Abstract
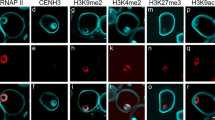
Histone H3.3, a gene that is differentially expressed in the vegetative cell of lily pollen, was characterized immunologically. Antibody raised against a specific peptide fragment clearly recognized histone H3.3 in mature pollen, and did not cross-react with somatic histone H3s. Immunoblot analysis indicated that the variant histone H3.3 increased during the development of late-bicellular pollen to mature pollen. Immunofluorescence labeling of pollen grains using the specific antibody revealed the presence of variant histone H3.3 only in the vegetative cell nucleus and not in the generative cell nucleus. This is the first study to demonstrate a differentially expressed variant histone H3.3 present in the vegetative cell nucleus. Since the chromatin of the vegetative cell nucleus is largely diffuse and transcriptionally active, the accumulation of a specialized histone H3.3 in the vegetative cell nucleus may potentially control condensation of chromatin and regulate the upregulation of pollen-enhanced genes expressed in the course of pollen germination and tube growth.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- VN:
-
Vegetative nucleus
- GN:
-
Generative nucleus
References
Ahmad K, Henikoff S (2002) Histone H3 variants specify modes of chromatin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16477–16484
Akhmanova A, Miedema K, Wang Y, van Bruggen M, Berden JHM, Moudrianakis EN, Hennig W (1997) The localization of histone H3.3 in germ line chromatin of Drosophila males as established with a histone H3.3-specific antiserum. Chromosoma 106:335–347
Arents G, Moudrianakis EN (1993) Topography of the histone octamer surface: repeating structural motifs utilized in the docking of nucleosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10489–10493
Chaubet N, Clement B Gigot C (1992) Genes encoding a histone H3.3-like variant in Arabidopsis contain intervening sequences. J Mol Biol 225:569–574
Chaubet-Gigot N, Kapros T, Flenet M, Kahn K, Gigot C, Waterborg JH (2001) Tissue-dependent enhancement of transgene expression by introns of replacement histone H3 genes of Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 45:17–30
Eissenberg JC, Elgin SC (2000) The HP1 protein family: getting a grip on chromatin. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:204–210
Fransz PF, de Jong JH (2002) Chromatin dynamics in plants (Review). Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:560–567
Honys D, Twell D (2003) Comparative analysis of the Arabidopsis pollen transcriptome. Plant Physiol 132:640–652
Kapros T, Bogre L, Nemeth K, Bako L, Gyorgyey J, Wu SC, Dudits D (1992) Differential expression of histone H3 gene variants during cell cycle and somatic embryogenesis in alfalfa. Plant Physiol 98:621–625
Mito Y, Henikoff JG, Henikoff S (2005) Genome-scale profiling of histone H3.3 replacement patterns. Nature Genet 37:1090–1097
Okada T, Endo M, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (2005) Analysis of the histone H3 gene family in Arabidopsis and identification of the male-gamete-specific variant AtMGH3. Plant J 44:557–568
Palmer DK, O’Day K, Wener MH, Andrews BS, Margolis RL. (1987) A 17-kD centromere protein (CENP-A) copurifies with nucleosome core particles and with histones. J Cell Biol 104:805–815
Robertson AJ, Kapros T, Dudits D, Waterborg JH (1996) Identification of three highly expressed replacement histone H3 genes of alfalfa. DNA Seq 6:137–146
Sano Y, Tanaka I (2005) A histone H3.3-like gene specifically expressed in the vegetative cell of developing pollen. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1299–1308
Tagami H, Ray-Gallet D, Almouzni G, Nakatani Y (2004) Histone H3.1 and H3.3 complexes mediate nucleosome assembly pathways dependent or independent of DNA synthesis. Cell 116:51–61
Talbert PB, Masuelli R, Tyagi AP, Comai L, Henikoff S (2002) Centromeric localization and adaptive evolution of an Arabidopsis histone H3 variant. Plant Cell 14:1053–1066
Tanaka I (1993) Development of male gametes in flowering plants. J Plant Res 106:55–63
Tanaka I (1997) Differentiation of generative and vegetative cells in angiosperm pollen. Sex Plant Reprod 10:1–7
Tanaka I, Ono K, Fukuda T (1998) The developmental fate of angisperm pollen is associated with a preferential decrease in the level of histone H1 in the vegetative nucleus. Planta 206:561–569
Ueda K, Tanaka I (1994) The basic proteins of male gametic nuclei isolated from pollen grains of Lilium longiflorum. Planta 192:446–452
Ueda K, Tanaka I (1995a) Male gametic nucleus-specific H2B and H3 histones, designated gH2B and gH3, in Lilium longiflorum. Planta 197:289–295
Ueda K, Tanaka I (1995b) The appearance of male gamete-specific histones gH2B and gH3 during pollen development in Lilium longiflorum. Dev Biol 169:210–217
Ueda K, Kinoshita Y, Xu ZJ, Ide N, Ono M, Akahori Y, Tanaka I, Inoue M (2000) Unusual core histones specifically expressed in male gametic cells of Lilium longiflorum. Chromosoma 108:491–500
Waterborg JH (1990) Sequence analysis of acetylation and methylation in two histone H3 variants of alfalfa. J Biol Chem 256:17157–17161
Zhong CX, Marshall JB, Topp C, Mroczek R, Kato A, Nagaki K, Birchler JA, Jiang J, Dawe RK (2002) Centromeric retroelements and satellites interact with maize kinetochore protein CENH3. Plant Cell 14:2825–2836
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. H. Shiota and Dr. N. Mogami (Yokohama City University) for helpful advice. We also thank Prof. S. Russell (University of Oklahoma) for critical reading of the manuscript and suggestions. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (Project number 16570057 and 18570061 to I.T).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Scott Russell.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sano, Y., Tanaka, I. Detection of differentially expressed variant histone H3.3 in the vegetative nucleus of lily pollen. Sex Plant Reprod 20, 27–33 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-006-0040-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-006-0040-6