Abstract
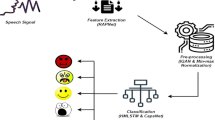
The emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) provides brand-new technical support and a broader resource platform for college oral English teaching and evaluation. The advancement of science, technology, and networks has resulted in significant educational changes. Because of these, the demand for English instruction is rising quickly, along with the level of cultural integration. However, due to the limits of conventional teaching techniques and the slow expansion of information technology, oral English classes have been discarded and discontinued for a long time. Based on the preceding, this paper first addresses the shortcomings of traditional college-level spoken English instruction by exposing content and timing deficiencies. It then describes how spoken English data are collected, preprocessed, and framed before being standardized for consistency. After that, this paper uses mapping recognition results using a DBN speech model and correlation coefficients in the evaluation. In addition, it uses the Pairwise Variability Index in rhythm evaluation to assess stress distribution differences between test and standard pronunciation. Besides the above, the proposed approach uses Support Vector Machine (SVM) optimization inside statistical learning to improve phoneme recognition and reliability, especially when dealing with difficult-to-distinguish phoneme sets. Further analysis is carried out using neural networks, which include excitation functions and error computations. Finally, the complete design emphasizes user-centric functional characteristics such as practicability, user needs, and robust system management subsystems. Experiments suggest that the natural language processing-based oral English teaching mode can increase students' overall oral English skills. These results reveal that students' excitement increased by 33.3%, their verbal fluency increased by 86%, and their vocabulary learning increased by 16.1%. The results show that this method can effectively assist students in learning oral English.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Ali M, Yin B, Kumar A, Sheikh AM et al (2020) Reduction of multiplications in convolutional neural networks. Chin Control Conf (CCC). https://doi.org/10.23919/CCC50068.2020.9188843
Aslam MS, Xisheng D, Jun H, Qianmu L, Rizwan U, Zhen N, Yaozong L (2020) Reliable control design for composite-driven scheme based on delay networked T-S fuzzy system. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 30(4):1622–1642
Chen Z (2019) Observer-based dissipative output feedback control for network T-S fuzzy systems under time delays with mismatch premise. Nonlinear Dyn 95:2923–2941
Chen G, Chen P, Huang W, Zhai J (2022) Continuance intention mechanism of middle school student users on online learning platform based on qualitative comparative analysis method. Math Probl Eng 2022:12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3215337
Cheng L, Yin F, Theodoridis S, Chatzis S, Chang T (2022) Rethinking Bayesian learning for data analysis: the art of prior and inference in sparsity-aware modeling. IEEE Signal Process Mag. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2022.3198201
Hazrat B, Yin B, Kumar A, Ali M, Zhang J, Yao J (2023) Jerk-bounded trajectory planning for rotary flexible joint manipulator: an experimental approach. Soft Comput 27(7):4029–4039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-07923-5
Kumar A, Shaikh AM, Li Y et al (2021) Pruning filters with L1-norm and capped L1-norm for CNN compression. Appl Intell 51:1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01894-y
Kusal S, Patil S, Choudrie J, Kotecha K, Vora D, Pappas I (2023) A systematic review of applications of natural language processing and future challenges with special emphasis in text-based emotion detection. Artif Intell Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-023-10509-0
Li W, Wang Y, Su Y, Li X, Liu A, Zhang Y (2023) Multi-scale fine-grained alignments for image and sentence matching. IEEE Trans Multimed 25:543–556. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3128744
Liu A, Zhai Y, Xu N, Nie W, LiZhang WY (2022a) Region-aware image captioning via interaction learning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(6):3685–3696. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3107035
Liu D, Cao Z, Jiang H, Zhou S, Xiao Z, Zeng F (2022b) Concurrent low-power listening: a new design paradigm for duty-cycling communication. ACM Trans Sens Netw. https://doi.org/10.1145/3517013
Liu X, Shi T, Zhou G, Liu M, Yin Z, YinZheng LW (2023a) Emotion classification for short texts: an improved multi-label method. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10(1):306. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01816-6
Liu X, Zhou G, Kong M, Yin Z, Li X, YinZheng LW (2023b) Developing multi-labelled corpus of twitter short texts: a semi-automatic method. Systems 11(8):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11080390
