Abstract
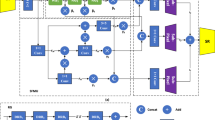
The low-light image enhancement algorithm aims to solve the problem of poor contrast and low brightness of images in low-light environments. Although many image enhancement algorithms have been proposed, they still face the problems of loss of significant features in the enhanced image, inadequate brightness improvement, and a large number of algorithm-specific parameters. To solve the above problems, this paper proposes a Fast Multi-scale Residual Network (FMR-Net) for low-light image enhancement. By superimposing highly optimized residual blocks and designing branching structures, we propose light-weight backbone networks with only 0.014M parameters. In this paper, we design a plug-and-play fast multi-scale residual block for image feature extraction and inference acceleration. Extensive experimental validation shows that the algorithm in this paper can improve the brightness and maintain the contrast of low-light images while keeping a small number of parameters, and achieves superior performance in both subjective vision tests and image quality tests compared to existing methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, X.: Infrared image filtering and enhancement processing method based upon image processing technology. J. Electron. Imaging 31(5), 051408 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JEI.31.5.051408
Gao, X., Liu, S.: DAFuse: a fusion for infrared and visible images based on generative adversarial network. J. Electron. Imaging 31(4), 043023 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JEI.31.4.043023
Yue, G., Li, Z., Tao, Y., Jin, T.: Low-illumination traffic object detection using the saliency region of infrared image masking on infrared-visible fusion image. J. Electron. Imaging 31(3), 033029 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JEI.31.3.033029
Ye, Y.X., Shen, L.: HOPC: a novel similarity metric based on geometric structural properties for multi-modal remote sensing image matching. In: Proceedings of ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, vol. 3, pp. 9–16 (2016)
Li, S., Jin, W., Li, L., Li, Y.: An improved contrast enhancement algorithm for infrared images based on adaptive double plateaus histogram equalization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 90, 164–174 (2018)
Wan, M., Gu, G., Qian, W., Ren, K., Chen, Q., Maldague, X.: Infrared image enhancement using adaptive histogram partition and brightness correction. Remote Sens. 10(5), 682 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050682
Li, Y., Liu, N., Xu, J., Wu, J.: Detail enhancement of infrared image based on bi-exponential edge preserving smoother. Optik 199, 163300 (2019)
Katırcıoğlu, F., Çay, Y., Cingiz, Z.: Infrared image enhancement model based on gravitational force and lateral inhibition networks. Infrared Phys. Technol. 100, 15–27 (2019)
Wang, B., Zhang, B., Liu, X.W., Zou, F.C.: Novel infrared image enhancement optimization algorithm combined with DFOCS. Optik 224, 165476 (2020)
Zhang, Z., Zheng, H., Hong, R., Xu, M., Yan, S., Wang, M.: Deep color consistent network for low-light image enhancement. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2022, pp. 1889–1898. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00194
Singh, K., Parihar, A.S.: DSE-Net: deep simultaneous estimation network for low-light image enhancement. J. Vis. Comun. Image Represent. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2023.103780
Hai, J., Xuan, Z., Yang, R., Hao, Y., Zou, F., Lin, F., Han, S.: R2RNet: low-light image enhancement via real-low to real-normal network. J. Vis. Comun. Image Represent. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2022.103712
Fan, S., Liang, W., Ding, D., Yu, H.: LACN: a lightweight attention-guided ConvNeXt network for low-light image enhancement. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 117(B), 105632 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105632
Cui, H., Li, J., Hua, Z., Fan, L.: TPET: two-stage perceptual enhancement transformer network for low-light image enhancement. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105411
Lore, K.G., Akintayo, A., Sarkar, S., et al.: LLNet: a deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 61, 650–662 (2017). arXiv:1808.04560
Wei, C., Wang, W., Yang, W., et al.: Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[EB/OL] (2018). arXiv:1808.04560
Jiang, Y., et al.: EnlightenGAN: deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 2340–2349 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3051462
Guo, C., Li, C., Guo, J., et al.: Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020, pp. 1777–1786 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00185
Zhu, A., Zhang, L., Shen, Y., Ma, Y., Zhao, S., Zhou, Y.: Zero-shot restoration of underexposed images via robust retinex decomposition. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), London, UK, pp. 1–6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME46284.2020.9102962
Ghosh, S., et al.: Iegan: multi-purpose perceptual quality image enhancement using generative adversarial network. In: 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). IEEE, pp. 11–20 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Di, X., Wu, J., et al.: A fast and lightweight network for low-light image enhancement (2023). arXiv:2304.02978
