Abstract
Purpose
Many head and neck cancer patients who receive radiation therapy experience radiation-induced dysgeusia (RID), which has no standard treatment. The only supplement controlled clinical trials have evaluated for the treatment of RID is zinc. However, the results of these and other studies investigating the use of zinc for RID have been inconsistent. To assess the validity of zinc as a treatment for RID, we conducted a systematic literature search and performed a meta-analysis to determine the extent to which zinc affects RID incidence and the degree to which ongoing RID responds to zinc.
Methods
We searched the Ovid MEDLINE, Ovid Embase, PubMed, and Cochrane Library databases to identify studies investigating the use of zinc-based therapy for RID in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiation that were published between January 1, 2003, and November 9, 2017. Using American Society of Clinical Oncology criteria, we selected studies with a high level of evidence for inclusion in the meta-analysis.
Results
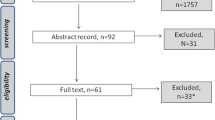
Of the 32 full-text articles eligible for inclusion, three were included in the final review and meta-analysis. The meta-analysis showed that, compared with placebo, zinc reduces the incidence of RID (risk ratio, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.67–0.92) but does not improve taste acuity more rapidly following radiation therapy (risk ratio, 2.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.97–6.88).
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that zinc-based therapy reduces the incidence of RID but has a minimal effect on ongoing RID. Our findings also highlight the need for additional evidence-based research on this topic.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, WJC, upon reasonable request.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69(1):7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Pytynia KB, Dahlstrom KR, Sturgis EM (2014) Epidemiology of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol 50(5):380–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.12.019
D'Souza G, Kreimer AR, Viscidi R, Pawlita M, Fakhry C, Koch WM, Westra WH, Gillison ML (2007) Case-control study of human papillomavirus and oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med 356(19):1944–1956. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa065497
Gillison ML, Koch WM, Capone RB, Spafford M, Westra WH, Wu L, Zahurak ML, Daniel RW, Viglione M, Symer DE, Shah KV, Sidransky D (2000) Evidence for a causal association between human papillomavirus and a subset of head and neck cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(9):709–720
Ang KK, Harris J, Wheeler R, Weber R, Rosenthal DI, Nguyen-Tan PF, Westra WH, Chung CH, Jordan RC, Lu C, Kim H, Axelrod R, Silverman CC, Redmond KP, Gillison ML (2010) Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med 363(1):24–35. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0912217
Baharvand M, ShoalehSaadi N, Barakian R, Moghaddam EJ (2013) Taste alteration and impact on quality of life after head and neck radiotherapy. Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine 42(1):106–112. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0714.2012.01200.x
Ruo Redda MGA, S. (2006) Radiotherapy-induced taste impairment. Cancer Treat Rev 32(7):541–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2006.06.003
Alvarez-Camacho M, Gonella S, Ghosh S, Kubrak C, Scrimger RA, Chu KP, Wismer WV (2016) The impact of taste and smell alterations on quality of life in head and neck cancer patients. Qual Life Res 25(6):1495–1504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-015-1185-2
McLaughlin L (2013) Taste dysfunction in head and neck cancer survivors. Oncol Nurs Forum 40(1):E4–E13. https://doi.org/10.1188/13.ONF.E4-E13
McLaughlin LM, S. (2014) A meta-analysis of the relationship among impaired taste and treatment, treatment type, and tumor site in head and neck cancer treatment survivors. Oncol Nurs Forum 41(3):E194–E202. https://doi.org/10.1188/14.ONF.E194-E202
Ravasco P (2005) Aspects of taste and compliance in patients with cancer. Eur J Oncol Nurs 9(Suppl 2):S84–S91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejon.2005.09.003
Hutton JL, Baracos VE, Wismer WV (2007) Chemosensory dysfunction is a primary factor in the evolution of declining nutritional status and quality of life in patients with advanced cancer. J Pain Symptom Manag 33(2):156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.07.017
