Abstract
Purpose
Anxiety, depression, sleep disorder, fatigue, and pain develop as common psychoneurological symptoms in patients with glioma, and their occurrence and development are potentially related to inflammatory factors. However, this theory has not been proven within the context of glioma. This study aimed to estimate interconnections among psychoneurological symptoms and inflammatory biomarkers by a network analysis.
Patients and methods
We selected 203 patients with stage I–IV glioma from a tertiary hospital in China using convenient sampling method. Patients completed the self-made questionnaires, Hamilton Anxiety Scale-14 (HAMA-14), Hamilton Depression Scale-24 (HAMD-24), Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory-20 (MFI-20), and pain Numerical Rating Scale (NRS). The plasma inflammatory cytokines were examined. Partial correlation network analysis was performed to illustrate interactions of symptoms and inflammatory biomarkers.
Results
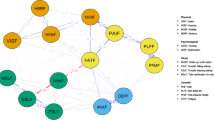
Among the 203 included patients, all psychoneurological symptoms, except for depression and pain, exhibited significant connections with each other. Depression, anxiety, fatigue, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) with higher strength centrality indices were identified as the most central node within the symptom-biomarker network.
Conclusions
Depression, anxiety, fatigue, IL-6, and TNF-α play a significant role in the symptom-biomarker network in patients with glioma. Medical staff should strengthen the dynamic evaluation of the involved symptoms and inflammatory cytokines and take effective measures to alleviate the burden of symptoms and improve the quality of life of patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original information supporting our consequences can be gettable upon request.
References
Yang K, Wu Z, Zhang H, Zhang N, Wu W, Wang Z, Dai Z, Zhang X, Zhang L, Peng Y, Ye W, Zeng W, Liu Z, Cheng Q (2022) Glioma targeted therapy: insight into future of molecular approaches. Mol Cancer 21(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-022-01513-z
Fox SW, Lyon D, Farace E (2007) Symptom clusters in patients with high-grade glioma. J Nurs Scholarsh 39(1):61–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2007.00144.x
Coomans MB, Dirven L, Aaronson NK, Baumert BG, Van Den Bent M, Bottomley A, Brandes AA, Chinot O, Coens C, Gorlia T, Herrlinger U, Keime-Guibert F, Malmstrom A, Martinelli F, Stupp R, Talacchi A, Weller M, Wick W, Reijneveld JC, Taphoorn MJB (2019) Symptom clusters in newly diagnosed glioma patients: which symptom clusters are independently associated with functioning and global health status? Neuro Oncol 21(11):1447–1457. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noz118
Ij-K M, Snijders TJ, de Graeff A, Teunissen S, de Vos FYF (2018) Prevalence of symptoms in glioma patients throughout the disease trajectory: a systematic review. J Neurooncol 140(3):485–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-03015-9
Armstrong TS, Cohen MZ, Eriksen LR, Hickey JV (2004) Symptom clusters in oncology patients and implications for symptom research in people with primary brain tumors. J Nurs Scholarsh 36(3):197–206. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2004.04038.x
Valko PO, Siddique A, Linsenmeier C, Zaugg K, Held U, Hofer S (2015) Prevalence and predictors of fatigue in glioblastoma: a prospective study. Neuro Oncol 17(2):274–281. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou127
Armstrong TS, Gilbert MR (2012) Practical strategies for management of fatigue and sleep disorders in people with brain tumors. Neuro Oncol 14(Suppl 4(Suppl 4)):iv65-72. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos210
Choi S, Ryu E (2018) Effects of symptom clusters and depression on the quality of life in patients with advanced lung cancer. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 27(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecc.12508
Boele FW, Rooney AG, Grant R, Klein M (2015) Psychiatric symptoms in glioma patients: from diagnosis to management. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11(6):1413–1420. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S65874
Blamire AM (2018) MR approaches in neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 108(10):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnmrs.2018.11.001
Xu J, Wang J, Wimo A, Qiu C (2016) The economic burden of mental disorders in China, 2005-2013: implications for health policy. BMC Psychiatry 16(5):137. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-016-0839-0
Song L, Quan X, Su L, Wang K, Wang H, Wu L, Chen C, Li S, Xiang W, Chen L, Zhou J (2020) Inflammation and behavioral symptoms in preoperational glioma patients: Is depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment related to markers of systemic inflammation? Brain Behav 10(9):e01771. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1771
Kwekkeboom KL, Tostrud L, Costanzo E, Coe CL, Serlin RC, Ward SE, Zhang Y (2018) The role of inflammation in the pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbance symptom cluster in advanced cancer. J Pain Symptom Manage 55(5):1286–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.01.008
