Abstract
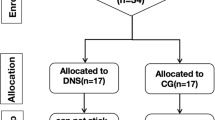
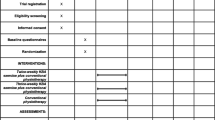
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) can generate postural control impairments which can increase fall risk. Land-based exercise (LBE) and balneotherapy are two modalities currently prescribed, but the impact of the latter on balance control has not been studied. This study aimed to compare two programs of balneotherapy with or without LBE to improve postural control, looking at frequency and duration of treatment. A total of 236 KOA patients (mean age = 64 years) were included in this prospective and randomized study: 122 patients went through 3 weeks of standardized continuous balneotherapy (high frequency/short duration) program (Gr1) and 114 went through 3 weeks of discontinuous (low frequency) balneotherapy program followed by 3 weeks of LBE (Gr2). The total number of treatment sessions was the same for both groups. Posturography was carried out before balneotherapy (W0) and at 3 (W3), 6 (W6), and 12 (W12) weeks after the beginning of treatment. Postural control increased in Gr1 from W0 to W3 and from W0 to W12 and in Gr2 from W0 to W6 and from W3 to W6. The improvement was greater in Gr1 from W0 to W3 and from W6 to W12 and in Gr2 from W3 to W6. High-frequency intensive balneotherapy improved posture control at 3 weeks, while low-frequency balneotherapy did not. This improvement persisted over a 12-week assessment period at the same level. LBE generated an improvement that did not persist over time. Sustained improvement of postural control requires high-frequency repetition of consecutive balneotherapy sessions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole G, Borenstien D, Brandt K et al (1986) Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnosis and therapeutic criteria committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum 29(8):1039–1049
Assemblée Nationale, Rapport 3811 enregistré à la Présidence de l’Assemblée nationale le 8 juin 2016 (2016) Comité d’évaluation et de contrôle des politiques publiques sur l’évaluation du soutien public au thermalisme, presented by D. Dord and J. Dubié
Barthels EM, Juhl CB, Christensen R, Hagen KB, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, Dagfinrud H, Lund H et al (2016) Aquatic exercise for the treatment of knee and hip osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 3:CD005523. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005523.pub3
Berger L, Martinie P, Livain T, Bergeau J, Rougier P (2006) Immediate effects of physiotherapy session of lower limb by balneotherapy on postural control. Ann Readapt Med Phys 49:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annrmp.2005.08.003
Buatois S, Gauchard G, Aubry C, Benetos A, Perrin P (2007) Current physical activity improves balance control during sensory conflicting conditions in older adults. Int J Sports Med 28(1):53–58. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-924054
Chun SW, Kim KE, Jang SN, Kim KI, Paik NJ, Kim KW, Jang HC, Lim JY (2013) Muscle strength is the main associated factor of physical performance in older adults with knee osteoarthritis regardless of radiographic severity. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 56(2):377–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2012.10.013
Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Nolte S, Ackerman I, Fransen M, Bridgett L, Williams S, Guillemin F, Hill CL, Laslett LL, Jones G, Cicuttini F, Osborne R, Vos T, Buchbinder R, Woolf A, March L (2014) The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1323–1330. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204763
Ettinger WH Jr, Burns R, Messier SP, Applegate W, Rejeski WJ, Morgan T et al (1997) A randomized trial comparing aerobic exercise and resistance exercise with a health education program in older adults with knee osteoarthritis (FAST). JAMA 277(1):25–31
Fioravanti A, Cantarini L, Guidelli GM, Galeazzi M (2011) Mechanisms of action of spa therapies in rheumatic diseases: what scientific evidence is there? Rheumatol Int 31(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1628-6
Forestier R, Desfour H, Tessier JM, Françon A, Foote AM, Genty C et al (2010) Spa therapy in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a large randomized multicenter trial. Ann Rheum Dis 69:660–665. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.113209
Forestier R, Erol Forestier FB, Françon A (2016) Spa therapy and knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 59(3):216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rehab.2016.01.010
Galloway MT, Jokl P (1993) The role of exercise in the treatment of inflammatory arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis 42:1–4
