Abstract
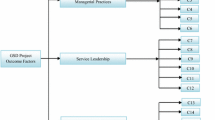
The offshore/on-site teams’ service climate is one of the key predictors of attaining the global software development (GSD) project outcome from the software service outsourcing perspective. This study aims at proposing a comprehensive methodology for measuring offshore/on-site team-level service climate (TSC) in the context of the GSD project outcome. For the evaluation of TSC in GSD projects, synthesizing literature reviews, extensive investigations are taken into account and to extend our earlier works (Sangaiah and Thangavelu in Int Rev Comput Softw 7(5):2159–2172, 2012; Sangaiah and Thangavelu in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer communication and informatics (ICCCI), 2013; Sangaiah and Thangavelu in Cent Eur J Eng 3(3):419–435, 2013; Sangaiah and Thangavelu in Aust J Basic Appl Sci 7(8):374–385, 2013). Therefore, consistent with earlier studies on IT service climate, we have classified TSC characteristics of offshore/on-site teams’ into three main dimensions: managerial practices (deliver quality of service), global service climate (measure overall perceptions), and service leadership (goal setting, work planning, and coordination) which covers twenty-five offshore/on-site teams’ service climate attributes. For evaluating the TSC, we have considered adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system, which is more suitable to find interrelationship between service climate criteria. Finally, this study empirically assesses with 338 experts in India to explore offshore/on-site team-level service climate and GSD project outcome relationship.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sangaiah AK, Thangavelu AK (2013) Measuring IT service quality in the context of team-level service climate and GSD project outcome relationship. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 7(8):374–385. http://www.ajbasweb.com/ajbas/2013/June/374-385.pdf
Jia R, Reich BH (2013) IT service climate, antecedents and IT service quality outcomes: some initial evidence. J Strateg Inf Syst 22(1):51–69
Schneider B, White SS, Paul MC (1998) Linking service climate and customer perceptions of service quality: test of a causal model. J Appl Psychol 83(2):150–163
Schneider B, Bowen DE (1993) The service organization: human resources management is crucial. Organ Dyn 21(4):39–52
De Jong A, de Ruyter K, Lemmink J (2005) Service climate in self-managing teams: mapping the linkage of team member perceptions and service performance outcomes in a business-to-business setting. J Manag Stud 42(8):1593–1620
Liao H, Chuang A (2007) Transforming service employees and climate: a multilevel, multisource examination of transformational leadership in building long-term service relationships. J Appl Psychol 92(4):1006–1019
Salanova M, Agut S, Peiró JM (2005) Linking organizational resources and work engagement to employee performance and customer loyalty: the mediation of service climate. J Appl Psychol 90(6):1217–1227
Kankanhalli A, Tan B, Wei K–K (2005) Contributing knowledge to electronic knowledge repositories: an empirical investigation. MIS Q 29(1):113–143. http://www.jstor.org/stable/25148670
Iacovou CL, Thompson RL, Smith HJ (2009) Selective status reporting in information systems projects: a dyadic-level investigation. MIS Q 33(4):785–810
Rai A, Maruping LM, Venkatesh V (2009) Offshore information systems project success: the role of social embeddedness and cultural characteristics. MIS Q 33(3):617–641, http://www.winfobase.de/lehre%5Clv_materialien.nsf/intern01/632C3F776761A11BC1257871005959C6/$FILE/Paper%201.pdf
Susskind AM, Kacmar KM, Borchgrevink CP (2003) Customer service providers’ attitudes relating to customer service and customer satisfaction in the customer–server exchange. J Appl Psychol 88(1):179–187
Sangaiah AK, Thangavelu AK (2012) Exploring the influence of partnership quality factors towards the outcome of global software development projects. Int Rev Comput Softw 7(5):2159–2172. http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-84869825785&partnerID=40&md5=88c1674a41df8de307de1a1401bf8a32