Logan HL, Bartoshuk LM, Fillingim RB, Tomar SL, Mendenhall WM (2008) Metallic taste phantom predicts oral pain among 5-year survivors of head and neck cancer. Pain 140(2):323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2008.09.004
Sandow PL, Hejrat-Yazdi M, Heft MW (2006) Taste loss and recovery following radiation therapy. J Dent Res 85(7):608–611
National Cancer Institute (U.S.) (2009) Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE). NIH publication, vol no 10–5410, Rev. edn. U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md
Germano F, Melone P, Testi D, Arcuri L, Marmiroli L, Petrone A, Arcuri C (2015) Oral complications of head and neck radiotherapy: prevalence and management. Minerva Stomatol 64(4):189–202
Leyrer CM, Chan MD, Peiffer AM, Horne E, Harmon M, Carter AF, Hinson WH, Mirlohi S, Duncan SE, Dietrich AM, Lesser GJ (2014) Taste and smell disturbances after brain irradiation: a dose-volume histogram analysis of a prospective observational study. Practical Radiation Oncology 4(2):130–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2013.06.003
Dorr EA, S.: Dorr, W. (2014) Dysgeusia during radio(chemo)therapy for head-and-neck tumors: a prospective study in 356 patients. Radiotherapy and Oncology Conference:2014 Annual Conference of the European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology, ESTRO 2033. Vienna Austria. Conference Publication: (var.pagings). 2111 (pp S2020)
Hovan AJW, P. M.: Stevenson-Moore, P.: Wahlin, Y. B.: Ohrn, K. E.: Elting, L. S.: Spijkervet, F. K.: Brennan, M. T.: Dysgeusia Section, Oral Care Study Group Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer International Society of Oral Oncology (2010) A systematic review of dysgeusia induced by cancer therapies. Support Care Cancer 18(8):1081–1087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-010-0902-1
Yamashita H, Nakagawa K, Tago M, Nakamura N, Shiraishi K, Eda M, Nakata H, Nagamatsu N, Yokoyama R, Onimura M, Ohtomo K (2006) Taste dysfunction in patients receiving radiotherapy. Head & Neck 28(6):508–516. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.20347
Ogama N, Suzuki S, Umeshita K, Kobayashi T, Kaneko S, Kato S, Shimizu Y (2010) Appetite and adverse effects associated with radiation therapy in patients with head and neck cancer. Eur J Oncol Nurs 14(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejon.2009.07.004
Kamprad F, Ranft D, Weber A, Hildebrandt G (2008) Functional changes of the gustatory organ caused by local radiation exposure during radiotherapy of the head-and-neck region. Strahlenther Onkol 184(3):157–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-008-1780-z
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Update of recommendations for the use of hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors: evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. American Society of Clinical Oncology (1996) J Clin Oncol 14(6):1957–1960. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1996.14.6.1957
The periodic health examination. Canadian Task Force on the Periodic Health Examination (1979) Can. Med Assoc J 121(9):1193–1254
Higgins JPT GS, eds. (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Sterne JA, Egger M (2001) Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: guidelines on choice of axis. J Clin Epidemiol 54(10):1046–1055
Buntzel J, Micke O, Glatzel M, Schafer U, Riesenbeck D, Kisters K, Bruns F, Schonekaes KG, Dawczynski H, Mucke R (2010) Selenium substitution during radiotherapy in head and neck cancer. Trace Elements and Electrolytes 27(4):235–239
Jham BC, Chen H, Carvalho AL, Freire AR (2009) A randomized phase III prospective trial of bethanechol to prevent mucositis, candidiasis, and taste loss in patients with head and neck cancer undergoing radiotherapy: a secondary analysis. J Oral Sci 51(4):565–572
Heiser C, Hofauer B, Scherer E, Schukraft J, Knopf A (2016) Liposomal treatment of xerostomia, odor, and taste abnormalities in patients with head and neck cancer. Head & Neck 38(Suppl 1):E1232–E1237. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.24198
Halyard MY, Jatoi A, Sloan JA, 3rd Bearden JD, Vora SA, Atherton PJ, Perez EA, Soori G, Zalduendo AC, Zhu A, Stella PJ, Loprinzi CL (2007) Does zinc sulfate prevent therapy-induced taste alterations in head and neck cancer patients? Results of phase III double-blind, placebo-controlled trial from the North Central Cancer Treatment Group (N01C4). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67(5):1318–1322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.10.046
