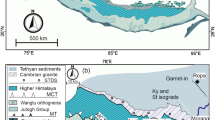
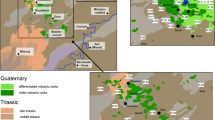
Abstract
New geochemical, isotopic, and geochronological data and interpretations are presented for late Neoproterozoic intrusive carbonates and related rocks of southern Sinai, Egypt (northernmost Arabian–Nubian Shield). The Tarr carbonates are coarsely crystalline and related to explosive emplacement of hypabyssal and volcanic albitite at 605 ± 13 Ma. The carbonates associated with the albitites are divisible into two types: primary dolomitite and secondary breunneritite (Fe-rich magnesite). The dolomitite was clearly intrusive but differs from classic igneous carbonatites, containing much lower abundances of incompatible elements, such as REE, U, Th, Rb, Nb, Y, P, Sr, Zr, Ba, and total alkalies. The breunneritite is a secondary replacement of dolomitite, probably marking the roots of a vigorous hydrothermal system. Albitites show pristine abundances of major and trace elements and were not subjected to a major metamorphic overprint. They are relatively more fractionated, alkaline and related to within-plate A-type magmas, were emplaced in an extensional or non-compressive tectonic regime in the cupola of high-level A-type granite. Tarr albitites may represent residual magma remaining after near-total crystallization of an A-type granite pluton at depth, forcibly emplaced into the roof above the cooling pluton. The intrusive dolomitite exsolved from highly differentiated albitite melt, in the apical regions of a still-buried alkaline “A-type” granite pluton that was rich in CO2; these volatiles migrated upwards and towards the cooler margins of the magma body. Late NNE-SSW extension allowed a shallow-level cupola to form, into which albitite melts and carbonate fluids migrated, culminating in explosive emplacement of albitite breccia and intrusive carbonate. Isotopic compositions of Tarr dolomitite and albitite indicate these are consanguineous and ultimately of mantle origin. Magmatic volatiles fenitized the wall rock, while submarine hydrothermal activity transformed some of the dolomitite into breunneritite. Recognition of Tarr-type should encourage similar hypabyssal complex intrusions to be sought for in association with A-type granitic plutons elsewhere.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla HM, Ishihara S, Matsueda H, Abdel Monem AA (1996) On the albite-enriched granitoids Um Ara area, Southeastern Desert, Egypt. 1. Geochemical, ore potentiality and fluid inclusion studies. J Geochem Explor 57:127–138. doi:10.1016/S0375-6742(96)00029-5
Abou El Maaty MA, Ali Bik MW (2000) Petrology of alkali feldspar granites of Nuweibi and Gebel El-Mueilha, central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Egypt J Geol 44:127–148
Abu El-Enen MM, Makroum FM (2003) Tectonometamorphic evolution of the northeastern Kid Belt, Southeast Sinai, Egypt. Ann Geol Surv Egypt VXXVI:19–37
Andresen A, El-Rus MAA, Myre PI, Boghdady GY (2008) Corfu F U-Pb TIMS age constraints on the evolution of the Neoproterozoic Meatiq Gneiss Dome, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Int J Earth Sci (in press)
Arslan AI, Helba HA, Khalil SO, Morteani G (1997) Bedrock geochemical prospecting and ore potentiality of the rare metal-bearing granite at Nuweibi area, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. In: 3rd inter geoch Alexandria univ proc, pp 375–387
Azer MK (2006) The Petrogenesis of late Precambrian felsic alkaline magmatism in South Sinai, Egypt. Act Geol Polon 56:463–484
Barker DS (1993) Diagnostic magmatic features in carbonatites: implication for the origins of dolomite- and ankerite-rich carbonatites. S Afr J Geol 96:131–138
Batchelor RA, Bowden P (1985) Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters. Chem Geol 45:43–55. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(85)90034-8
Be’eri-Shlevin Y (2008a) The origin and evolution of Neoproterozoic magmatism in the northern Arabian–Nubian-shield (Sinai Peninsula, Egypt and Southern Israel): evidence from the stable and radiogenic isotope record. PhD thesis, Ben-Gurion University
