitumor effects of parthenolide on glioblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:453.
Buontempo F, Chiarini F, Bressanin D, Tabellini G, Melchionda F, Pession A, et al. Activity of the selective IkappaB kinase inhibitor BMS-345541 against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: involvement of FOXO3a. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:2467–75.
Singh S, Shi Q, Bailey ST, Palczewski MJ, Pardee AB, Iglehart JD, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB activation: a molecular therapeutic target for estrogen receptor-negative and epidermal growth factor receptor family receptor-positive human breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:1973–82.
Jakubowska-Mucka A, Sienko J, Zapala L, Wolny R, Lasek W. Synergistic cytotoxic effect of sulindac and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate against ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2012;27:1245–50.
Li Q, Yu YY, Zhu ZG, Ji YB, Zhang Y, Liu BY, et al. Effect of NF-kappaB constitutive activation on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cell lines. Eur Surg Res. 2005;37:105–10.
Fujita T, Doihara H, Washio K, Ino H, Murakami M, Naito M, et al. Antitumor effects and drug interactions of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS341) in gastric cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2007;18:677–86.
Zaidi SF, Yamamoto T, Refaat A, Ahmed K, Sakurai H, Saiki I, et al. Modulation of activation-induced cytidine deaminase by curcumin in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. Helicobacter. 2009;14:588–95.
Mino K, Ozaki M, Nakanishi K, Haga S, Sato M, Kina M, et al. Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB suppresses peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer by blocking cancer cell adhesion. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:1052–8.
Sohma I, Fujiwara Y, Sugita Y, Yoshioka A, Shirakawa M, Moon JH, et al. Parthenolide, an NF-kappaB inhibitor, suppresses tumor growth and enhances response to chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2011;8:39–47.
Ruan Y, Sun L, Hao Y, Wang L, Xu J, Zhang W, et al. Ribosomal RACK1 promotes chemoresistance and growth in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:2554–66.
Oliver FJ, de la Rubia G, Rolli V, Ruiz-Ruiz MC, de Murcia G, Murcia JM. Importance of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and its cleavage in apoptosis. Lesson from an uncleavable mutant. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:33533–9.
Lipton SA, Bossy-Wetzel E. Dueling activities of AIF in cell death versus survival: DNA binding and redox activity. Cell. 2002;111:147–50.
Kurokawa M, Kornbluth S. Caspases and kinases in a death grip. Cell. 2009;138:838–54.
Fuchs Y, Steller H. Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell. 2011;147:742–58.
Tait SW, Green DR. Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:621–32.
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR, Berneman ZN. The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 2003;36:131–49.
Fuchs O. Transcription factor NF-kappaB inhibitors as single therapeutic agents or in combination with classical chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2010;3:98–122.
Kim HJ, Hawke N, Baldwin AS. NF-kappaB and IKK as therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:738–47.
Murata T, Shimada M, Kadono H, Sakakibara S, Yoshino T, Masuda T, et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel IKK-beta inhibitors. Part 2: improvement of in vitro activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004;14:4013–7.
Ziegelbauer K, Gantner F, Lukacs NW, Berlin A, Fuchikami K, Niki T, et al. A selective novel low-molecular-weight inhibitor of IkappaB kinase-beta (IKK-beta) prevents pulmonary inflammation and shows broad anti-inflammatory activity. Br J Pharmacol. 2005;145:178–92.
Lam LT, Davis RE, Pierce J, Hepperle M, Xu Y, Hottelet M, et al. Small molecule inhibitors of IkappaB kinase are selectively toxic for subgroups of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma defined by gene expression profiling. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:28–40.
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Hideshima T, Richardson PG, Anderson KC. Proteasome inhibition as a new therapeutic principle in hematological malignancies. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7:1341–7.
Pierce JW, Schoenleber R, Jesmok G, Best J, Moore SA, Collins T, et al. Novel inhibitors of cytokine-induced IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression show anti-inflammatory effects in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:21096–103.
Fernandez-Majada V, Aguilera C, Villanueva A, Vilardell F, Robert-Moreno A, Aytes A, et al. Nuclear IKK activity leads to dysregulated notch-dependent gene expression in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:276–81.
Hernandez-Vargas H, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Julian-Tendero M, Sanchez-Rovira P, Cuevas C, Anton A, et al. Gene expression profiling of breast cancer cells in response to gemcitabine: NF-kappaB pathway activation as a potential mechanism of resistance. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;102:157–72.
Keller SA, Schattner EJ, Cesarman E. Inhibition of NF-kappaB induces apoptosis of KSHV-infected primary effusion lymphoma cells. Blood. 2000;96:2537–42.