Gauchard G, Jeandel C, Tessier A, Perrin P (1999) Beneficial effect of proprioceptive physical activities on balance control in elderly human subjects. Neurosci Lett 273(2):81–84
Gauchard G, Vançon G, Meyer P, Mainard D, Perrin P (2010) On the role of knee joint in balance control and postural strategies: effects of total knee replacement in elderly subjects with knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture 32(2):155–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2010.04.002
Groll DL, To T, Bombardier C, Wright JG (2005) The development of a comorbidity index with physical function as the outcome. J Clin Epidemiol 58:595–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.10.018
Hall JBD, O’Hare P (1990) The physiology of immersion. Physiotherapy 9:206–215
Harrison R, Bulstrode S (1987) Percentage weight-bearing during partial immersion. Physiother Pract 3:60–63
Horak FB (1987) Clinical measurement of postural control in adults. Phys Ther 67:1881–1885
Horn LB, Rice T, Stoskus JL, Lambert KH, Dannenbaum E, Scherer MR (2015) Measurement characteristics and clinical utility of the clinical test of sensory interaction on balance (CTSIB) and modified CTSIB in individuals with vestibular dysfunction. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 96(9):1747–1748
Julh C, Christensen R, Roos EM, Zhang W, Lund H (2014) Impact of exercise type and dose on pain and disability in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and eta-regression analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(3):622–636. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38290
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 16(4):494–502
Kemoun G, Watelain E, Carette P (2006) Hydrokinésithérapie. EMC (Elsevier SAS, Paris), Kinésithérapie-Médecine physique-Réadaptation 26-140-A-10
Lephart SM, Pincivero DM, Giraldo JL, Fu FH (1997) The role of proprioception in the management and rehabilitation of athletic injuries. Am J Sports Med 25:130–137
Levinger P, Menz HB, Wee E, Feller JA, Bartlett JR, Bergman NR (2011) Physiological risk factors for falls in people with knee osteoarthritis before and early after knee replacement surgery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(7):1082–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1325-8
Levinger P, Dunn J, Bifera N, Butson M, Elias G, Hill KD (2017) High-speed resistance training and balance training for people with knee osteoarthritis to reduce falls risk: study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial. Trials 18(1):384. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-017-2129-7
Lion A, Spada RS, Bosser G, Gauchard GC, Anello G, Bosco P, Calabrese S, Iero A, Stella G, Elia M, Perrin PP (2013) Biological determinants of postural disorders in elderly women. Int J Neurosci 123(1):24–30. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2012.722570
Massion J (1994) Postural control system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 4(6):877–887
Mat S, Ng CT, Tan PJ, Ramli N, Fadzli F, Rozalli FI, Mazlan M, Hill KD, Tan MP (2018) Effect of modified Otago exercises on postural balance, fear of falling, and fall risk in older fallers with knee osteoarthritis and impaired gait and balance: a secondary analysis. PM R 10(3):254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2017.08.405
Özkuk K, Gürdal H, Karagülle M, Barut Y, Eröksüz R, Karagülle MZ (2017) Balneological outpatient treatment for patients with knee osteoarthritis; an effective non-drug therapy option in daily routine? Int J Biometeorol 61(4):719–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-016-1250-8
Paillard J (1973) Proprioception musculaire et sens de la position. Arch Ital Biol 3:451–461
Pélissier J, Brun V, Enjalbert M (1993) Posture, équilibration : quelques repères pour le rééducateur. In: Pélissier J, Brun V, Enjalbert M (eds) Posture, équilibration et médecine de rééducation, vol 26. Masson, Paris, pp 1–9
Perrin P (2004) Prévention des troubles de l’équilibre de la personne âgée par les activités physiques. Revue Officielle de la Société Française d’ORL 83:51–55
Perrin P, Jeandel C, Perrin CA, Béné MC (1997) Influence of visual control, conduction, and central integration on static and dynamic balance in healthy older adults. Gerontology 43(4):223–231
Perrin P, Gauchard G, Perrot C, Jeandel C (1999) Effects of physical and sporting activities on balance control in elderly people. Br J Sports Med 33(2):121–126
Perrin P, Deviterne D, Hugel F, Perrot C (2002) Judo, better than dance, develops sensorimotor adaptabilities involved in balance control. Gait Posture 15(2):187:194
Perrin P, Mallinson A, Van Nechel C, Peultier-Celli L, Petersen H, Magnusson M et al (2018) Defining clinical-posturographic and intra-posturographic discordances: what do these two concepts mean? J Int Adv Otol 14:127–129. https://doi.org/10.5152/iao.2018.4349