Be’eri-Shlevin Y, Katzir Y, Whitehouse M (2008b) Post-collisional tectono-magmatic evolution in the northern Arabian–Nubian Shield (ANS): time constraints from ion-probe U–Pb dating of zircon. J Geol Soc Lond (in press)
Bentor YK (1985) The crustal evolution of the Arabo–Nubian massif with special reference to the Sinai Peninsula. Precam Res 28:1–74. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(85)90074-9
Bentor YK, Eyal M (1987) The geology of Sinai, its implication for the evolution of the Arabo–Nubian massif, Jebel Sabbagh sheet. The Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities, pp 484
Beyth M, Grunhagen H, Zilberfarb A (1978) An ultramafic rock in the Precambrian of eastern Sinai. Geol Mag 115:373–378
Beyth M, Stern RJ, Altherr R, Kröner A (1994) The Late Precambrian Timna igneous complex, Southern Israel: evidence for comagmatic-type Sanukitoid monzodiorite and alkali granite magma. Lithos 31:103–124. doi:10.1016/0024-4937(94)90003-5
Bielski M (1982) Stages in the evolution of the Arabian–Nubian massif in Sinai. PhD thesis, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, p 155
Bielski M, Jager E, Steinitz G (1979) The geochronology of Iqna granite (Wadi Kid Pluton), Southern Sinai. Contrib Miner Petrol 70:159–165. doi:10.1007/BF00374445
Blasband B, Brooijimans P, Dirks P, Visser W, White S (1997) A Pan-African core complex in the Sinai, Egypt. Geol Mijnb 76:247–266. doi:10.1023/A:1003089218512
Blasband B, White S, Brooijmans P, De Boorder H, Visser W (2000) Late Proterozoic extensional collapse in the Arabian–Nubian Shield. J Geol Soc Lond 157:615–628
Blasy M, Baroudy AF, Kharbish SM (2001) Geochemical characteristics of Wadi Tarr albitite, Southeastern Sinai, Egypt. Egypt J Geol 42:767–780
Bogoch R, Magaritz M (1983) Immiscible silicate–carbonate liquids as evidenced from ocellar diabase dykes, Southeast Sinai. Contrib Miner Petrol 83:227–230. doi:10.1007/BF00371190
Bogoch R, Halicz L, Nathan Y (1982) Breunnerite from the Tarr albitite complex, Sinai. Am Miner 67:822–825
Bogoch R, Eldad H, Nathan Y (1984) Scandium-bearing carbonates of the Tarr albitite complex, Southeast Sinai. Geochem Cosmochem Acta 48:885–887. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(84)90110-8
Bogoch R, Magaritz M, Michard A (1986) Dolomite of possible mantle origin, Southeast Sinai. Chem Geol 56:281–288. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(86)90009-4
Bogoch R, Bahat D, Kisch H (1987) The Tarr albitite: a metasomatic plagiogranite from mainly non-intrusive protoliths. Ofioliti 12:8–22
Boynton WV (1984) Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed) Rare earth element geochemistry. Developments in geochemistry 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 510
Brassinnes S, Balaganskaya E, Demaiffe D (2005) Magmatic evolution of the differentiated ultramafic, alkaline and carbonatite intrusion of Vuoriyarvi (Kola Peninsula, Russia), A LA-ICP-MS study of apatite. Lithos 85:76–92. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2005.03.017
Brooijmans P, Blasband B, White SH, Visser WJ, Dirks P (2003) Geothermobarometric evidence for a metamorphic core complex in Sinai, Egypt. Precam Res 123:249–268. doi:10.1016/S0301-9268(03)00071-8
Castorina F, Stoppa F, Cundari A, Barbieri M (2000) An enriched mantle source for Italy's melilitite–carbonatite association as inferred by its Nd–Sr isotope signature. Miner Mag 64:625–639. doi:10.1180/002646100549652
Cathelineau M (1988) Accessory mineral alteration in peraluminous granites at the hydrothermal stage: a review. Rend Soc Ital Miner Petrol 43:499–508
Chaudhri N, Kaur P, Okrusch M, Schimrascczyk A (2003) Characterization of the Dabla granitoids, North Khetri Copper Belt, Rayasthan, India: evidence of bimodal anorogenic felsic magmatism. Gond Res 6:879–895. doi:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)71032-7
Chauris L (1985) Premières donnèes gèochimiques sur les albitites metasomatiques des environs de Brest (Finistère, France). Bull Soc Geol Fr 8:885–889