Sangaiah AK, Thangavelu AK (2013) Factors affecting the outcome of global software development projects: an empirical study. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer communication and informatics (ICCCI), pp 1–10. doi:10.1109/ICCCI.2013.6466113
Sangaiah AK, Thangavelu AK (2013) An exploration of FMCDM approach for evaluating the outcome/success of GSD projects. Cent Eur J Eng (Springer) 3(3):419–435. doi:10.2478/s13531-012-0070-9
Parasuraman A, Zeithaml VA, Berry LL (1985) Conceptual model of services quality and its implication for future research. J Mark 49(4):41–50
Jia R, Reich BH, Pearson JM (2008) IT service climate: an extension to IT service quality research. J Assoc Inf Syst 9(5):294–320. http://aisel.aisnet.org/jais/vol9/iss5/13
Pitt LF, Watson RT, Kavan CB (1995) Service quality: a measure of information systems effectiveness. MIS Q 19(2):173–188
Campion MA, Medsker GJ, Higgs AC (1993) Relations between work group characteristics and effectiveness: implications for designing effective work groups. Pers Psychol 46(4):823–852
Oldham GR, Cummings A (1996) Employee creativity: personal and contextual factors at work. Acad Manag J 39(3):607–634
Bateni SM, Jeng D-S (2007) Estimation of pile group scour using adaptive neuro-fuzzy approach. Ocean Eng 34(8–9):1344–1354
Saghaei A, Didehkhani H (2011) Developing an integrated model for the evaluation and selection of six sigma projects based on ANFIS and fuzzy goal programming. Expert Syst Appl 38(1):721–728
Taylan O, Karagözoğlu B (2009) An adaptive neuro-fuzzy model for prediction of student’s academic performance. Comput Ind Eng 57(3):732–741
Kwong CK, Wong TC, Chan KY (2009) A methodology of generating customer satisfaction models for new product development using a neuro-fuzzy approach. Expert Syst Appl 36(8):11262–11270
Fayaed SS, El-Shafie A, Jaafar O (2013) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system–based model for elevation–surface area–storage interrelationships. Neural Comput Appl 22:987–988. doi:10.1007/s00521-011-0790-4
Bambang RT (2007) Filtered-X adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy inference systems for nonlinear active noise control. In: Advances in neural networks–ISNN 2007, vol. 4491, pp 54–63. Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-72383-7_8
Aziz D, Ali MA, Gan KB, Saiboon I (2012) Initialization of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system using fuzzy clustering in predicting primary triage category. In: IEEE International conference on intelligent and advanced systems (ICIAS) (vol. 1, pp. 170–174) doi:10.1109/ICIAS.2012.6306181
Chang Z, Liu L, Li Z (2007) Prediction of amount of imports based on adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. In: IEEE International conference on intelligent pervasive computing, pp 437–440. doi:10.1109/IPC.2007.36
Hamam A, Georganas ND (2008) A comparison of Mamdani and Sugeno fuzzy inference systems for evaluating the quality of experience of Hapto-Audio-Visual applications. In: IEEE international workshop on Haptic Audio visual Environments and Games (HAVE 2008), pp 87–92. doi:10.1109/HAVE.2008.4685304
Mun J, Shin M, Lee K, Jung M (2009) Manufacturing enterprise collaboration based on a goal-oriented fuzzy trust evaluation model in a virtual enterprise. Comput Ind Eng 56(3):888–901
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Westner M, Strahringer S (2010) Determinants of success in IS offshoring projects: results from an empirical study of German companies. Inf Manag 47(5):291–299
Chen S-H, Lin Y-H, Chang L-C, Chang F-J (2006) The strategy of building a flood forecast model by neuro-fuzzy network. Hydrol Process 20(7):1525–1540. doi:10.1002/hyp.5942
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sangaiah, A.K., Thangavelu, A.K. An adaptive neuro-fuzzy approach to evaluation of team-level service climate in GSD projects. Neural Comput & Applic 25, 573–583 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1521-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1521-9