Abstract
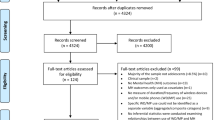
Young children are thought to be particularly sensitive to heat waves, but relatively less research attention has been paid to this field to date. A systematic review was conducted to elucidate the relationship between heat waves and children’s health. Literature published up to August 2012 were identified using the following MeSH terms and keywords: “heatwave”, “heat wave”, “child health”, “morbidity”, “hospital admission”, “emergency department visit”, “family practice”, “primary health care”, “death” and “mortality”. Of the 628 publications identified, 12 met the selection criteria. The existing literature does not consistently suggest that mortality among children increases significantly during heat waves, even though infants were associated with more heat-related deaths. Exposure to heat waves in the perinatal period may pose a threat to children’s health. Pediatric diseases or conditions associated with heat waves include renal disease, respiratory disease, electrolyte imbalance and fever. Future research should focus on how to develop a consistent definition of a heat wave from a children’s health perspective, identifying the best measure of children’s exposure to heat waves, exploring sensitive outcome measures to quantify the impact of heat waves on children, evaluating the possible impacts of heat waves on children’s birth outcomes, and understanding the differences in vulnerability to heat waves among children of different ages and from different income countries. Projection of the children’s disease burden caused by heat waves under climate change scenarios, and development of effective heat wave mitigation and adaptation strategies that incorporate other child protective health measures, are also strongly recommended.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Environmental Health (2003) In: Etzel RA (ed) Pediatric Environmental Health, 2nd edn. American Academy of Pediatrics, Elk Grove Village, IL
Anderson BG, Bell ML (2009) Weather-related mortality: How heat, cold, and heat waves affect mortality in the United States. Epidemiology 20(2):205–213. doi: 210.1097/EDE.1090b1013e318190ee318108
Balogun ABI, Adeyewa Z (2010) Comparisons of urban and rural heat stress conditions in a hothumid tropical city. Glob Health Action 3. doi:10.3402/gha.v3403i3400.5614
Basagaña X, Sartini C, Barrera-Gómez J, Dadvand P, Cunillera J, Ostro B, Sunyer J, Medina-Ramón M (2011) Heat waves and cause-specific mortality at all Ages. Epidemiology 22(6):765–772, 710.1097/EDE.1090b1013e31823031c31823035
Blum LN, Bresolin LB, Williams MA, From the AMA Council on Scientific Affairs (1998) Heat-related illness during extreme weather emergencies. JAMA 279(19):1514. doi:10.1001/jama.279.19.1514
Boer JD, Dubouloz M (2000) Handbook of disaster medicine. International Society of Disaster Medicine, Brill, Leiden
Bouchama A, Knochel JP (2002) Heat Stroke. N Engl J Med 346(25):1978–1988. doi:10.1056/NEJMra011089
Bunyavanich S, Landrigan C, McMichael A, Epstein P (2003) The impact of climate change on child health. Ambul Pediatr 3(1):44–52
Burton I, Huq S, Lim B, Pilifosova O, Schipper EL (2002) From impacts assessment to adaptation priorities: the shaping of adaptation policy. Clim Policy 2:145–149
Danks D, Webb D, Allen S (1962) Heat illness in infants and young children. BMJ 2:287–293
Dematte JE, O’Mara K, Buescher J, Whitney CG, Forsythe S, McNamee T, Adiga RB, Ndukwu IM (1998) Near-fatal heat stroke during the 1995 heat wave in Chicago. Ann Intern Med 129(3):173–181. doi:10.1059/0003-4819-129-3-199808010-00001
Department of Human Services, Victoria Government (2009) Heatwave planning guide. Development of heatwave plans in local councils in Victoria. Rural and Regional Health and Aged Care Services Division. Victorian Government Department of Human Services, Melbourne
Díaz J, Linares C, Tobías A (2006) A critical comment on heat wave response plans. Eur J Public Health 16(6):600. doi:10.1093/eurpub/ckl228
Feld LG, Hyams JS (2005) Fever in infants and children. Consens Pediatr 1(7):1–19
Fouillet A, Rey G, Laurent F, Pavillon G, Bellec S, Guihenneuc-Jouyaux C, Clavel J, Jougla E, Hémon D (2006) Excess mortality related to the August 2003 heat wave in France. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 80(1):16–24. doi:10.1007/s00420-006-0089-4
Huang W, Kan H, Kovats S (2010) The impact of the 2003 heat wave on mortality in Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 408(11):2418–2420
Huang C, Barnett AG, Wang X, Tong S (2012) The impact of temperature on years of life lost in Brisbane, Australia. Nat Clim Chang 2(4):265–270
Hutter HP, Moshammer H, Wallner P, Leitner B, Kundi M (2007) Heatwaves in Vienna: effects on mortality. Wien Klin Wochenschr 119(7):223–227. doi:10.1007/s00508-006-0742-7
Infoplease (2007) Droughts and heat waves. http://www.infoplease.com/ipa/A0886145.html.