Mori N, Yamada Y, Ikeda S, Yamasaki Y, Tsukasaki K, Tanaka Y, et al. Bay 11-7082 inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood. 2002;100:1828–34.
Pickering BM, de Mel S, Lee M, Howell M, Habens F, Dallman CL, et al. Pharmacological inhibitors of NF-kappaB accelerate apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. Oncogene. 2007;26:1166–77.
Catz SD, Johnson JL. Transcriptional regulation of bcl-2 by nuclear factor kappa B and its significance in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2001;20:7342–51.
Luo JL, Kamata H, Karin M. IKK/NF-kappaB signaling: balancing life and death—a new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:2625–32.
Lupino E, Buccinna B, Ramondetti C, Lomartire A, De Marco G, Ricotti E, et al. In CD28-costimulated human naive CD4+ T cells, I-kappaB kinase controls the expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins via interleukin-2-independent mechanisms. Immunology. 2010;131:231–41.
Topping RJ, Jones MM. Optimal dithiocarbamate structure for immunomodulator action. Med Hypotheses. 1988;27:55–7.
Beligni MV, Fath A, Bethke PC, Lamattina L, Jones RL. Nitric oxide acts as an antioxidant and delays programmed cell death in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 2002;129:1642–50.
Iseki A, Kambe F, Okumura K, Hayakawa T, Seo H. Regulation of thyroid follicular cell function by intracellular redox-active copper. Endocrinology. 2000;141:4373–82.
Zheng X, Chang RL, Cui XX, Avila G, Huang MT, Liu Y, et al. Inhibition of NF-kappaB by (E)3-[(4-methylphenyl)-sulfonyl]-2-propenenitrile (BAY11-7082; BAY) is associated with enhanced 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced growth suppression and apoptosis in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Int J Oncol. 2008;32:257–64.
Xue W, Meylan E, Oliver TG, Feldser DM, Winslow MM, Bronson R, et al. Response and resistance to NF-kappaB inhibitors in mouse models of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2011;1:236–47.
Li B, Li YY, Tsao SW, Cheung AL. Targeting NF-kappaB signaling pathway suppresses tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis of human esophageal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:2635–44.
Scaife CL, Kuang J, Wills JC, Trowbridge DB, Gray P, Manning BM, et al. Nuclear factor kappaB inhibitors induce adhesion-dependent colon cancer apoptosis: implications for metastasis. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6870–8.
Keller SA, Hernandez-Hopkins D, Vider J, Ponomarev V, Hyjek E, Schattner EJ, et al. NF-kappaB is essential for the progression of KSHV- and EBV-infected lymphomas in vivo. Blood. 2006;107:3295–302.
Miyamoto R, Ito T, Nomura S, Amakawa R, Amuro H, Katashiba Y, et al. Inhibitor of IkappaB kinase activity, BAY 11-7082, interferes with interferon regulatory factor 7 nuclear translocation and type I interferon production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R87.
Jia YT, Ma B, Wei W, Xu Y, Wang Y, Tang HT, et al. Sustained activation of nuclear factor-kappaB by reactive oxygen species is involved in the pathogenesis of stress-induced gastric damage in rats. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1582–91.
Kumar A, Negi G, Sharma SS. Suppression of NF-kappaB and NF-kappaB regulated oxidative stress and neuroinflammation by BAY 11-7082 (IkappaB phosphorylation inhibitor) in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Biochimie. 2012;94:1158–65.
Piechota A, Goraca A. Influence of nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition on endothelin-1 induced lung edema and oxidative stress in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;62:183–8.
Shah MA, Power DG, Kindler HL, Holen KD, Kemeny MM, Ilson DH, et al. A multicenter, phase II study of bortezomib (PS-341) in patients with unresectable or metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Invest New Drugs. 2011;29:1475–81.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China 973 Program (Grant Nos. 2012CB822104, 2010CB912104), the State Key Project Specialized for Infectious Diseases of China (Grant Nos. 2012ZX10002-008, 2012ZX10002-012), the National High-Tech R&D 863 Program (Grant No. 2012AA020203), the National Natural Science Fund (Grant Nos. 30930025, 31010103906, 31170766, 31100629, 31270863), and the Key Project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant Nos. 09DZ1950101, 11411951000).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
L. Chen, Y. Ruan and X. Wang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Ruan, Y., Wang, X. et al. BAY 11-7082, a nuclear factor-κB inhibitor, induces apoptosis and S phase arrest in gastric cancer cells. J Gastroenterol 49, 864–874 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0848-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0848-4