Abstract
Objectives
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy is frequently a dose-limiting factor in cancer treatment and may cause pain and irreversible function loss in cancer survivors. We tested whether alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) could decrease the severity of peripheral neuropathy symptoms in patients undergoing platinum-based chemotherapy.
Methods
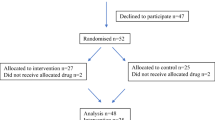
Cancer patients 18 years or older were randomly selected to receive either 600 mg ALA or a placebo three times a day orally for 24 weeks while receiving chemotherapy regimens including cisplatin or oxaliplatin. Neuropathy was measured by the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy/Gynecologic Oncology Group-Neurotoxicity (FACT/GOG-Ntx) scale and the NCI Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events neurotoxicity grades. Results from timed functional tests and the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) were secondary endpoints.
Results
Seventy of 243 (29 %) patients completed the study (24 weeks). Both the ALA and the placebo arms had a comparable drop-out rate. No statistically significant differences were found between the ALA and the placebo groups for FACT/GOG-Ntx scores, BPI scores, and patients' functional outcomes.
Conclusion
This strategy of oral ALA administration was ineffective at preventing neurotoxicity caused by oxaliplatin or cisplatin. High attrition rates due to poor patient compliance and manner of dosage administration in this trial demonstrated a lack of feasibility for this intervention. Future studies to explore ALA as a neuroprotective agent should take heed of the barriers confronted in this study.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tofthagen C (2010) Patient perceptions associated with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Clin J Oncol Nurs 14(3):E22–E28. doi:10.1188/10.CJON.E22-E28
Hausheer FH, Schilsky RL, Bain S, Berghorn EJ, Lieberman F (2006) Diagnosis, management, and evaluation of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Semin Oncol 33(1):15–49. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2005.12.010
Verstappen CC, Heimans JJ, Hoekman K, Postma TJ (2003) Neurotoxic complications of chemotherapy in patients with cancer: clinical signs and optimal management. Drugs 63(15):1549–1563
Park SB, Krishnan AV, Lin CS, Goldstein D, Friedlander M, Kiernan MC (2008) Mechanisms underlying chemotherapy-induced neurotoxicity and the potential for neuroprotective strategies. Curr Med Chem 15(29):3081–3094
Krishnan AV, Goldstein D, Friedlander M, Kiernan MC (2005) Oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity and the development of neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 32(1):51–60. doi:10.1002/mus.20340
Uwah AN, Ackler J, Leighton JC, Pomerantz S, Tester W (2012) The effect of diabetes on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy. Clin Colorectal Cancer 11(4):275–279. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2012.05.002
Argyriou AA, Polychronopoulos P, Koutras A, Xiros N, Petsas T, Argyriou K, Kalofonos HP, Chroni E (2007) Clinical and electrophysiological features of peripheral neuropathy induced by administration of cisplatin plus paclitaxel-based chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 16(3):231–237. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2354.2006.00718.x
Cersosimo RJ (1989) Cisplatin neurotoxicity. Cancer Treat Rev 16(4):195–211
Extra JM, Marty M, Brienza S, Misset JL (1998) Pharmacokinetics and safety profile of oxaliplatin. Semin Oncol 25(2 Suppl 5):13–22
Eng C (2009) Toxic effects and their management: daily clinical challenges in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(4):207–218. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.16
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, Boni C, Cortes-Funes H, Cervantes A, Freyer G, Papamichael D, Le Bail N, Louvet C, Hendler D, de Braud F, Wilson C, Morvan F, Bonetti A (2000) Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 18(16):2938–2947
Tofthagen C, McAllister RD, McMillan SC (2011) Peripheral neuropathy in patients with colorectal cancer receiving oxaliplatin. Clinical journal of oncology nursing 15(2):182–188. doi:10.1188/11.cjon.182-188
Mols F, Beijers T, Lemmens V, van den Hurk CJ, Vreugdenhil G, van de Poll-Franse LV (2013) Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy and its association with quality of life among 2- to 11-year colorectal cancer survivors: results from the population-based PROFILES registry. J Clin Oncol 31(21):2699–2707. doi:10.1200/jco.2013.49.1514
Land SR, Kopec JA, Cecchini RS, Ganz PA, Wieand HS, Colangelo LH, Murphy K, Kuebler JP, Seay TE, Needles BM, Bearden JD, Colman LK, Lanier KS, Pajon ER, Cella D, Smith RE, O'Connell MJ, Costantino JP, Wolmark N (2007) Neurotoxicity from oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol 25(16):2205–2211. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.08.6652
Pietrangeli A, Leandri M, Terzoli E, Jandolo B, Garufi C (2006) Persistence of high-dose oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy at long-term follow-up. Eur Neurol 56(1):13–16. doi:10.1159/000094376
Schloss JM, Colosimo M, Airey C, Masci PP, Linnane AW, Vitetta L (2013) Nutraceuticals and chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): a systematic review. Clin Nutr 32(6):888–893. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2013.04.007
Kopec JA, Land SR, Cecchini R, Ganz P, Cella D, Costantino J, Wieand HS, Smith RE, Kuebler JP, Wolmark N (2006) Validation of a self-reported neurotoxicity scale in patients with operable colon cancer receiving oxaliplatin. J Support Oncol 4(8):W1–W7
