Abstract
The incidence of diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is continuously increasing worldwide. However, the specific mechanisms of NAFLD patients with diabetes are still not clear. Recent studies have indicated that integrins play an important role in NAFLD. In this study, we considered the relationship between integrin αv (IGTAV)/FAK pathway and sinusoidal capillarization. We investigated the difference between the expression of IGTAV, laminin (LN), focal adhesion kinase (FAK), and phosphor-FAK protein in human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (HLSECs) to explore the specific mechanisms of the diseases of NAFLD with diabetes under high glucose. We cultured and identified the HLSECs and constructed the recombinant lentivirus vector with IGTAV shRNA by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) to silence the IGTAV gene. Cells were divided into groups of 25 mmol/L glucose and 25 mmol/L mannitol. We measured the protein levels of IGTAV, LN, FAK, and phosphor-FAK by western blot at 2 h, 6 h, and 12 h before and after IGTAV gene silencing. The lentivirus vector was successfully constructed with IGTAV shRNA. The HLSECs under high glucose were observed by scanning electron microscope. SPSS19.0 was used for statistical analysis. High glucose significantly increased the expression of IGTAV, LN, and phosphor-FAK protein in HLSECs; the shRNA IGTAV could effectively inhibit the expression of phosphor-FAK and LN at 2 h and 6 h. Inhibition of the phosphor-FAK could effectively decrease the expression of LN in HLSECs at 2 h and 6 h under high glucose. Inhibition of IGTAV gene of HLSECs under high glucose could improve hepatic sinus capillarization. Inhibition of IGTAV and phosphor-FAK decreased the expression of LN. High glucose led to hepatic sinus capillarization via IGTAV/ FAK pathway.
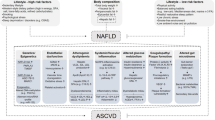
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable
Change history
30 November 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04792-4
Abbreviations
- NAFLD:
-
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- LSECs:
-
liver sinusoidal endothelial cells
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- LN:
-
laminin
- GPI:
-
glycosylphosphatidylinositol
- FAK:
-
focal adhesion kinase
- IGTAV:
-
integrin αv
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- HLSECs:
-
human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells
- shRNA:
-
short hairpin RNA
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- cDNA:
-
complementary DNA
- qRT-PCR:
-
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- 2-DDCT:
-
delta-delta CT
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
References
De Alwis, N. M. W., & Day, C. P. (2008). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The mist gradually clears. Journal of Hepatology, 48, S104–S112.
Couvelard, A., Scoazec, J. Y., Dauge, M. C., Bringuier, A. F., Potet, F., & Feldmann, G. (1996). Structural and functional differentiation of sinusoidal endothelial cells during liver organogenesis in humans. Blood, 87, 4568–4580.
Braet, F., & Wisse, E. (2002). Structural and functional aspects of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrae: A review. Comparative Hepatology, 1(1), 1.
Paolillo, M., Serra, M., & Schinelli, S. (2016). Integrins in glioblastoma: Still an attractive target? Pharmacological Research, 113, 55–61.
Hynes, R. O. (2002). Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell, 110, 673–687.
Xiong, J., Balcioglu, H. E., & Danen, E. H. (2013). Integrin signaling in control of tumor growth and progression. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 45, 1012–1015.
Scales, T. M., & Parsons, M. (2011). Spatial and temporal regulation of integrin signalling during cell migration. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 23, 562–568.
Oh, J. E., Da, H. J., Kim, H., Kang, H. K., Chung, C. P., Park, W. H., & Min, B. M. (2009). α 3 β 1 integrin promotes cell survival via multiple interactions between 14-3-3 isoforms and proapoptotic proteins. Experimental Cell Research, 315, 3187–3200.
Jain, P., Coisne, C., Enzmann, G., Rottapel, R., & Engelhardt, B. (2010). Alpha4beta1 integrin mediates the recruitment of immature dendritic cells across the blood-brain barrier during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Journal of Immunology, 184, 7196–7206.
Roy, S., Ruest, P. J., & Hanks, S. K. (2002). FAK regulates tyrosine phosphorylation of CAS, paxillin, and PYK2 in cells expressing v-Src, but is not a critical determinant of v-Src transformation. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 84, 377–388.
Strömblad, S., & Cheresh, D. A. (1996). Integrins, angiogenesis and vascular cell survival. Chemistry & Biology, 3, 881–885.
Shakado, S., Skaisaka, S., Noguchi, K., et al. (1995). Effects of extracellular matriceson tube formation of cultured rat hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells. Hepatology, 22, 969–973.
Hynes, R. O. (1987). Interins: A family of cell surface receptors. Cell, 48(4), 549–554.
Yong-Su, H., Ok-Sun, B., Eun-Jung, J., Jae-Han, P., Jong-Kyung, S., & Shin-Sung, K. (2004). High dose of glucose promotes chondrogenesis via PKCα and MAPK signaling pathways in chick mesenchymal cells. Cell and Tissue Research, 318, 571–578.
Parsons, J. T. (2003). Focal adhesion kinase: The first ten years. Journal of Cell Science, 116, 1409–1416.
Mitra, S. K., Hanson, D. A., & Schlaepfer, D. D. (2005). Focal adhesion kinase: In command and control of cell motility. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 6, 56–68.
Daneker, G. W., Lund, S. A., Caughman, S. W., Swerlick, R. A., Fischer, A. H., Staley, C. A., & Ades, E. W. (1998). Culture and characterization of sinusoidal endothelial cells isolated from human liver. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal, 34, 370–377.