Cloos M (2001) Bubbling magma chambers, cupolas, and porphyry copper deposits. Int Geol Rev 43:285–311
De la Roche H, Leterrier J, Grandclaude P, Marchal M (1980) A classification of volcanic and plutonic rocks using R1–R2 diagrams and major-element analyses: its relation with current nomenclature. Chem Geol 29:183–210. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(80)90020-0
Deer WA, Howie RA, Zussman J (1992) An introduction to the rock forming minerals, 2nd edn. Longman Scientific and Technical, London, p 696
Demange M (1975) Zonation métasomatique autour des albitites de la région de Saint Chély D, Apcher (Lozère). Bull Soc Fr Miner Cristallogr 98:186–190
DePaolo DJ (1988) Neodymium isotope geochemistry. Springer, New York, p 187
El-Gaby S, Khudeir AA, Abdel Tawab M, Attla RF (1991) The metamorphosed volcano-sedimentary succession of Wadi Kid, Southeastern Sinai, Egypt. Ann Geol Surv Egypt 17:19–35
El-Haddad MA, Hashad MH (1984) The major and minor elements chemistry of Gebel Tarbtie carbonatites South, Egypt. Bull Fac Sci Assuit Univ 13:205–217
El-Haddad MA, Gwozdz R, Heydorn K (1984) Carbonatites with peculiar trace element abundances. Bull Fac Sci Assuit Univ 13:191–203
El-Metwally AA, El-Aasy IE, Ibrahim ME, Essawy MA, El-Mowafy AA (1999) Petrological, structural and geochemical studies on the basement rocks of Gabal Um-Zariq-Wadi Kid area, South Eastern Sinai. Egypt J Geol 43:147–180
El-Nisr SA, Saleh GM (2001) Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous Mansouri Ring Complex, Southeastern Desert, Egypt. J Afr Earth Sc 32:87–102. doi:10.1016/S0899-5362(01)90020-X
El-Ramly MF, Budanov VI, Hussein AA (1971) The alkaline rocks of South Eastern Egypt. Geol Surv Egypt, 111 pp, paper No. 53
El-Tabal HK (1979) Mineralogical studies on some rare metal apogranites from Nuweibi and Abu Dabbab areas, Eastern Desert, Egypt. MSc thesis, Al-Azhar Universiti, Cairo, pp 112
El-Tokhi M (2001) Petrogenesis and geochemistry of some quartz-syenites from Southern Sinai, Egypt. 2nd inter conf geol afr Assiut Univ Egypt, pp 239–253
Fanelli MT, Cava N, Wyllie PJ (1986) Calcite and dolomite without portlandite at a new eutectic in CaO–MgO–CO2–H2O with applications to carbonatites. In: Morphology and phase of minerals. Proceedings of the 13th general meeting of the International Mineralogical Association, Bulgarian Academy of Science, Sofia, 313–322
Furnes H, Shimron AE, Roberts D (1985) Geochemistry of Pan-African volcanic arc sequences in Southeastern Sinai Peninsula and plate tectonic implications. Precam Res 29:359–382. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(85)90043-9
Gaby S, List FK, Tehrani R (1990) The basement complex of the Eastern Desert and Sinai. In: Said R (ed) The geology of Egypt. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 175–184
Gittins J (1989) The origin and evolution of carbonatite magmas. In: Bell K (ed) Carbonatites: genesis and evolution. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 580–600
Gittins J, Harmer RE (2003) Myth and reality in the carbonatite-silicate rock “association”. Period Miner 72:19–26
Hafez AMA, Abdel Wahed M, Shallaly NA (2007) Microfabric, geochemistry and clockwise P-T path of the Precambrian metasediments in the central Wadi Kid area, Southeastern Sinai. In: The fifteen symposium on Precambrian and development (abstract)
Haidinger WM (1825) Treatise on Mineralogy. In: Mohs F (ed) translation with considerable additions. 3 volumes. Edinburg 1:411
Halama R, Vennemann T, Siebel W, Markl G (2005) The Grønnedal-Ika carbonatite–syenite complex, South Greenland: carbonatite formation by liquid immiscibility. J Petrol 46:191–217. doi:10.1093/petrology/egh069
Halverson GP, Dudás FO, Maloof AC, Bowring SA (2007) Evolution of the 87Sr/86Sr composition of Neoproterozoic seawater. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 256:103–129. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.02.028
Hanson GN (1978) The application of trace elements to the petrogenesis of igneous rocks of granitic composition. Earth Planet Sci Lett 38:26–43. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(78)90124-3
