Abstract
Background
The apelin receptor (APJ) is related to angiotensin-like-receptor 1 (AGTRL1). This study was designed to elucidate the in vivo localization and changes of APJ in cirrhotic liver, and the in vitro changes of APJ expression in cultured hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and capillarized sinusoidal endothelial cells (SECs) activated by growth factors.
Methods
In vivo studies used control liver samples, cirrhotic liver samples from patients with Child’s A cirrhosis undergoing surgical resection (Child-A-LC), and cirrhotic liver samples from autopsied cases of decompensated Child’s C cirrhosis (Child-C-LC). Immunohistochemical (IHC), Western blot, laser-capture microdissection (LCM) coupled with reverse transcription -polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and immunoelectron microscopic (IEM) studies for APJ expression were conducted. In vitro examinations used commercial human HSCs and SECs. APJ expression was examined in cultured HSCs activated by growth factors and in capillarized SECs activated by angiogenic factors.
Results
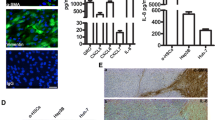
The IHC study of liver samples revealed only slight APJ expression in hepatic sinusoids in control liver tissue. In cirrhotic liver (Child-A-LC and Child-C-LC), APJ expression was evident mainly along the sinusoids and on portal fibroblasts in fibrotic septa. Western blot analysis of whole-liver homogenate and LCM–PCR of sinusoids revealed overexpression of APJ in Child-C-LC samples. The results of IEM studies showed that APJ expression was increased significantly on HSCs, but it was sparse on SECs in Child-C-LC tissue. In vitro examination revealed that APJ was overexpressed in cultured HSCs activated by platelet-derived growth factor-β.
Conclusions
Enhanced expression of APJ on HSCs in cirrhosis indicates markedly increased vascular remodeling.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung S, Funakoshi T, Civelli O. Orphan PCR research. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;153(Suppl 1):S339–46.
O’Dowd BF, Heiber M, Chan A, Heng HH, Tsui LC, Kennedy JL, et al. A human gene that shows identity with the gene encoding the angiotensin receptor is located on chromosome 11. Gene. 1993;136:355–60.
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R, Kakegawa T, Zou MX, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;251:471–6.
Chen MM, Ashley EA, Deng DX, Tsalenko A, Deng A, Tabibiazar R, et al. A novel role for the potent endogenous inotrope apelin in human cardiac dysfunction. Circulation. 2003;108:1432–9.
Kleinz MJ, Davenport AP. Immunocytochemical localization of the endogenous vasoactive peptide apelin to human vascular and endocardial endothelial cells. Regul Pept. 2004;118:119–25.
Kleinz MJ, Skepper JN, Davenport AP. Immunocytochemical localisation of the apelin receptor, APJ, to human cardiomyocytes, vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Regul Pept. 2005;126:233–40.
Sheikh AY, Chun HJ, Glassford AJ, Kundu RK, Kutschka I, Ardigo D, et al. In vivo genetic profiling and cellular localization of apelin reveals a hypoxia-sensitive, endothelial-centered pathway activated in ischemic heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;294:H88–98.
Ishida J, Hashimoto T, Hashimoto Y, Nishiwaki S, Iguchi T, Harada S, et al. Regulatory roles for APJ, a seven-transmembrane receptor related to angiotensin-type 1 receptor in blood pressure in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:26274–9.
Ashley E, Chun HJ, Quertermous T. Opposing cardiovascular roles for the angiotensin and apelin signaling pathways. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006;41:778–81.
Japp AG, Newby DE. The apelin-APJ system in heart failure: pathophysiologic relevance and therapeutic potential. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;75:1882–92.
Principe A, Melgar-Lesmes P, Fernández-Varo G, Del Arbol LR, Ros J, Morales-Ruiz M, et al. The hepatic apelin system: a new therapeutic target for liver disease. Hepatology. 2008;48:1193–201.
Mancini R, Jezequel AM, Benedetti A, Paolucci F, Trozzi L, Orlandi F. Quantitative analysis of proliferating sinusoidal cells in dimethylnitrosamine-induced cirrhosis. An immunohistochemical study. J Hepatol. 1992;15:361–6.
Pinzani M, Gesualdo L, Sabbah GM, Abboud HE. Effects of platelet derived growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens on DNA synthesis and growth of cultured rat liver fat-storing cells. J Clin Invest. 1989;84:1786–93.
Fukuda Y, Nagura H, Imoto M, Koyama Y. Immunohistochemical studies of structural changes of the hepatic lobules in chronic liver diseases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1986;81:1149–55.
Yokomori H, Oda M, Yoshimura K, Nagai T, Fujimaki K, Watanabe S, et al. Caveolin-1 and Rac regulate endothelial capillary-like tubular formation and fenestral contraction in sinusoidal endothelial cells. Liver Int. 2009;29:266–76.
Lam CM, Fan ST, Lo CM, Wong J. Major hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with an unsatisfactory indocyanine green clearance test. Br J Surg. 1999;86:1012–7.
Hamilton PW, Allen DC. Morphometry in histopathology. J Pathol. 1995;175:369–79.
Schutze K, Posl H, Lahr G. Laser micromanipulation systems as universal tools in cellular and molecular biology and in medicine. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 1998;44:735–46.
Emmert-Buck MR, Bonner RF, Smith PD, Chuaqui RF, Zhuang Z, Goldstein SR, et al. Laser capture microdissection. Science. 1996;274:998–1001.
Humbel BM, Sibon OC, Stierhof Y-D, Schwarz H. Ultra-small gold particles and silver enhancement as a detection system in immunolabeling and in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1995;43:735–7.
Bataller R, Sancho-Bru P, Ginès P, Lora JM, Al-Garawi A, Solé M, et al. Activated human hepatic stellate cells express the renin-angiotensin system and synthesize angiotensin II. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:117–25.
Lindahl P, Johansson BR, Leveen P, Betsholtz C. Pericyte loss and microaneurysm formation in PDGF-B-deficient mice. Science. 1997;277:242–5.
Kasai A, Shintani N, Oda M, Kakuda M, Hashimoto H, Matsuda T, et al. Apelin is a novel angiogenic factor in retinal endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;325:395–400.
Sorli SC, Van den Berghe L, Masri B, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y. Therapeutic potential of interfering with apelin signalling. Drug Discov Today. 2006;11:1100–6.
Hashimoto T, Kihara M, Ishida J, Imai N, Yoshida S, Toya Y, et al. Apelin stimulates myosin light chain phosphorylation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1267–72.
Tiani C, Garcia-Pras E, Mejias M, de Gottardi A, Berzigotti A, Bosch J, et al. Apelin signaling modulates splanchnic angiogenesis and portosystemic collateral vessel formation in rats with portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2009;50:296–305.
Masri B, Lahlou H, Mazarguil H, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y. Apelin (65–77) activates extracellular signal-regulated kinases via a PTX-sensitive G protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;290:539–45.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate technical advice from Kumiko Komatsu and Masumi Akita (Division of Morphological Science, Biomedical Research Center, Saitama Medical School).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yokomori, H., Oda, M., Yoshimura, K. et al. Overexpression of apelin receptor (APJ/AGTRL1) on hepatic stellate cells and sinusoidal angiogenesis in human cirrhotic liver. J Gastroenterol 46, 222–231 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0296-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0296-3