Ripamonti C, Zecca E, Brunelli C, Fulfaro F, Villa S, Balzarini A, Bombardieri E, De Conno F (1998) A randomized, controlled clinical trial to evaluate the effects of zinc sulfate on cancer patients with taste alterations caused by head and neck irradiation. Cancer 82(10):1938–1945
Watanabe TI, Ishihara M, Matsuura K, Mizuta K, Itoh Y (2010) Polaprezinc prevents oral mucositis associated with radiochemotherapy in patients with head and neck cancer. Int J Cancer 127(8):1984–1990. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25200
Silverman JE, Weber CW, Jr Silverman S, Coulthard SL, Manning MR (1983) Zinc supplementation and taste in head and neck cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy. J Oral Med 38(1):14–16
Najafizade N, Hemati S, Gookizade A, Berjis N, Hashemi M, Vejdani S, Ghannadi A, Shahsanaee A, Arbab N (2013) Preventive effects of zinc sulfate on taste alterations in patients under irradiation for head and neck cancers: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences 18(2):123–126
Miura H, Barlow LA (2010) Taste bud regeneration and the search for taste progenitor cells. Arch Ital Biol 148(2):107–118
Just T, Pau HW, Bombor I, Guthoff RF, Fietkau R, Hummel T (2005) Confocal microscopy of the peripheral gustatory system: comparison between healthy subjects and patients suffering from taste disorders during radiochemotherapy. Laryngoscope 115(12):2178–2182. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.MLG.0000181502.07160.86
Comeau TB, Epstein JB, Migas C (2001) Taste and smell dysfunction in patients receiving chemotherapy: a review of current knowledge. Support Care Cancer 9(8):575–580
Frank SJ, Blanchard P, Lee JJ, Sturgis EM, Kies MS, Machtay M, Vikram B, Garden AS, Rosenthal DI, Gunn GB, Fuller CD, Hutcheson K, Lai S, Busse PM, Lee NY, Lin A, Foote RL (2018) Comparing intensity-modulated proton therapy with intensity-modulated photon therapy for oropharyngeal cancer: the journey from clinical trial concept to activation. Semin Radiat Oncol 28(2):108–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2017.12.002
Mossman KL, Henkin RI (1978) Radiation-induced changes in taste acuity in cancer-patients. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics 4(7–8):663–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-3016(78)90190-6
Thomsen M, Vitetta L (2018) Adjunctive treatments for the prevention of chemotherapy- and radiotherapy-induced mucositis. Integr Cancer Ther 17(4):1027–1047. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534735418794885
Rink L, Gabriel P (2001) Zinc and the immune system. TreatmentUpdate 13(2):1–2
Andreini C, Banci L, Bertini I, Rosato A (2006) Counting the zinc-proteins encoded in the human genome. J Proteome Res 5(1):196–201. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr050361j
Yan M, Song Y, Wong CP, Hardin K, Ho E (2008) Zinc deficiency alters DNA damage response genes in normal human prostate epithelial cells. J Nutr 138(4):667–673. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/138.4.667
Hamano H, Yoshinaga K, Eta R, Emori Y, Kawasaki D, Iino Y, Sawada M, Kuroda H, Takei M (2006) Effect of polaprezinc on taste disorders in zinc-deficient rats. Biofactors 28(3–4):185–193
Takei M (2012) Development of polaprezinc research. Yakugaku Zasshi 132(3):271–277
Alvarez-Camacho M, Gonella S, Campbell S, Scrimger RA, Wismer WV (2017) A systematic review of smell alterations after radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 54:110–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.02.003
Bressan V, Stevanin S, Bianchi M, Aleo G, Bagnasco A, Sasso L (2016) The effects of swallowing disorders, dysgeusia, oral mucositis and xerostomia on nutritional status, oral intake and weight loss in head and neck cancer patients: a systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev 45:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.03.006
Sapir E, Tao Y, Feng F, Samuels S, El Naqa I, Murdoch-Kinch CA, Feng M, Schipper M, Eisbruch A (2016) Predictors of dysgeusia in patients with oropharyngeal cancer treated with chemotherapy and intensity modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 96(2):354–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.05.011
Sio TT, Lin HK, Shi Q, Gunn GB, Cleeland CS, Lee JJ, Hernandez M, Blanchard P, Thaker NG, Phan J, Rosenthal DI, Garden AS, Morrison WH, Fuller CD, Mendoza TR, Mohan R, Wang XS, Frank SJ (2016) Intensity modulated proton therapy versus intensity modulated photon radiation therapy for oropharyngeal cancer: first comparative results of patient-reported outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95(4):1107–1114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.02.044