Clevenger L, Schrepf A, Christensen D, DeGeest K, Bender D, Ahmed A, Goodheart MJ, Penedo F, Lubaroff DM, Sood AK, Lutgendorf SK (2012) Sleep disturbance, cytokines, and fatigue in women with ovarian cancer. Brain Behav Immun 26(7):1037–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2012.04.003
Himbert C, Ose J, Lin T, Warby CA, Gigic B, Steindorf K, Schrotz-King P, Abbenhardt-Martin C, Zielske L, Boehm J, Ulrich CM (2019) Inflammation- and angiogenesis-related biomarkers are correlated with cancer-related fatigue in colorectal cancer patients: results from the ColoCare Study. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 28(4):e13055. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecc.13055
Miranda DO, Anatriello E, Azevedo LR, Cordeiro JFC, Peria FM, Floria-Santos M, Pereira-da-Silva G (2018) Elevated serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines potentially correlate with depression and anxiety in colorectal cancer patients in different stages of the antitumor therapy. Cytokine 104(4):72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2017.09.030
Wu JM, Yang HT, Ho TW, Shun SC, Lin MT (2019) Association between interleukin-6 levels and perioperative fatigue in gastric adenocarcinoma patients. J Clin Med 8(4):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040543
Xiao C, Beitler JJ, Higgins KA, Conneely K, Dwivedi B, Felger J, Wommack EC, Shin DM, Saba NF, Ong LY, Kowalski J, Bruner DW, Miller AH (2016) Fatigue is associated with inflammation in patients with head and neck cancer before and after intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Brain Behav Immun 52(2):145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.10.016
Oliveira KG, von Zeidler SV, Lamas AZ, Podesta JR, Sena A, Souza ED, Lenzi J, Lemos EM, Gouvea SA, Bissoli NS (2014) Relationship of inflammatory markers and pain in patients with head and neck cancer prior to anticancer therapy. Braz J Med Biol Res 47(7):600–604. https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431x20143599
Jin X, Kim SH, Jeon HM, Beck S, Sohn YW, Yin J, Kim JK, Lim YC, Lee JH, Kim SH, Kang SH, Pian X, Song MS, Park JB, Chae YS, Chung YG, Lee SH, Choi YJ, Nam DH et al (2012) Interferon regulatory factor 7 regulates glioma stem cells via interleukin-6 and Notch signalling. Brain 135(Pt 4):1055–1069. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws028
Contreras A, Nieto I, Valiente C, Espinosa R, Vazquez C (2019) The study of psychopathology from the network analysis perspective: a systematic review. Psychother Psychosom 88(2):71–83. https://doi.org/10.1159/000497425
Rea IM, Gibson DS, McGilligan V, McNerlan SE, Alexander HD, Ross OA (2018) Age and age-related diseases: role of inflammation triggers and cytokines. Front Immunol 9(4):586. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00586
Kalaoja M, Corbin LJ, Tan VY, Ahola-Olli AV, Havulinna AS, Santalahti K, Pitkanen N, Lehtimaki T, Lyytikainen LP, Raitoharju E, Seppala I, Kahonen M, Ripatti S, Palotie A, Perola M, Viikari JS, Jalkanen S, Maksimow M, Salomaa V et al (2021) The role of inflammatory cytokines as intermediates in the pathway from increased adiposity to disease. Obesity (Silver Spring) 29(2):428–437. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.23060
Schag CC, Heinrich RL, Ganz PA (1984) Karnofsky performance status revisited: reliability, validity, and guidelines. J Clin Oncol 2(3):187–193. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1984.2.3.187
Hamilton M (1959) The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol 32(1):50–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8341.1959.tb00467.x
Hamilton M (1960) A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23(1):56–62. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.23.1.56
Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ (1989) The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res 28(2):193–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4
Huang Y, Jiang ZJ, Deng J, Qi YJ (2020) Sleep quality of patients with postoperative glioma at home. World J Clin Cases 8(20):4735–4742. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4735
Smets EM, Garssen B, Bonke B, De Haes JC (1995) The Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory (MFI) psychometric qualities of an instrument to assess fatigue. J Psychosom Res 39(3):315–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3999(94)00125-o
van Coevorden-van Loon EMP, Heijenbrok-Kal MH, Horemans HLD, Boere R, de Bat R, Vincent A, van den Bent MJ, Ribbers GM (2022) The relationship between mental fatigue, cognitive functioning, and employment status in patients with low-grade glioma: a cross-sectional single-center study. Disabil Rehabil 44(24):7413–7419. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2021.1991013
Jensen MP (2003) The validity and reliability of pain measures in adults with cancer. J Pain 4(1):2–21. https://doi.org/10.1054/jpai.2003.1
McNally RJ (2016) Can network analysis transform psychopathology? Behav Res Ther 86:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2016.06.006
Bringmann LF, Elmer T, Epskamp S, Krause RW, Schoch D, Wichers M, Wigman JTW, Snippe E (2019) What do centrality measures measure in psychological networks? J Abnorm Psychol 128(8):892–903. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000446