Wolf S, Barton D, Kottschade L, Grothey A, Loprinzi C (2008) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: prevention and treatment strategies. Eur J Cancer 44(11):1507–1515. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.04.018
Albers JW, Chaudhry V, Cavaletti G, Donehower RC (2011) Interventions for preventing neuropathy caused by cisplatin and related compounds. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2, CD005228. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005228.pub3
Ibrahimpasic K (2013) Alpha lipoic acid and glycaemic control in diabetic neuropathies at type 2 diabetes treatment. Med Arh 67(1):7–9
Snedecor SJ, Sudharshan L, Cappelleri JC, Sadosky A, Mehta S, Botteman M (2013) Systematic review and meta-analysis of pharmacological therapies for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pain Pract. doi:10.1111/papr.12054
Roelofs RI, Hrushesky W, Rogin J, Rosenberg L (1984) Peripheral sensory neuropathy and cisplatin chemotherapy. Neurology 34(7):934–938
Evans P, Halliwell B (1999) Free radicals and hearing. Cause, consequence, and criteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci 884:19–40
Gedlicka C, Scheithauer W, Schull B, Kornek GV (2002) Effective treatment of oxaliplatin-induced cumulative polyneuropathy with alpha-lipoic acid. J Clin Oncol 20(15):3359–3361
Ruhnau KJ, Meissner HP, Finn JR, Reljanovic M, Lobisch M, Schutte K, Nehrdich D, Tritschler HJ, Mehnert H, Ziegler D (1999) Effects of 3-week oral treatment with the antioxidant thioctic acid (alpha-lipoic acid) in symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetic medicine : a journal of the British Diabetic Association 16(12):1040–1043
Ziegler D, Reljanovic M, Mehnert H, Gries FA (1999) Alpha-lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy in Germany: current evidence from clinical trials. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes : Official Journal, German Society of Endocrinology [and] German Diabetes Association 107(7):421–430. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1212132
Huang HQ, Brady MF, Cella D, Fleming G (2007) Validation and reduction of FACT/GOG-Ntx subscale for platinum/paclitaxel-induced neurologic symptoms: a gynecologic oncology group study. Int J Gynecol Cancer 17(2):387–393. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1438.2007.00794
Cella D, Peterman A, Hudgens S, Webster K, Socinski MA (2003) Measuring the side effects of taxane therapy in oncology: the functional assesment of cancer therapy-taxane (FACT-taxane). Cancer 98(4):822–831. doi:10.1002/cncr.11578
Calhoun EA, Welshman EE, Chang CH, Lurain JR, Fishman DA, Hunt TL, Cella D (2003) Psychometric evaluation of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy/Gynecologic Oncology Group-Neurotoxicity (Fact/GOG-Ntx) questionnaire for patients receiving systemic chemotherapy. Int J Gynecol Cancer 13(6):741–748
Cella D (1997) FACIT manual: manual of the functional assessment of chronic illness therapy (FACIT) measurement system. Center on Outcomes, Research and Education
(CDC) CfDCaP (2011) Cancer survivors--United States, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 60 (9):269–272
Simmonds MJ (2002) Physical function in patients with cancer: psychometric characteristics and clinical usefulness of a physical performance test battery. J Pain Symptom Manage 24(4):404–414
Cleeland C (1991) Research in cancer pain. What we know and what we need to know. Cancer 67(3 Suppl):823–827
Atkinson TM, Mendoza TR, Sit L, Passik S, Scher HI, Cleeland C, Basch E (2010) The Brief Pain Inventory and its "pain at its worst in the last 24 hours" item: clinical trial endpoint considerations. Pain medicine (Malden, Mass) 11(3):337–346. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00774.x
Program CTE (2006) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v3.0 (CTCAE). http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcaev3.pdf. Accessed 1 Oct 2013
Osterberg L, Blaschke T (2005) Adherence to medication. N Engl J Med 353(5):487–497. doi:10.1056/NEJMra050100
Haynes RB, McDonald HP, Garg AX (2002) Helping patients follow prescribed treatment: clinical applications. JAMA 288(22):2880–2883
Waterhouse DM, Calzone KA, Mele C, Brenner DE (1993) Adherence to oral tamoxifen: a comparison of patient self-report, pill counts, and microelectronic monitoring. J Clin Oncol 11(6):1189–1197
Joseph EK, Chen X, Bogen O, Levine JD (2008) Oxaliplatin acts on IB4-positive nociceptors to induce an oxidative stress-dependent acute painful peripheral neuropathy. J Pain 9(5):463–472. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2008.01.335
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted as a collaborative trial of MD Anderson Cancer Center and the MD Anderson Cancer Center Community Clinical Oncology Program Research Base and was supported in part by NCI grant U10CA045809. MD Anderson is supported in part by the National Institutes of Health through a Cancer Center Support Grant, CA016672. The ALA and placebo were provided by Jarrow Formulas, Inc., without charge.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was presented previously as an oral abstract at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Conference, Chicago, Illinois, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Jones, D., Palmer, J.L. et al. Oral alpha-lipoic acid to prevent chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Support Care Cancer 22, 1223–1231 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-013-2075-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-013-2075-1