Zhang, Q., Liu, J., Liu, J., Huang, W., Tian, L., Quan, J., Wang, Y., & Niu, R. (2014). oxLDL induces injury and defenestration of human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells via LOX1. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 53, 281–293.
Ross, R. S. (2004). Molecular and mechanical synergy: Cross-talk between integrins and growth factor receptors. Cardiovascular Research, 63, 381–390.
Jia, F., Howlader, M. A., & Cairo, C. W. (2016). Integrin-mediated cell migration is blocked by inhibitors of human neuraminidase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1861, 1170–1179.
Li, J., Chen, H., Xu, Y., Hu, J., Xie, F. Q., & Yang, C. (2016). Integrin endocytosis on elastic substrates mediates mechanosensing. Journal of Biomechanics, 49, 2644–2654.
Hu, L., Wang, J., Wang, Y., & Xu, H. (2016). An integrin αvβ3 antagonistic modified peptide inhibits tumor growth through inhibition of the ERK and AKT signaling pathways. Oncology Reports, 36, 1953–1962.
Duperret, E. K., Dahal, A., & Ridky, T. W. (2015). Focal-adhesion-independent integrin-αv regulation of FAK and c-Myc is necessary for 3D skin formation and tumor invasion. Journal of Cell Science, 128, 3997–4013.
Ji, S., Zheng, Y., Shao, G., Zhou, Y., & Liu, S. (2013). Integrin αvβ3-targeted radiotracer 99mTc-3P-RGD2 useful for noninvasive monitoring of breast tumor response to antiangiogenic linifanib therapy but not anti-integrin αvβ3 RGD2 therapy. Theranostics, 3, 816–830.
Zhang, L., & Zou, W. (2015). Inhibition of integrin β1 decreases the malignancy of ovarian cancer cells and potentiates anticancer therapy via the FAK/STAT1 signaling pathway. Molecular Medicine Reports, 12, 7869–7876.
Beier, J. I., Guo, L., Ritzenthaler, J. D., Joshibarve, S., Roman, J., & Arteel, G. E. (2016). Fibrin-mediated integrin signaling plays a critical role in hepatic regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice. Annals of Hepatology, 15, 762–772.
Sens, C., Altrock, E., Rau, K., Klemis, V., Von, A. A., Pettera, S., Uebel, S., Damm, T., Tiwari, S., & Moser, M. (2017). An O-glycosylation of fibronectin mediates hepatic osteodystrophy through α4β1 integrin. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 32, 70–81.
Abplanalp, W. T., Conklin, D. J., Cantor, J. M., Ginsberg, M. H., Wysoczynski, M., Bhatnagar, A., & O'Toole, T. E. (2016). Enhanced integrin α4β1-mediated adhesion contributes to a mobilization defect of endothelial progenitor cells in diabetes. Diabetes, 65, 3505–3515.
Jing, L., Quan, J., Jing, F., Qi, Z., Xu, Y., Jia, L., Huang, W., Liu, J., & Tian, L. (2016). High glucose regulates LN expression in human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells through ROS/integrin αvβ3 pathway. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 42, 231–236.
Ying, R. S., Zhu, C., Fan, X. G., Li, N., Tian, X. F., Liu, H. B., & Zhang, B. X. (2007). Hepatitis B virus is inhibited by RNA interference in cell culture and in mice. Antiviral Research, 73, 24–30.
George, J., & Tsutsumi, M. (2007). siRNA-mediated knockdown of connective tissue growth factor prevents N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gene Therapy, 14, 790–803.
Castanotto, D., & Rossi, J. J. (2009). The promises and pitfalls of RNA-interference-based therapeutics. Nature, 457, 426–433.
Du, J., Guo, X., Gao, S., Luo, J., Gong, X., Hao, C., Bo, Y., Tong, L., Shao, J., & Cong, G. (2014). Induction of protection against foot-and-mouth disease virus in cell culture and transgenic suckling mice by miRNA targeting integrin αv receptor. Journal of Biotechnology, 187, 154–161.
Vicentemanzanares, M., Choi, C. K., & Horwitz, A. R. (2009). Integrins in cell migration - The actin connection. Journal of Cell Science, 122, 199–206.
Cao, F. Y., Zhou, X. P., Su, J., Yang, X. H., Mu, F. H., Shen, J. Y., & Sun, W. (2016). Chemical structure characteristics and bioactivity of small moleCule FAK inhibitors. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 16, 934–941.
de Luo, Y., Wazir, R., Tian, Y., Yue, X., Wei, T. Q., & Wang, K. J. (2013). Integrin αv mediates contractility whereas integrin α4 regulates proliferation of human bladder smooth muscle cells via FAK pathway under physiological stretch. The Journal of Urology, 190, 1421–1429.
Mitra, S. K., & Schlaepfer, D. D. (2006). Integrin-regulated FAK–Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 18, 516–523.
Acknowledgements
Addressed all correspondence and requests for reprints to: Jing Liu, PhD, Department of Endocrinology, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou City, Gansu province, China, 730000. Email: yongshen986@163.com.
Funding
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, (81360131, 81560146, 81660148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jia Liu and Hengjiang Gong contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All work has been done under the guidelines of Institutional Ethics Committee.
Consent to Participate
All authors have their consent to participate.
Consent for Publication
All authors have their consent to publish their work.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 2168 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Gong, H., Quan, J. et al. Hepatic Sinusoid Capillarizate via IGTAV/FAK Pathway Under High Glucose. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 196, 1241–1254 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04605-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04605-8