Epskamp S, Borsboom D, Fried EI (2018) Estimating psychological networks and their accuracy: a tutorial paper. Behav Res Methods 50(1):195–212. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-017-0862-1
Cladder-Micus MB, Speckens AEM, Vrijsen JN, Donders AR, Becker ES, Spijker J (2018) Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for patients with chronic, treatment-resistant depression: a pragmatic randomized controlled trial. Depress Anxiety 35(10):914–924. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22788
Stepanski EJ, Walker MS, Schwartzberg LS, Blakely LJ, Ong JC, Houts AC (2009) The relation of trouble sleeping, depressed mood, pain, and fatigue in patients with cancer. J Clin Sleep Med 5(2):132–136
Whisenant M, Wong B, Mitchell SA, Beck SL, Mooney K (2019) Symptom trajectories are associated with co-occurring symptoms during chemotherapy for breast cancer. J Pain Symptom Manage 57(2):183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.11.010
Barsevick AM (2007) The elusive concept of the symptom cluster. Oncol Nurs Forum 34(5):971–980. https://doi.org/10.1188/07.ONF.971-980
Naufel MF, Boldarine VT, Oyama LM, do Nascimento CMO, Silva Dos Santos GM, Hachul H, Ribeiro EB (2019) Age and leptinemia association with anxiety and depression symptoms in overweight middle-aged women. Menopause 26(3):317–324. https://doi.org/10.1097/GME.0000000000001210
Bouchard LC, Antoni MH, Blomberg BB, Stagl JM, Gudenkauf LM, Jutagir DR, Diaz A, Lechner S, Gluck S, Derhagopian RP, Carver CS (2016) Postsurgical depressive symptoms and proinflammatory cytokine elevations in women undergoing primary treatment for breast cancer. Psychosom Med 78(1):26–37. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0000000000000261
Santoso AMM, Jansen F, Peeters CFW, Baatenburg de Jong RJ, Brakenhoff RH, Langendijk JA, Leemans CR, Takes RP, Terhaard CHJ, van Straten A, Verdonck-de Leeuw IM (2022) Psychoneurological symptoms and biomarkers of stress and inflammation in newly diagnosed head and neck cancer patients: a network analysis. Curr Oncol 29(10):7109–7121. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100559
Lippitz BE (2013) Cytokine patterns in patients with cancer: a systematic review. Lancet Oncol 14(6):e218–e228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70582-X
Albulescu R, Codrici E, Popescu ID, Mihai S, Necula LG, Petrescu D, Teodoru M (2013) Tanase CP (2013) Cytokine patterns in brain tumour progression. Mediators Inflamm 6:979748. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/979748
Menard C, Pfau ML, Hodes GE, Kana V, Wang VX, Bouchard S, Takahashi A, Flanigan ME, Aleyasin H, LeClair KB, Janssen WG, Labonte B, Parise EM, Lorsch ZS, Golden SA, Heshmati M, Tamminga C, Turecki G, Campbell M et al (2017) Social stress induces neurovascular pathology promoting depression. Nat Neurosci 20(12):1752–1760. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0010-3
Wohleb ES, Powell ND, Godbout JP, Sheridan JF (2013) Stress-induced recruitment of bone marrow-derived monocytes to the brain promotes anxiety-like behavior. J Neurosci 33(34):13820–13833. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1671-13.2013
Hart PC, Rajab IM, Alebraheem M, Potempa LA (2020) C-reactive protein and cancer-diagnostic and therapeutic insights. Front Immunol 11(11):595835. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.595835
Mihlan M, Blom AM, Kupreishvili K, Lauer N, Stelzner K, Bergstrom F, Niessen HW, Zipfel PF (2011) Monomeric C-reactive protein modulates classic complement activation on necrotic cells. FASEB J 25(12):4198–4210. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.11-186460
Kinzenbaw DA, Chu Y, Pena Silva RA, Didion SP, Faraci FM (2013) Interleukin-10 protects against aging-induced endothelial dysfunction. Physiol Rep 1(6):e00149. https://doi.org/10.1002/phy2.149
Paolucci EM, Loukov D, Bowdish DME, Heisz JJ (2018) Exercise reduces depression and inflammation but intensity matters. Biol Psychol 133(3):79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2018.01.015
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the guidance and help from Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute.
Funding
This research was supported by the Key Technology Research and Development Program of Shandong (2017GSF218028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Feng Li: conceptualization, project administration, and writing—review and editing. Huayu Li: investigation, methodology, software, and writing—original draft preparation. Xiaohan Shi: data collection supervision, formal analysis, and writing assisting. Jing Li: data collection supervision, software, and methodology. Xinrui Zhang: investigation, formal analysis, and methodology. The authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Review Board of School of Nursing and Rehabilitation, Shandong University (protocol code 2020-R-071).
Consent to participate
All patients provided informed consent prior to the study.
Consent to publish
The authors declare that all content of the article can be published.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Shi, X., Li, J. et al. Psychoneurological symptoms and inflammatory markers in patients with glioma in China: a network analysis. Support Care Cancer 31, 435 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-023-07873-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-023-07873-6