Wu, C., Dong, J., Tang, J.: LUT-GCE: lookup table global curve estimation for fast low-light image enhancement[J] (2023). arXiv:2306.07083
Zhang, Y., Teng, B., Yang, D., et al.: Learning a single convolutional layer model for low light image enhancement[J] (2023). arXiv:2305.14039
Du, Z., Liu, D., Liu, J., Tang, J., Wu, G., Fu, L.: Fast and memory-efficient network towards efficient image super-resolution. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2022, pp. 852–861. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW56347.2022.00101
Lim, B., Son, S., Kim, H., et al.: Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 136–144 (2017)
Chen, G.-H., Yang, C.-l., Xie, S.-l.: Gradient-based structural similarity for image quality assessment. In: 2006 International Conference on Image Processing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2006, pp. 2929–2932. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2006.313132
Wei, C., Wang, W., Yang, W., et al.: Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[J] (2018). arXiv:1808.04560
Yang, W., Wang, W., Huang, H., Wang, S., Liu, J.: Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 2072–2086 (2021). 5, 6
Sun, Y., Qin, J., Gao, X., et al.: Attention-enhanced multi-scale residual network for single image super-resolution. SIViP 16, 1417–1424 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-02095-x
Tai, Y., Yang, J., Liu, X.: Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3147–3155 (2017)
Han, W., Chang, S., Liu, D., et al.: Image super-resolution via dual-state recurrent networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1654–1663 (2018)
Du, Z., Liu, D., Liu, J., Tang, J., Wu, G., Fu, L.: Fast and memory-efficient network towards efficient image super-resolution. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2022, pp. 852–861. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW56347.2022.00101
Li, J., Fang, F., Mei, K., et al.: Multi-scale residual network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 517–532 (2018)
Wang, L.-W., Liu, Z.-S., Siu, W.-C., Lun, D.P.K.: Lightening network for low-light image enhancement. In: IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 29, pp. 7984–7996 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3008396
Zhang, F., Shao, Y., Sun, Y., et al.: Self-supervised low-light image enhancement via histogram equalizationprior. Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV), pp. 3–75. Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore (2023)
Liu, R., Ma, L., Zhang, J., Fan, X., Luo, Z.: Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 2021, pp. 10556–10565. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01042
Ma, L., Ma, T., Liu, R., Fan, X., Luo, Z.: Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2022, pp. 5627–5636. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00555
Wu, W., Weng, J., Zhang, P., Wang, X., Yang, W., Jiang, J.: URetinex-Net: retinex-based deep unfolding network for low-light image enhancement. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2022, pp. 5891–5900. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00581
Li, C., Guo, C., Loy, C.C.: Learning to enhance low-light image via zero-reference deep curve estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(8), 4225–4238 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3063604
Rahman, Z., Aamir, M., Ali, Z., et al.: Efficient contrast adjustment and fusion method for underexposed images in industrial cyber-physical systems. IEEE Syst J. 17(4), 5085–5096 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2023.3262593
Rahman, Z., Pu, Y.F., Aamir, M., et al.: Structure revealing of low-light images using wavelet transform based on fractional-order denoising and multiscale decomposition. Vis. Comput. 37, 865–880 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01838-0
Deng, W., Yuan, H., Deng, L., et al.: Reparameterized residual feature network for lightweight image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1712–1721 (2023)
Liu, J., Tang, J., Wu, G.: Residual feature distillation network for lightweight image super-resolution. In Computer Vision-ECCV 2020 Workshops: Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part III 16, pp. 41–55. Springer, Berlin (2020). 2, 4, 6, 7
Funding
This search received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, YC; methodology, YC; software, YC; validation, YC; investigation, YC; resources, GZ and XW; data curation, YC and YS; writing—original draft preparation, YC; writing—review and editing, GZ and XW; visualization, YC; supervision, XW; project administration, GZ and XW. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Informed consent statement
Not applicable.
Institutional review board statement
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by T. Li.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhu, G., Wang, X. et al. FMR-Net: a fast multi-scale residual network for low-light image enhancement. Multimedia Systems 30, 73 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01252-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01252-1