Abstract
Purpose
Despite its widespread use as primary febrile neutropenia (FN) prophylaxis during chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer, the optimal duration of daily filgrastim is unknown. Using the minimum effective duration may improve patient comfort and acceptability while reducing costs. Yet, suboptimal dosing may also negatively impact patient care. A survey was performed to obtain information regarding current practices for granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) use.
Methods
Canadian oncologists involved in the treatment of breast cancer patients, as well as patients who had received neo/adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer, were surveyed. Standardized surveys were designed to collect information on perceived reasons for G-CSF use and current practices.
Results
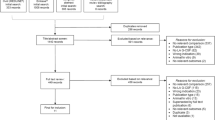
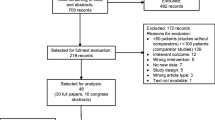
The surveys were completed by 38/50 (76%) physicians and 95/97 (98%) patients. For physicians, there was variability in the choice of chemotherapy regimens that required G-CSF support, the dose of filgrastim prescribed and the number of days prescribed. The majority of physicians reported using 5 (31.6%), 7 (47.4%), or 10 (13.2%) days of therapy. Nearly half of the patients (46.3%) recalled having experienced at least one of the chemotherapy-related complications including chemotherapy delays, dose reductions, and FN. While on filgrastim, 66.3% of patients reported myalgia and bone pain. Both physicians and patients expressed interest in participating in clinical trials designed to optimize the duration of filgrastim administration.
Conclusions
Significant variability in practice exists with respect to filgrastim administration. Definitive studies are therefore required to standardize and improve care, as this has the potential to impact treatment outcomes, patient quality of life, and cost savings.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factors or antibiotics for primary prophylaxis for febrile neutropenia. In: Editor (ed)^(eds) Book Granulocyte-colony Stimulating Factors or Antibiotics for Primary Prophylaxis for Febrile Neutropenia. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02816112, City
A Study to compare administration schedules of G-CSF (filgrastim) for primary prophylaxis of febrile neutropenia. In: Editor (ed) (eds) Book A Study to Compare Administration Schedules of G-CSF (Filgrastim) for Primary Prophylaxis of Febrile Neutropenia. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02816164, City
(2016) Cancer Care Ontario GCSF Recommendations 2016
Aapro MS, Bohlius J, Cameron DA, Dal Lago L, Donnelly JP, Kearney N, Lyman GH, Pettengell R, Tjan-Heijnen VC, Walewski J, Weber DC, Zielinski C, European Organisation for R, Treatment of C (2011) 2010 update of EORTC guidelines for the use of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in adult patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and solid tumours. Eur J Cancer 47:8–32
Collins D (2017) What could drive Amgen's growth in 2017. wwwmarketrealistcom http://marketrealist.com/2017/05/what-could-drive-amgens-growth-in-2017/: Accessed 9 November 2017
de Naurois J, Novitzky-Basso I, Gill MJ, Marti FM, Cullen MH, Roila F, Group EGW (2010) Management of febrile neutropenia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann Oncol 21(Suppl 5):v252–v256. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdq196
Fernandes R, Mazzarello S, Hutton B, Shorr R, Ibrahim MF, Jacobs C, Ong M, Clemons M (2017) A systematic review of the incidence and risk factors for taxane acute pain syndrome in patients receiving taxane-based chemotherapy for prostate cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer 15(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2016.07.018
Fernandes R, Mazzarello S, Majeed H, Smith S, Shorr R, Hutton B, Ibrahim MF, Jacobs C, Ong M, Clemons M (2016) Treatment of taxane acute pain syndrome (TAPS) in cancer patients receiving taxane-based chemotherapy-a systematic review. Support Care Cancer 24(4):1583–1594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-015-2941-0
Fernandes R, Mazzarello S, Stober C, Vandermeer L, Dudani S, Ibrahim MF, Majeed H, Perdrizet K, Shorr R, Hutton B, Fergusson D, Clemons M (2017) Optimal primary febrile neutropenia prophylaxis for patients receiving docetaxel-cyclophosphamide chemotherapy for breast cancer: a systematic review. Breast Cancer Res Treat 161(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-4028-0