Harmer RE, Lee CA, Eglington BM (1998) A deep mantle source for carbonatite magmatism: evidence from the nephelinites and carbonatites of the Buhera district, SE Zimbabwe, Earth Planet. Sci Lett 158:131–142. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00053-3
Hashad MH (1981) Contributions to the mineralogy and geology of carbonate rocks within the basement complex of Egypt. Unpublished PhD thesis, Al-Azhar University, p 240
Hashad AH, El-Reedy MWM (1980) Geochronology of the nonorogenic alkalic rocks, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. In: Proc 5th conf Afr geol
Helba HA (1994) Geochemical prospecting for rare metals in Nuweibi area, central Eastern desert, Egypt. PhD thesis, Alexandria University, pp 145
Helba RB, Trumbull G, Morteani SO, Khalil A, Arslan AI (1997) Geochemical and petrographic studies of Ta mineralization in the Nuweibi albite granite complex, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Miner Depos 32:164–179. doi:10.1007/s001260050082
Holtz F, Pichavant M, Barbey P, Johannes W (1992) Effect H2O on liquidus phase relations in the haplogranite system at 2 and 5 kbar. Am Miner 77:1233–1244
Höy T, Kwong YTJ (1986) The Mount Grace carbonatite-a Nb and light rare earth element-enriched marble of probable pyroclastics origin in the Shuswap complex, Southeastern British Columbia. Econ Geol 81:1374–1386
Iizumi S, Maehara K, Morris PA, Sawada Y (1994) Sr isotope data of some GSJ rock reference samples. Mem Fac Sci Shimane Univ 28:83–86
Iizumi S, Morris PA, Sawada Y (1995) Nd isotope data for GSJ reference samples JB-1a, JB-3 and JG-1a and the La Jolla standard. Mem Fac Sci Shimane Univ 29:73–76
Jarrar GH, Manton WI, Stern RJ, Zachmann D (2008) Late Neoproterozoic A-type granites in the northernmost Arabian–Nubian Shield formed by fractionation of basaltic melts. Chem Erde Geochem 68:295–312. doi:10.1016/j.chemer.2006.09.002
Katzir Y, Eyal M, Litvinovsky BA, Jahn BM, Zanilevich AN, Valley JW, Beeri Y, Shimshilashvili E (2007) Petrogenesis of A-type granites and origin of vertical zoning in the Katharina pluton, Gebel Mussa (Mt Moses) area, Sinai, Egypt. Lithos 95:208–228. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.07.013
Kimura JI, Yamada Y (1996) Evaluation of major and trace element XRF analyses using a flux to sample ratio of two to one glass beads. J Miner Petrol Econ Geol 91:62–72. doi:10.2465/ganko.91.62
Kimura JI, Yoshida T, Takaku Y (1995) Igneous rock analysis using ICP-MS with internal standardization, isobaric ion overlap correction, and standard addition methods. Sci Rep Fukushima Univ 56:1–12
Kimura JI, Manton WI, Sun CH, Iizumi S, Yoshida T, Stern RJ (2002) Chemical diversity of the Ueno Basalts, central Japan: identification of mantle and crustal contributions to arc basalts. J Petrol 43:1923–1946. doi:10.1093/petrology/43.10.1923
Kinnaird JA, Bowden P (1991) Magmatism and mineralization associated with Phanerozoic Anorogenic Plutonic complexes of the African plate. In: Kampunzu A, Lubala RT (eds) The phanerozoic African plate. Springer, Berlin, pp 410–485
Kovalenko VI (1978) The genesis of rare metal granitoids and related ore deposits. In: Stemprok M, Burnol L, Tischendorf G (eds) Metallization associated with acid magmatism Czech geological survey, 3, pp 235–247
Kröner A (1985) Ophiolites and the evolution of tectonic boundaries in the late Proterozoic Arabian–Nubian Shield of northeast Africa and Arabia. Precam Res 27:277–300. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(85)90016-6
Kröner A, Greiling R, Reischmann T, Hussein IM, Stern RJ, Durr S, Kruger J, Zimmer M (1987) Pan-African crustal evolution in northeast Africa. In: Kröner A (ed) Proterozoic lithospheric evolution, geodynamic series 17. American Geophysical Union, pp 235–257
Le Bas MJ (1981) Carbonatite magmas. Miner Mag 44:56–65. doi:10.1180/minmag.1981.044.334.02
Le Bas MJ, Subbarao KV, Walsh JN (2002) Metacarbonatite or marble? The case of the carbonate, pyroxenite, calcite–apatite rock complex at Borra, Eastern Ghats, India. J Asian Earth Sci 20:127–140. doi:10.1016/S1367-9120(01)00030-X