Lu W, Vivekananda GN, Shanthini A (2023a) Supervision system of English online teaching based on machine learning. Progr Artif Intell 12(2):187–198
Lu S, Ding Y, Liu M, Yin Z, YinZheng LW (2023b) Multiscale feature extraction and fusion of image and text in VQA. Int J Comput Intell Syst 16(1):54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44196-023-00233-6
Lumei W (2023) Database processing in Chinese classics translation system based on information search and IOT speech recognition. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-023-01999-w
Mahmud MAI, Talukder AT, Sultana A, Bhuiyan KIA, Rahman MS, Pranto TH, Rahman RM (2023) Toward news authenticity: synthesizing natural language processing and human expert opinion to evaluate news. IEEE Access 11:11405–11421
Mei J, Wang Y, Tu X, Dong M, He T (2023) Incorporating BERT with probability-aware gate for spoken language understanding. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 31:826–834
Muhammad SA, Irfan Q, Abdul M, Summera S (2023) Adaptive event-triggered robust H∞ control for Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy networked Markov jump systems with time-varying delay. Asian J Control 25(1):213–228
Peng Y, Arora S, Higuchi Y, Ueda Y, Kumar S, Ganesan K, Dalmia S, Chang X, Watanabe S (2023) A study on the integration of pre-trained ssl, asr, lm and slu models for spoken language understanding. In: 2022 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), IEEE pp 406–413
Salloum S, Gaber T, Vadera S, Shaalan K (2022) A systematic literature review on phishing email detection using natural language processing techniques. IEEE Access 10:65703–65727
Shamrooz M, Li Q, Hou J (2021) Fault detection for asynchronous T-S fuzzy networked Markov jump systems with new event-triggered scheme. IET Control Theory Appl 15(11):1461–1473
Tang J (2023) Artificial intelligence-based needs analysis for English specific purposes in digital environment. Learn Motiv 83:101914
Tang Y, Zeng X (2023) Application of intelligent audio data based on hash storage in vocal music teaching platform. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09118-4
Tyagi N, Bhushan B (2023) Demystifying the role of natural language processing (NLP) in smart city applications: background, motivation, recent advances, and future research directions. Wirel Pers Commun 130(2):857–908
Ullah R, Dai X, Sheng A (2020) Event-triggered scheme for fault detection and isolation of non-linear system with time-varying delay. IET Control Theory Appl 14(16):2429–2438
Wang L, Qiang Z, Baoqun Y et al (2019) Second-order convolutional network for crowd counting. Proc SPIE Fourth Int Workshop Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2540362
Weng X, Chiu TK (2023) Instructional design and learning outcomes of intelligent computer assisted language learning: systematic review in the field. Comput Educ 4:100117
Wu L (2020) Student model construction of intelligent teaching system based on Bayesian network. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 24(3):419–428
Wu C, Li X, Guo Y, Wang J, Ren Z, Wang M, Yang Z (2022) Natural language processing for smart construction: current status and future directions. Autom Constr 134:104059
Xiong Z, Liu Q, Huang X (2022) The infl uence of digital educational games on preschool children’s creative thinking. Comput Educ 189:104578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104578
Xu H, Sun Z, Cao Y et al (2023) A data-driven approach for intrusion and anomaly detection using automated machine learning for the Internet of Things. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09037-4
Yao W, Guo Y, Wu Y, Guo J (2017) Experimental validation of fuzzy PID control of flexible joint system in presence of uncertainties. Chin Control Conf (CCC). https://doi.org/10.23919/ChiCC.2017.8028015
Yin B, Khan J, Wang L, Zhang J, Kumar A (2019) Real-time lane detection and tracking for advanced driver assistance systems. Chin Control Conf (CCC). https://doi.org/10.23919/ChiCC.2019.8866334
Yin B, Aslam MS et al (2023) A practical study of active disturbance rejection control for rotary flexible joint robot manipulator. Soft Comput 27:4987–5001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08026-x
Zhou B, Yang G, Shi Z, Ma S (2022) Natural language processing for smart healthcare. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2022.3210270
Funding
No funding was provided for the completion of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Conflict of interest is not applicable in this work.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Human and animal rights
No violation of human and animal rights is involved.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Y., Zhang, Z. & Yang, H. Design of Oral English Teaching Assistant System based on deep belief networks. Soft Comput 27, 17403–17418 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09211-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09211-8