Inc AC (2016) Neulasta (pegfilgrastim) injection, for subcutaneous use In: Editor (ed)^(eds) Book Neulasta (pegfilgrastim) injection, for subcutaneous use City
Inc AC (2016) Product Monograph (filgrastim). Version Oct 2016. In: Editor (ed)^(eds) Book Product Monograph (filgrastim). Version Oct 2016., City
Jacobs C, Clemons M, Mazzarello S, Hutton B, Joy AA, Brackstone M, Freedman O, Vandermeer L, Ibrahim M, Fergusson D, Hilton J (2017) Enhancing accrual to chemotherapy trials for patients with early stage triple-negative breast cancer: a survey of physicians and patients. Support Care Cancer 25(6):1881–1886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-017-3580-4
Jacobs C, Hutton B, Mazzarello S, Smith S, Joy A, Amir E, Ibrahim MF, Gregario N, Daigle K, Eggert L, Clemons M (2015) Optimisation of steroid prophylaxis schedules in breast cancer patients receiving docetaxel chemotherapy-a survey of health care providers and patients. Support Care Cancer 23(11):3269–3275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-015-2731-8
Jacobs C, Ibrahim MF, Clemons M, Hutton B, Simos D, Caudrelier JM, Graham ID, Smith S, Addison C, Arnaout A (2015) Treatment choices for patients with invasive lobular breast cancer: a doctor survey. J Eval Clin Pract 21(4):740–748. https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.12379
Jones SE, Savin MA, Holmes FA, O'Shaughnessy JA, Blum JL, Vukelja S, McIntyre KJ, Pippen JE, Bordelon JH, Kirby R, Sandbach J, Hyman WJ, Khandelwal P, Negron AG, Richards DA, Anthony SP, Mennel RG, Boehm KA, Meyer WG, Asmar L (2006) Phase III trial comparing doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide with docetaxel plus cyclophosphamide as adjuvant therapy for operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(34):5381–5387. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.06.5391
Network NCC NCCN Clinical practice guidelines in oncology: myeloid growth factors, version 1.2010. In: Editor (ed)^(eds) Book NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: myeloid growth factors, version 1.2010, City
Programs OPD (2016) Grastofil (filgrastim) frequently asked questions. Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care http://www.health.gov.on.ca/en/pro/programs/drugs/opdp_eo/notices/fq_exec_office_20161221.pdf: Accessed September 9, 2017
Renner P, Milazzo S, Liu JP, Zwahlen M, Birkmann J, Horneber M (2012) Primary prophylactic colony-stimulating factors for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in breast cancer patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10:CD007913
Smith TJ, Bohlke K, Lyman GH, Carson KR, Crawford J, Cross SJ, Goldberg JM, Khatcheressian JL, Leighl NB, Perkins CL, Somlo G, Wade JL, Wozniak AJ, Armitage JO, American Society of Clinical O (2015) Recommendations for the Use of WBC Growth Factors: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update J Clin Oncol 33: 3199–3212
Smith TJ, Khatcheressian J, Lyman GH, Ozer H, Armitage JO, Balducci L, Bennett CL, Cantor SB, Crawford J, Cross SJ, Demetri G, Desch CE, Pizzo PA, Schiffer CA, Schwartzberg L, Somerfield MR, Somlo G, Wade JC, Wade JL, Winn RJ, Wozniak AJ, Wolff AC (2006) 2006 update of recommendations for the use of white blood cell growth factors: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol 24(19):3187–3205. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.06.4451
Warwick G, Lungu, E (2017) Potential Savings from Biosimilars Canada. Patented Medicine Prices Review Board https://www.cadth.ca/sites/default/files/symp-2017/presentations/april24-2017/Concurrent-Session-B4-Gary-Warwick.pdf Accessed 9 September, 2017
Zhu X, Bouganim N, Vandermeer L, Dent SF, Dranitsaris G, Clemons MJ (2012) Use and delivery of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy-single-centre experience. Curr Oncol 19(4):e239–e243. https://doi.org/10.3747/co.19.948
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all the patients and physicians who completed this study.
Funding
Funding for this project was from local sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Appendix 1
(DOCX 33 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hilton, J., Vandermeer, L., Sienkiewicz, M. et al. Filgrastim use in patients receiving chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer—a survey of physicians and patients. Support Care Cancer 26, 2323–2331 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4074-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4074-8