Le Maitre RW (ed) (2002) Igneous rocks: a classification and glossary of terms. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lentz DR (1999) Carbonatite genesis: a reexamination of the role of intrusion-related pneumatolytic skarn processes in limestone melts. Geology 27:335–338. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0335:CGAROT>2.3.CO;2
Liu Y, Berner Z, Massonne H, Zhong D (2006) Carbonatite-like dykes from the eastern Himalayan syntaxis: geochemical, isotopic, and petrogenetic evidence for melting of metasedimentary carbonate rocks within the orogenic crust. J Asian Earth Sci 26:105–120. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.10.003
Loizenbauer J, Wallbreeher E, Fritz H, Neumayr P, Khudeir AA, Kloetzli U (2001) Structural geology, simple zircon ages and fluid inclusion studies of the Meatiq metamorphic core complex: implications for Neoproterozoic tectonics in the Eastern Desert of Egypt. Precam Res 110:357–383. doi:10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00176-0
Lowell JD, Guilbert JM (1970) Lateral and vertical alteration-mineralization zoning in porphyry ore deposits. Econ Geol 65:373–408
Lowenstern JR, Clynne NA, Bullen TD (1997) Comagmatic A-type granophyre and rhyolites from the Alid Volcanic Center, Eritrea Northeast Africa. J Petrol 38:1707–1721. doi:10.1093/petrology/38.12.1707
Ludwig KR (2001) Isoplot/Ex, rev. 2.49. A geochronological toolkit for microsoft excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication No. 1a
Macdonald R, Kjarsgaard BA, Skilling IP, Davies GR, Hamilton DL, Black S (1993) Liquid immiscibility between trachyte and carbonate in ash flow tuffs from Kenya. Contrib Miner Petrol 114:276–287. doi:10.1007/BF00307762
Madbouly MI (1991) Petrology and geochemistry of some mafic ultramafic rocks of Sinai, Egypt. MSc thesis, Cairo University, pp 132
Martin RF, Bonin B (1976) Water and magma genesis: the association hypersolvus granite-subsolvus granite. Can Miner 14:228–237
McKay GA (1989) Partitioning of rare earth elements between major silicate minerals and basaltic melts. In: Lipin BR, McKay GA (eds) Geochemistry and mineralogy of rare earth elements. Miner Soc Amer 21: 45–77
Moghazi AM (1994) Geochemical and radiogenic isotope studies of some basement rocks at the Kid area, Southeastern Sinai, Egypt. PhD thesis, Alexandria University, Egypt
Moghazi AM, Andersen T, Oweiss GA, Bouseily AM (1998) Geochemical and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic data bearing on the origin of Pan-African granitoids in the Kid area, Southeast Sinai, Egypt. J Geol Soc Lond 155:697–710. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.155.4.0697
Moussa HE (2002) Mineral chemistry and geochemistry of some mafic-ultramafic intrusions in the South Eastern Desert and Sinai, Egypt. Egypt J Geol 46:213–238
Moussa EMM, Stern RJ, Manton WI, Ali KA (2008) SHRIMP zircon dating and Sm/Nd isotopic investigations of Neoproterozoic granitoids, Eastern desert, Egypt. Precam Res 160:341–356. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.08.006
Mushkin A, Navon O, Halicz L, Hartmann G, Stein M (2003) The petrogenesis of A-type magmas from the Amram Massif, Southern Israel. J Petrol 44:815–832. doi:10.1093/petrology/44.5.815
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 299:715–717. doi:10.1038/299715a0
Palache C, Berman H, Frondel C (1951) The system of mineralogy of James Dwight Dana and Edward Salisbury Dana, Yale University 1837–1892, vol II: halides, nitrates, borates, carbonates, sulfates, phosphates, arsenates, tungstates, molybdates, etc., 7th edn. Wiley, New York, p 162 (revised and enlarged)
Pearce JA, Parkinson IJ (1993) Trace element models for mantle melting: application to volcanic arc petrogenesis. In: Prichard HM, Alabaster T, Harris NBW, Neary CR (eds) Magmatic processes and plate tectonics, vol 76. Geol Soc Spec Pub, pp 373–403
Pell J, Höy T (1989) Carbonatites in a continental margin environment—the Canadian Cordillera. In: Bell K (ed) Carbonate—genesis and evolution. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 200–220