Spotten L, Corish C, Lorton C, Dhuibhir PU, O'Donoghue N, O'Connor B, Cunningham M, El Beltagi N, Gillham C, Walsh D (2016) Subjective taste and smell changes in treatment-naive people with solid tumours. Support Care Cancer 24(7):3201–3208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-016-3133-2
Thorne T, Olson K, Wismer W (2015) A state-of-the-art review of the management and treatment of taste and smell alterations in adult oncology patients. Support Care Cancer 23(9):2843–2851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-015-2827-1
Irune E, Dwivedi RC, Nutting CM, Harrington KJ (2014) Treatment-related dysgeusia in head and neck cancer patients. Cancer Treat Rev 40(9):1106–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.06.011
Nagraj SK, Naresh S, Srinivas K, Renjith George P, Shrestha A, Levenson D, Ferraiolo DM (2014) Interventions for the management of taste disturbances. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews (11):Cd010470. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010470.pub2
Yamashita H, Nakagawa K, Hosoi Y, Kurokawa A, Fukuda Y, Matsumoto I, Misaka T, Abe K (2009) Umami taste dysfunction in patients receiving radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol 45(3):e19–e23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2008.04.001
Mirza N, Machtay M, Devine PA, Troxel A, Abboud SK, Doty RL (2008) Gustatory impairment in patients undergoing head and neck irradiation. Laryngoscope 118(1):24–31. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLG.0b013e318155a276
Patton LL, Siegel MA, Benoliel R, De Laat A (2007) Management of burning mouth syndrome: systematic review and management recommendations. Oral surgery, oral medicine, oral pathology, oral radiology, and endodontics 103 Suppl:S39.e31-13. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2006.11.009
Yamashita H, Nakagawa K, Nakamura N, Abe K, Asakage T, Ohmoto M, Okada S, Matsumoto I, Hosoi Y, Sasano N, Yamakawa S, Ohtomo K (2006) Relation between acute and late irradiation impairment of four basic tastes and irradiated tongue volume in patients with head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66(5):1422–1429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.08.037
Shi HB, Masuda M, Umezaki T, Kuratomi Y, Kumamoto Y, Yamamoto T, Komiyama S (2004) Irradiation impairment of umami taste in patients with head and neck cancer. Auris Nasus Larynx 31(4):401–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2004.05.002
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ann Sutton and Joe Munch in Scientific Publications in MD Anderson’s Research Medical Library for editing the manuscript and thank Research Medical Library staff for helping conduct literature searches.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Ovid MEDLINE search strategy for radiation-induced dysgeusia
1 exp Radiotherapy
2 Radiotherap*.ti,ab,kf,fs.
3 Radiation/
4 exp radiation effects/
5 (radiation or irradiation* or irradiated).ti,ab,kf.
6 exp Radiotherapy Planning, Computer-Assisted/
7 (chemoradiation or "chemo-radiation" or "chemo-radiotherapy*" or chemoradiotherapy or radiochemo* or radio-chemo*).ti,ab,kf.
8 exp radiation dosage/
9 *radiation injuries/ or abnormalities, radiation-induced/
10 or/1-9
11 exp Taste Disorders/
12 exp Taste Perception/
13 Taste/ab, de, re [Abnormalities, Drug Effects, Radiation Effects]
14 Taste Buds/
15 Taste Threshold/
16 (dysgeusia* or parageusia* or ageusia* or hypogeusia*).ti,kf.
17 (taste adj5 (distort* or dysfunction* or disorder* or alter* or change* or abnormal* or blind* or impaired or impairment)).ti,kf.
18 (taste adj3 (loss* or acuity or damage* or disturbance* or sensation* or foul or aversion* or sense or sensitivity)).ti,kf.
19 (gustatory adj3 (perception* or sensitive* or distort*)).ti,ab,kf.
20 (taste or dysgeusia* or ageusia* or parageusia* or hypogeusia*).ab. /freq=2
21 or/11-20
22 10 and 21
23 limit 22 to english language
24 limit 23 to yr="2003 -Current"
25 (animals not (humans and animals)).sh.
26 24 not 25
27 (rat or rats or mouse or mice).ti.
28 26 not 27
29 case report*.pt,ti.
30 28 not 29
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chi, W.J., Myers, J.N., Frank, S.J. et al. The effects of zinc on radiation-induced dysgeusia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Support Care Cancer 28, 1–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05578-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05578-8