IPCC (2007) Summary for policymakers. In: Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kalkstein L, Jamason P, Greene J, Robinson I (1996) The Philadelphia hot weather-health watch/warning system: development and application, summer 1995. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:1519–1528
Kew MC, Abrahams C, Levin NW, Seftel HC, Rubenstein AH, Bersohni (1967) The effects of heatstroke on the function and structure of the kidney. Q J Med 36(3):277–300
Knowlton K, Rotkin-Ellman M, King G, Margolis HG, Smith D, Solomon G, Trent R, English P (2008) The 2006 California heat wave: impacts on hospitalizations and emergency department visits. Environ Health Perspect 117(1):61–67
Kovats RS, Kristie LE (2006) Heatwaves and public health in Europe. Eur J Public Health 16(6):592–599. doi:10.1093/eurpub/ckl049
Kovats RS, Hajat S, Wilkinson P (2004) Contrasting patterns of mortality and hospital admissions during hot weather and heat waves in Greater London, UK. Occup Environ Med 61(11):893–898. doi:10.1136/oem.2003.012047
Kysely J, Kim J (2009) Mortality during heat waves in South Korea, 1991 to 2005: How exceptional was the 1994 heat wave? Clim Res 38:105–116
Landrigan PJ, Suk WA, Amler RW (1999) Chemical wastes, children’s health, and the Superfund Basic Research Program. Environ Health Perspect 107(6):423–427
Leonardi GS, Hajat S, Kovats RS, Smith GE, Cooper D, Gerard E (2006) Syndromic surveillance use to detect the early effects of heat-waves: an analysis of NHS Direct data in England. Soz Praventivmed 51(4):194–201. doi:10.1007/s00038-006-5039-0
Luber G, McGeehin M (2008) Climate change and extreme heat events. Am J Prev Med 35(5):429–435
Mannino DM, Buist AS (2007) Global burden of COPD: risk factors, prevalence, and future trends. Lancet 370(9589):765–773
Meehl GA, Tebaldi C (2004) More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science 305:994–997
Metzger KB, Ito K, Matte TD (2009) Summer heat and mortality in New York City: How hot is too hot? Environ Health Perspect 118(1):80–86
Misset B, De Jonghe B, Bastuji-Garin S, Gattolliat O, Boughrara E, Annane D, Hausfater P, Garrouste-Orgeas M, Carlet J (2006) Mortality of patients with heatstroke admitted to intensive care units during the 2003 heat wave in France: a national multiple-center risk-factor study. Crit Care Med 34(4):1087–1092. doi: 1010.1097/1001.CCM.0000206469.0000233615.0000206402
Mogensen C, Christensen C, Vittinghus E (1983) The stages in diabetic renal disease. With emphasis on the stage of incipient diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes s32:64–78
Nicholls N, Skinner C, Loughnan M, Tapper N (2008) A simple heat alert system for Melbourne, Australia. Int J Biometeorol 52(5):375–384. doi:10.1007/s00484-007-0132-5
Nitschke M, Tucker GR, Bi P (2007) Morbidity and mortality during heatwaves in metropolitan Adelaide. Med J Aust 187(11):662–665
Nitschke M, Tucker GR, Hansen AL, Williams S, Zhang Y, Bi P (2011) Impact of two recent extreme heat episodes on morbidity and mortality in Adelaide, South Australia: a case-series analysis. Environ Health 10(42). doi: 10.1186/1476-069X-10-42
O’Neill MS, Ebi KL (2009) Temperature extremes and health: impacts of climate variability and change in the United States. J Occup Environ Med 51(1):13–25. doi:10.1097/JOM.1090b1013e318173e318122
Romero J, Clement PF, Belden C (2000) Neuropsychological sequelae of heat stroke: report of three cases and discussion. Mil Med 165(6):500–503
Ostro B, Rauch S, Green R, Malig B, Basu R (2010) The effects of temperature and use of air conditioning on hospitalizations. Am J Epidemiol 172(9):1053–1061. doi:10.1093/aje/kwq231