Reymer APS (1983) Metamorphism and tectonics of Pan-African terrain in Southeastern Sinai. Precam Res 19:225–238. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(83)90015-3
Riad AM (1979) Geology and petrology on some apogranite occurrence, Nuweibi area, Eastern Desert, Egypt. M.Sc. thesis, Al-Azhar University of Cairo, pp 132
Rollinson H (1994) Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation. Longman/Wiley, London/New York, p 352
Rugless CS, Pirajno F (1996) Geology and geochemistry of the Copperhead albitite “carbonate” complex, east Kimberley, Western Australia. Aust Earth Sci 43:311–322. doi:10.1080/08120099608728258
Sabet AH, Tsogoev VB, Baburin LM, Raid AM, Zakhari A, Armanius LK (1976a) Geologic structure and laws of localization of tantalum mineral zonation at the Nuweibi deposit. Ann Geol Surv Egypt VI:119–156
Sabet AH, Tsogoev VB, Baburin LM, Zharkov VM (1976b) Manifestation of rare metal mineralization of apogranite type in the central Eastern desert of Egypt. Ann Geol Surv Egypt VI:75–95
Samoilov VS (1991) The main geochemical features of carbonatites. J Geochem Explor 40:251–262. doi:10.1016/0375-6742(91)90041-R
Santosh M, Omori S (2008) CO2 windows from mantle to atmosphere: models on ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism and speculations on the link with melting of snowball Earth. Gond Res 14:82–96. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2007.11.001
Schwartz MO (1992) Geochemical criteria for distinguishing magmatic and metasomatic albite-enrichment in granitoids: examples from the Ta–Li granite Yichun (China) and the Sn–W deposit Tikus (Indonesia). Miner Depos 27:101–108. doi:10.1007/BF00197092
Scogings AJ, Forster IF (1989) Gneissose carbonatites in the Bull, s Run complex, Natal. S Afr Geol 92:1–10
Serencsits CM, Faul H, Foland KA, El-Ramly MF, Hussein AA (1979) Alkaline ring complexes in Egypt: their ages and relationship to tectonic development of the Red Sea. Ann Geol Surv Egypt 9:102–116
Shahien MG (2002) Petrochemistry and petrogenesis of Kid granitoids, South Eastern Sinai, Egypt. 6th Inter Conf Geol Arab Word, Cairo University, pp 101–118
Shimron AE (1975) Petrogenesis of the Tarr albitite–carbonatite complex, Sinai Peninsula. Miner Mag 40:13–24. doi:10.1180/minmag.1975.040.309.03
Shimron AE (1980) Proterozoic island arc volcanism and sedimentation in Sinai. Precam Res 12:437–458. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(80)90039-X
Shimron AE, Brookins DG, Magaritz M, Bartov Y (1973) Origin of the intrusive carbonate rocks between the Gulf of Elat and Gulf of Suez Rifts. Isr J Earth Sci 22:243–254
Soliman KA, Tolba ME, El-Manakhly MM, Madbouly ME, Hasan MM, Abd El Magid EA, Khyamy AA, Abd El Mola AF, Mohamed HA (1992) Geology of the albitite rock, Wadi El-Tarr, Southern Sinai. Ann Geol Surv Egypt 18:29–37
Srivastava RK, Heaman LM, Sinha AK, Shiha S (2005a) Emplacement age and isotope geochemistry of Sung Valley alkaline-carbonatite complex, Shillong Plateau, northeastern India: implications for primary carbonate melt and genesis of the associated silicate rocks. Lithos 81:33–54. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.09.017
Srivastava RK, Mohan A, Filho CFF (2005b) Hot-fluid Driven Metasomatism of Samalpatti carbonatites, South India: evidence from petrology, mineral chemistry, trace elements and stable isotope compositions. Gond Res 8:77–85. doi:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70264-1
Stacey JS, Kramers JD (1975) Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a 2-stage model. Earth Planet Sci Lett 26:207–221
Steiger RH, Jäger E (1977) Subcommission on geochronology: convention of the use of decay constants in geo- and cosmochronology. Earth Planet Sci Lett 36:359–362
Stern RJ (1981) Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of late Precambrian ensimatic volcanic rocks, central Eastern desert of Egypt. Precam Res 16:195–230. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(81)90013-9