Petersson IF, Jacobsson LT (2002) Osteoarthritis of the peripheral joints. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 16:741–760
Peultier L, Lion A, Chary-Valckenaere I, Loeuille D, Zhang Z, Rat AC, Gueguen R, Paysant J, Perrin P (2016) Influence of meteorological elements on balance control and pain in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Int J Biometeorol 61:903–910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-016-1269-x
Peultier-Celli L, Mainard D, Wein F, Paris N, Boisseau P, Ferry A, Gueguen R, Chary-Valckenaere I, Paysant J, Perrin P (2017) Comparison of an innovative rehabilitation, combining reduced conventional rehabilitation with balneotherapy, and a conventional rehabilitation after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in athletes. Front Surg 4:67. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2017.00061
Pöyhönen T, Kyröläinen H, Keskinen KL, Hautala A, Savolainen J, Mälkiä E (2001) Electromyographic and kinematic analysis of therapeutic knee exercises under water. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 16(6):496–504
Rätsepsoo M, Gapeyeva H, Sokk J, Ereline J, Haviko T, Pääsuke M (2013) Leg extensor muscle strength stability and fear of falling after a 2-month home exercise program in women with severe knee joint osteoarthritis. Medicina (Kaunas) 49(8):347–353
Redon C, Hay L, Velay JL (1991) Proprioceptive control of goal-directed movements in man, studied by means of vibratory muscle tendon stimulation. J Mot Behav 23:101–108
Roll JP, Roll R (1988) From eye to foot. A proprioceptive chain involved in postural control. In: Amblard B, Berthoz A, Clarac F (eds) Posture and gait: development, adaptation and modulation. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 95–104
Sherrington C, Lord SR (1998) Increased prevalence of fall risk factors in older people following hip fracture. Gerontology 44(6):340–344
Shumway-Cook A, Horak F (1986) Assessing the influence of sensory interaction on balance. Phys Ther 66(10):1548–1550
Smith TO, Higson E, Pearson M, Mansfield M (2016) Is there an increased risk of falls and fractures in people with early diagnosed hip and knee osteoarthritis? Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Int J Rheum Dis 21:1193–1201. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12871
Speers RA, Kuo AD, Horak FB (2002) Contributions of altered sensation and feedback responses to changes in coordination of postural control due to aging. Gait Posture 16:20–30
Tarantola J, Nardone A, Tacchini E, Schieppati M (1997) Human stability improves with the repetition of the task: effect of foot position and visual condition. Neurosci Lett 228(2):75–78
Vouriot A, Hannhart B, Gauchard G, Barot A, Ledin T, Mur JM et al (2005) Long-term exposure to solvents impairs vigilance and postural control in serigraphy workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 78:510–515
Zelen M (1979) A new design for randomized clinical trials. N Engl J Med 300(22):1242–1245
Zhang Z, Lion A, Chary-Valckenaere I, Loeuille D, Rat AC, Paysant J, Perrin PP (2015) Diurnal variation on balance control in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 61(1):109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2015.03.009
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the staff of the rheumatology department for participant recruitment; Ms. Amandine Vallata and the staff of Clinical Epidemiology Centre (CEC), especially Prof. Francis Guillemin, Head of the CEC, for project management.
The authors acknowledge Dr. Art Mallinson (Vancouver, BC, Canada) for his helpful advice in the final read-through of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was promoted by the Nancy University Hospital, France, with a grant from the Métropole du Grand Nancy, France.
The authors acknowledge the University of Wuhan, China, for the grants in the field of the “Filière médicale francophone”/French-speaking medical network.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Accordingly, all participants gave written informed consent before the study, which was approved by the French Medical Ethical Committee (Comité de Protection des Personnes de Lorraine).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peultier-Celli, L., Lion, A., Chary-Valckenaere, I. et al. Comparison of high-frequency intensive balneotherapy with low-frequency balneotherapy combined with land-based exercise on postural control in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Biometeorol 63, 1151–1159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01727-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01727-9