Pascal M, Laaidi K, Ledrans M, Baffert E, Caserio-Schönemann C, Le Tertre A, Manach J, Medina S, Rudant J, Empereur-Bissonnet P (2006) France’s heat health watch warning system. Int J Biometeorol 50(3):144–153. doi:10.1007/s00484-005-0003-x
Perera FP (2008) Children are likely to suffer most from our fossil fuel addiction. Environ Health Perspect 116(8):987–990
Poumadère M, Mays C, Le Mer S, Blong R (2005) The 2003 heat wave in France: dangerous climate change here and now. Risk Anal 25(6):1483–1494. doi:10.1111/j.1539-6924.2005.00694.x
Raju S, Robinson G, Bower J (1973) The pathogenesis of acute renal failure in heat stroke. South Med J 66:330–333
Rav-Acha M, Shuvy M, Hagag S, Gomori M, Biran I (2007) Unique persistent neurological sequelae of heat stroke. Mil Med 172(6):603–606
Rollet C (2010) La canicule de 1911. Observations démographiques et médicales et réactions politiques. Ann Démogr Hist 2:105–130
Rooney C, McMichael A, Kovats R, Coleman M (1998) Excess mortality in England and Wales, and in Greater London, during the 1995 heatwave. J Epidemiol Community Health 53(8):482–486
Rosenthal J, Sclar E, Kinney P, Knowlton K, Crauderueff R, Brandt-Rauf P (2007) Links between the built environment, climate and population health: Interdisciplinary environmental change research in New York City. Ann Acad Med Singapore 36:834–846
Semenza JC, Rubin CH, Falter KH, Selanikio JD, Flanders WD, Howe HL, Wilhelm JL (1996) Heat-related deaths during the July 1995 heat wave in Chicago. N Engl J Med 335(2):84–90. doi:10.1056/NEJM199607113350203
Semenza JC, McCullough JE, Flanders WD, McGeehin MA, Lumpkin JR (1999) Excess hospital admissions during the July 1995 heat wave in Chicago. Am J Prev Med 16(4):269–277
Sheffield PE, Knowlton K, Carr JL, Kinney PL (2011) Modeling of regional climate change effects on ground-level ozone and childhood asthma. Am J Prev Med 41(3):251–257
Son JY, Lee JT, Anderson GB, Bell ML (2012) The impact of heat waves on mortality in seven major cities in Korea. Environ Health Perspect 120(4):566–571
Stafoggia M, Forastiere F, Agostini D, Caranci N, de’ Donato F, Demaria M, Michelozzi P, Miglio R, Rognoni M, Russo A, Perucci CA (2008) Factors affecting in-hospital heat-related mortality: a multi-city case-crossover analysis. J Epidemiol Community Health 62(3):209–215. doi:10.1136/jech.2007.060715
Strand LB, Barnett AG, Tong S (2012) Maternal exposure to ambient temperature and the risks of preterm birth and stillbirth in Brisbane, Australia. Am J Epidemiol 175(2):99–107. doi:10.1093/aje/kwr404
Tong S, Wang XY, Barnett AG (2010) Assessment of heat-related health impacts in Brisbane, Australia: Comparison of different heatwave definitions. PLoS One 5(8):e12155
Turley KR, Wilmore JH (1997) Cardiovascular responses to treadmill and cycle ergometer exercise in children and adults. J Appl Physiol 83(3):948–957
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2011) Exposure factors handbook: 2011 edition, vol EPA/600/R-09/052F. National Center for Environmental Assessment, Washington, DC
Acknowledgments
We thank Cunrui Huang and Yuming Guo for their valuable comments. Z.X. is supported by a China Scholarship Council Postgraduate Scholarship and Queensland University of Technology fee waiving scholarship; S.T. is supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council Research Fellowship (#553043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Sheffield, P.E., Su, H. et al. The impact of heat waves on children’s health: a systematic review. Int J Biometeorol 58, 239–247 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-013-0655-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-013-0655-x