Stern RJ (1985) The Najd Fault System, Saudi Arabia and Egypt: a late Precambrian rift-related transform system. Tectonics 4:497–511. doi:10.1029/TC004i005p00497
Stern RJ (1994) Arc assembly and continental collision in the Neoproterozoic East African Orogen: implications for the consolidation of Gondwanaland. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 22:319–351
Stern RJ (2002) Crustal evolution in the East African Orogen: a Neodymium isotopic perspective. J Afr Earth Sc 34:109–117. doi:10.1016/S0899-5362(02)00012-X
Stern RJ, Gwinn CJ (1990) Origin of late Precambrian intrusive carbonates, Eastern Desert of Egypt and Sudan: C, O and Sr isotopic evidence. Precam Res 46:259–272. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(90)90005-B
Stern RJ, Gottfried D, Hedge CE (1984) Late Precambrian rifting and crustal evolution in the Northeastern Desert of Egypt. Geology 12:168–171. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1984)12<168:LPRACE>2.0.CO;2
Streckeisen A (1980) Classification and nomenclature of volcanic rocks, lamprophyres, carbonatites and melilitic rocks IUGS Subcommission on the systematics of igneous rocks. Geol Rundsch 69:194–207. doi:10.1007/BF01869032
Taubald H, Morteani G, Satir M (2004) Geochemical and isotopic (Sr, C, O) data from the alkaline complex of Grønnedal-l’ka (South Greenland): evidence for unmixing and crustal contamination. Int J Earth Sci 93:348–360. doi:10.1007/s00531-004-0392-9
Tuttle CF, Bowen NL (1958) Origin of granite in the light of experimental studies in the system NaAlSi3O8–KAlSi3O8–SiO2–H2O. Geol Soc Am Memoir 74:153
Wagner C, Mokhtari A, Deloule E, Chabraux F (2003) Carbonatite and alkaline magmatism in Taourirt (Morocco): petrological, geochemical and Sr–Nd isotope characteristics. J Petrol 44:937–965. doi:10.1093/petrology/44.5.937
Whitehouse MJ, Kamber BS (2005) Assigning dates to thin gneissic veins in high-grade metamorphic terranes: a cautionary tale from Akilia, southwest Greenland. J Petrol 46:291–318
Whitehouse MJ, Kamber B, Moorbath S (1999) Age significance of U–Th–Pb zircon data from early Archaean rocks of west Greenland—a reassessment based on combined ion-microprobe and imaging studies. Chem Geol 160:201–224
Wiedenbeck M, Allé P, Corfu F, Griffin WL, Meier M, Oberli F, von Quadt A, Roddick JC, Spiegel W (1995) Three natural zircon standards for U–Th–Pb, Lu–Hf, trace element and REE analysis. Geostandards Newsl 19:1–23
Woolley AR (2003) Igneous silicate rocks associated with carbonatites: their diversity, relative abundance and implications for carbonatite genesis. Period Miner 72:9–17
Woolley AR, Kempe PRC (1989) Carbonatites: nomenclature, average chemical composition and element distribution. In: Bell K (ed) Carbonatites: genesis and evolution. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 1–14
Wyllie PJ, Tuttle OF (1960) The system CaO–CO2–H2O and the origin of carbonatites. J Petrol 1:1–46
Acknowledgments
We appreciate stimulating discussions with Prof. M.D. Samuel of the Egypt National Research Centre. We greatly appreciate the assistance of K. Ali and M. Whitehouse for zircon dating, B. Woldemichael for isotopic analyses and Y. Sawada for XRF facility. We thank Yaron Be’eri-Shlevin for sharing new geochronologic results on Sinai granites and the use of Fig. 1. This research was partly supported by NSF OCE 0804749 under the US-Egypt Joint Fund Program. The NordSIM ion microprobe facility is financed and operated under an agreement between the research councils of Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and the Geological Survey of Finland and the Swedish Museum of Natural History; this is NordSIM publication number 222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azer, M.K., Stern, R.J. & Kimura, JI. Origin of a late Neoproterozoic (605 ± 13 Ma) intrusive carbonate–albitite complex in Southern Sinai, Egypt. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 99, 245–267 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-008-0385-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-008-0385-1