Abstract
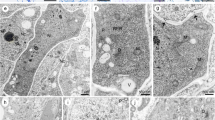
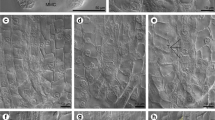
The development of the egg and canal cells in the fern Osmunda japonica Thunb. was studied during oogenesis by transmission electron microscopy. The mature egg possesses no fertilization pore and no typical egg envelope. In addition, an extra wall formed around the canal cells during oogenesis and apparently blocked protoplasmic connections between the egg and the canal cells. The periodic acid Schiff (PAS) reaction revealed that the extra wall was most likely composed of polysaccharides. Maturation of the egg was accompanied by the formation of a separation cavity above the egg and by some changes in the morphology of the nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles. The chromatin of the nucleus becomes condensed and the upper surface of the nucleus becomes closely associated with the plasmalemma. Amyloplasts in the egg cytoplasm were numerous and conspicuous, with most in close proximity to the nucleus. Finally, the cytoplasm on one side of the egg became vesiculated and the overlying plasmalemma was easily disrupted. These cytological features of the egg and the canal cells during oogenesis in O. japonica are markedly different from those of the leptosporangiate ferns and suggest a significant evolutionary divergence in reproductive cellular features between Osmundaceae and leptosporangiate ferns.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao WM, Cao JG, Dai SJ (2003) Ultrastructure of oogenesis in Osmunda cinnamomea var. asiatica. Acta Bot Sin 45:843–851
Bao WM, He Q, Wang QX, Tian GW, Cao JG (2005) Ultrastructure of oogenesis in Dryopteris crassirhizoma Nakai. J Integr Plant Biol 47:201–213
Bell PR (1980) Nucleocytoplasmic interaction during maturation of the egg of the fern Histiopteris incisa (Thunb.). J Smith Ann Bot 45:475–481
Bell PR (1986) Features of egg cells of living representatives of ancient families of ferns. Ann Bot 57:613–621
Bell PR, Duckett JG (1976) Gametogenesis and fertilization in Pteridium. Bot J Linn Soc 73:47–78
Bell PR, Mühlethaler K (1962a) The fine structure of the cells taking part in oogenesis in Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn. J Ultrastruct Res 7:452–466
Bell PR, Mühlethaler K (1962b) A membrane peculiar to the egg in the gametophyte of Pteridium aquilinum. Nature 195:198
Cao JG, Bao WM, Dai SJ (2003) Ultrastructure of the blepharoplast and the multilayered structure in spermatogenesis in Osmunda cinnamomea var. asiatica. Acta Bot Sin 45:832–842
Cao JG, Yang NY, Wang QX (2008) Observations on the formation and ultrastructure of the egg membrane in the fern Ceratopteris thalictroides (L.) Brongn. Acta Bot Yunnan 30:543–548
Cao JG, Yang NY, Wang QX (2009) Ultrastructure of the mature egg and fertilization in the fern Ceratopteris thalictroides (L.) Brongn. J Integr Plant Biol 51:243–250
Cao JG, Wang QX, Bao WM (2010a) Formation of the fertilization pore during oogenesis of the fern Ceratopteris thalictroides. J Integr Plant Biol 52:518–527
Cao JG, Wang QX, Dai XL, Duckett JG (2010b) Ultrastructural observations of oogenesis in the fern Adiantum flabellulatum L. (Adiantaceae). Am Fern J 100:93–102
Cao JG, Wang QX, Yang NY, Bao WM (2010c) Cytological events during zygote formation of the fern Ceratopteris thalictroides. J Integr Plant Biol 52:254–264
Cave CF, Bell PR (1973) The cytochemistry of the walls of the spermatocytes of Ceratopteris thalictroides. Planta 109:99–104
Cave CF, Bell PR (1975) Evidence for the association of acyl transferases with the production of nuclear evaginations in maturing eggs of the fern Dryopteris filix-mas. Histochemistry 44:57–65
Ching RC (1978) The Chinese fern families and genera: systematic arrangement and historical origin. Acta Phytotaxon Sin 16:1–19
Christensen C (1938) Filicinae. In: Verdoorn F (ed) Manual of pteridology. Martinus Nijhoff, The Hague, pp 522–550
Dai XF, Jiang N, Cao JG, Wang QX (2010) Primary study on the archegonium formation and oogenesis in the fern Phymatosorus hainanensis. Bull Bot Res 30:411–415
Fasciati R, Schneller J, Jenni V, Roos UP (1994) Fertilization in the fern Athyrium filix–femina (Pterophyta): II. Ultrastructure. Crypt Bot 4:356–367
Lal M, Kaur G, Chauhan E (1982) Ultrastructural studies on archegonial development in the moss Physcomitrium cyathicarpum. New Phytol 92:441–452
Mickel JT (1974) Phyletic lines in the modern ferns. Ann Mo Bot Gard 61:474–482
Smith AR, Pryer KM, Schuettpelz E, Korall P, Schneider H, Wolf PG (2006) A classification for extant ferns. Taxon 55:705–731
Wu S, Ching R (1991) Fern families and genera of China. Science Press, Beijing, pp 147–148
Zinsmeister DD, Carothers ZB (1974) The fine structure of oogenesis in Marchantia polymorpha. Am J Bot 61:499–512
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers and Ms. Katherine Wenzell for editing the language and useful suggestions; we also thank Ms. Nai-Ying Yang for help with transmission electron microscopy. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30970267), Leading Academic Discipline Project and Key Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (J50401, 12ZZ128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Scott Russell.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, JG., Dai, XF. & Wang, QX. Cytological features of oogenesis and their evolutionary significance in the fern Osmunda japonica . Sex Plant Reprod 25, 61–69 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-011-0179-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-011-0179-7